
MOBILE APPLICATION
DEVELOPMENT
“The search for common ground in a divided
market”
Ben Feigin

IN THE BEGINNING…

MOTOROLA DYNATAC 8000X

EARLY SMART PHONES
IBM Simon
Nokia 9000 Series

WHAT IS A “SMARTPHONE”
Semi-Smart: Phone that offers features beyond
making calls
E-mail
Take pictures
Plays mp3
…
Phone that runs a complete Operating System
Offers a standardized platform for development
Able to execute arbitrary 3
rd
party applications

QUICK FACTS
Today
Cell phones in use today ~ 1.2 billion
Smartphones account for 14% ~ 170 Million
Projected 2012
Cell phones ~ 1.7 billion
Smartphones 29% ~ 500 Million
300% Smartphone growth in three years

MOBILE DEVELOPMENT

MOBILE DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
Java ME
Symbian
UIQ
S60
Android
BlackBerry
OVI
Windows Mobile
iPhone
LiMo
Ångström distribution
Adobe Flash Light
BREW
OpenMoko
Palm OS (Garnet OS, Cobalt OS)
Palm webOS
Mojo

WHY?
Different Phones Different Uses
Phones for consumer or phone for business
V-Cast vs Palm
Money
Hardware made money
Tried to maintain control over content and services.
Wanted to charge 3
rd
party developers for the
privilege of using their platform.
Digital signing
Distribution mechanisms.

COMMON PROBLEM: ABSTRACTION
Interface / GUI
How does the developer create an interface
Different interaction techniques
Graphical capabilities of the phone
Phone Services and Security
What resources are available to your program
What types of boundaries or constraints are put on
applications
How can code be considered “safe”

OTHER ISSUES
Distribution
Centralized repository
Direct OTI
From PC
Development
Language familiarity
Porting
IDEs?
Debugging
Emulation Vs on Phone
Performance
Very limited resources
Battery

THREE TIERED SOLUTION
Virtual Environment
Java ME
BREW *
Core Operating System
Symbian
LiMo
Rich Operating System
Android
iPhone

VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS
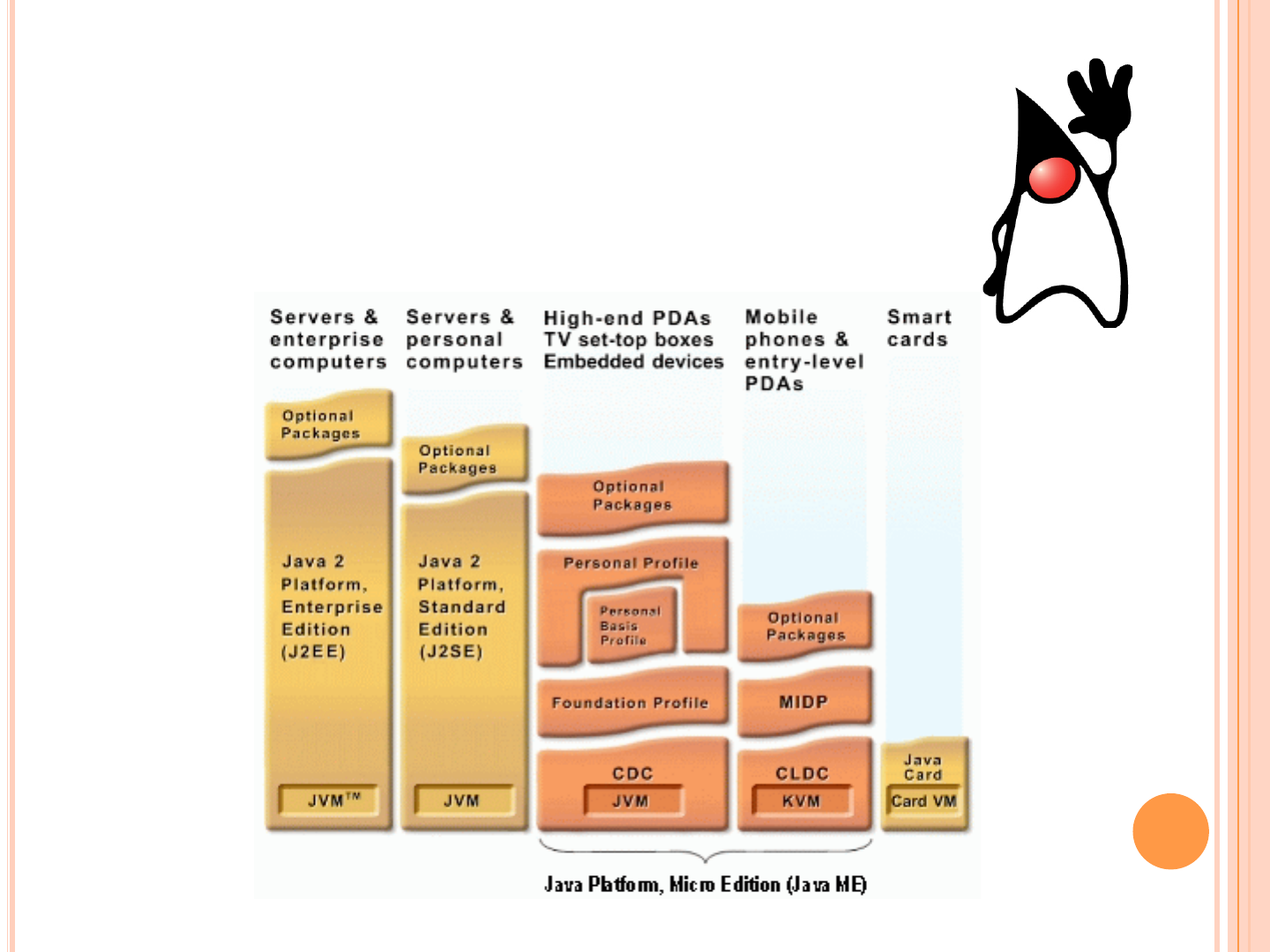
JAVA PLATFORM

KVM / CLDC
Specially designed mobile virtual machine
Original Ran with 128k Memory footprint
Paired down to bare bones
Reduced versions of classes
String, Object, Hashtable, Vector, Math, Simple Errors
Yank out features
No long, float, double
Class Loaders
Threading
Multi dimensional arrays
But Each phone implementation can add them back
Takes a profile to complete the stack

MOBILE INFORMATION
DEVICE PROFILE
Mobile Information Device Profile
Adds libraries specific to Mobile phones
IO
Record management system
Basic media playback system
LCDUI- 2D drawing library typically used for
sprite based 2d games
Optional packages
SMS control
PIM personal info management (Contact list control)

JAVA MICRO EDITION
Almost all phones include a runtime
Pluggable Architecture
Attempted to be ubiquitous language for
development
Security Model
Relied heavily on digital signing
Fell short of expectations
Phone specific plug-ins
Applications could be blocked without specific
certificates.
Currently paired down version of java 1.3

JAVA MICRO EDITION
New Version 3.0 just released
Offers support for several new features
GPS
New Graphics library LWUIT
Screen orientation
Only available for windows
Updated CLDC.

BINARY RUNTIME ENVIRONMENT FOR
WIRELESS (BREW)
Developed by QUALCOMM
V-Cast
Similar to Java ME
C/C++ vs Java
Smaller subset of phones
Tighter integration then ME
Start to finish development integration
High barrier to entry
Number of large steps at high cost
Java ME can be as simple as publish and go

OPERATING SYSTEMS
SYMBIAN

SYMBIAN: AT A GLANCE
Huge Market Share
45%
Robust and well
vetted platform
Very open
Low overhead event-
based programming
Strange flavor of C++
Java and others with
SDK
Resource
management is
cumbersome
Two popular SDK’s
that are incompatible
Good Bad

UIQ VS S60
Rival SDK’s for the Symbian OS
UIQ
Sony Ericsson
Touch screen phones
S60
Developed and owned by Nokia
Current industry leader
Will become standard in late 2009
Both offer a full development stack

S60 DEVELOPMENT:
THE STACK

S60 DEVELOPMENT:
IDE
Carbide.c++
Developed by Nokia
IDE based on Eclipse platform
Provides a set of tools for debugging
SDK independent
Carbide.vs
Visual studio implementation
Similar feature set

S60 DEVELOPMENT:
APPLICATION STRUCTURE
All applications are treated as dll’s and have a
single entry point
Main: Application Class
Uses MVC style organization
M: Document Class
V: Container / ContainerView Class
C: AppUI Class

S60 DEVELOPMENT:
CLASSES AND VARIABLES
Prefix
Category
Description
T
Type
Data container
C
Class
Class model
R
Resource
Manages external state
M
Mixin
Interface
Static
Factories and utility
Prefix
Category
Description
E
Enum
Values in enumeration
K
Constant
Class model
i
Member
Variable
Non-static ‘instance’ variable
a
Argument
Function argument
Automatic
Variable
Managed variable, destroyed
when out of scope

S60 DEVELOPMENT:
ACTIVE OBJECTS

S60 DEVELOPMENT: ERROR HANDLING
LEAVE and TRAP vs try/catch
Try Catch has large overhead
Use TRAP Macro
Cleanup is an issue
Tint error;
TRAP(error, fooL());{
If(error!=KErrNon)
{
// Handel exception
}
Void Ctest::FooL()
{
CBar* v1= new (Eleave) Cbar;
CleanupStack::PushL(v1);
//Do dangerious things
EvilMethodL();
CleanupStack::PopAndDestroy();
};

S60 DEVELOPMENT: SECURITY MODEL
Data caging
/Resource
/Sys
/Private
/“Anything else”
Capabilities
Open to all
Granted by user at install
Symbian Signed
OEM

S60 DEVELOPMENT: FUTURE
June 24, 2008:
Nokia outright purchased the Symbian OS
Symbian Foundation Formed
Goals
“Provide a royalty-free open platform and accelerate
innovation”
Combine Symbian OS, S60, UIQ
Move code base to open source in next two years
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UxGa6kyPOjk&feature=player_embedded
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gAg_MOFNfFc&feature=player_embedded

OPERATING SYSTEMS
iPHONE


NUMBERS
SDK Released March 6
th
2008
Billion apps downloaded as of April 23
rd
Includes both pay and free
Assuming 10% paid downloads
lowest price of $.99/app
$99 Million
17% Market share just in front of Blackberry
Still well behind Symbian but growing very fast

iPHONE DEVELOPMENT
Objective-C
Message based architecture
Similar to Smalltalk
No Java VM or other 3
rd
party plugins
“An Application may not itself install or launch
other executable code by any means, including
without limitation through the use of a plug-in
architecture, calling other frameworks, other
APIs or otherwise. No interpreted code may be
downloaded and used in an Application except for
code that is interpreted and run by Apple’s
Published APIs and built-in interpreter(s).” –
iPhone SDK EULA

iPHONE DEVELOPMENT:
SDK
Four distinctive framework API’s
Cocoa Touch Layer
Media Layer
Core Services Layer
Core OS Layer
IDE
Xcode
Interface Builder
iPhone Simulator
On phone application development

iPHONE DEVELOPMENT:
INTERFACE BUILDER / XCODE
Design for graphical,
event-driven
applications
Pallet of GUI widgets to
use in your views.
Drag and drop widgets
onto views
Links between objects
can be created
graphically
MVC pattern designed
here
Graphically declare
hooks into a program
Produces Nib Files

iPHONE DEVELOPMENT:
DESIGN PATTERNS
Delegation
Don’t Subclass
Method calls are
messages
[Object Message]
Both are dynamic
Managed Memory
Auto release
{
NSString *string =[... Alloc]…;
[string release];
return string; //??
}
{
NSString *string =[... Alloc]…;
[string autorelease];
return string;
}

iPHONE DEVELOPMENT:
APPLICATION LIFE CYCLE

iPHONE DEVELOPMENT:
SECURITY MODEL
Originally all applications ran as root
Not a whole lot better now
All apps run as “mobile” user
Survived this year’s Pwn2Own
Security based on delivery mechanism
All applications must be delivered through the
iTunes App Store
Requires apple approval and testing
$99 App Store
$299 Enterprise
Digitally signed by developer

iPHONE DEVELOPMENT:
FUTURE
iPhone OS 3.0
In app purchases
Accessory APIs
Peer to Peer connectivity
New Game Kit
iPod library access
Embedded maps
Copy & Paste
Video

OPERATING SYSTEMS
Android

YEAR OF THE ANDROID?
Averaged 47% growth/month
over first four months
iPhone 88%
Currently only on HTC
Dream(G1)
Really cool concept but will it
penetrate the market

WHAT IS ANDROID
Full Stack
OS
Middleware
Applications
IDE
Fully Open
Source and Ideology
User Control
Can establish preferred applications
Application Modularity
Apps provide functionality that can be used by others

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
THE STACK

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
JVM
Dalvik
Register-based Java virtual machine
Runs .dex files
Similar to a JAR
Used a cross compiler tool ‘dx’
Optimized for multiple instances
Why not Java ME?
Not fully open source
Still under control of Sun Micro
Veto on any proposed changes

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
APPLICATION OVERVIEW
Packaged in one .apk file
Each application lives in its “own phone”
Its own Linux process
Its own JVM
Its own “file system”
Component based architecture
Activities
Services
Broadcast receivers
Content providers
Manifest file provides information about
components

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
ACTIVITIES
A visual interface for one task a user will attempt
Each activity gets a window to draw in.
Similar to a controller, takes view objects to
display in the window
Views can nest within each other
Application can designate one activity as first

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
SERVICES
Background process
No UI
Example: Media player
Can connect (bind) to a service
Currently running
Or by starting it
Once bound can communicate through predefined
interface
Media Player: start, stop..

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
BROADCAST RECEIVERS / CONTENT PROVIDERS
Broadcast Receivers
Event listeners
No UI
Can broadcast events
On event execute activity or display notification
Content Providers
Opens specific part of an applications data
Uses Content Resolvers
Not called directly
Returns a cursor object

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
INTENTS
Contains the target object, the target method,
and a URI of data to act on
Activates components
Aside from content providers
Intent can call startActivity, startService,
sendBroadcast

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
ACTIVITY LIFE CYCLE

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
DEMO
Video: Example integration using android
http://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=3LkNlTNHZzE&feature=PlayList&p=611F8C5DB
F49CEC6&index=2

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
SECURITY
Sand Box
Without explicit permission
can’t get outside
Each application can
control what gets exposed
Permissions are declared at
install time and can’t
change
App signing
Digitally signed by
developer

ANDROID DEVELOPMENT:
FUTURE
Could have changed
everything
iPhone got there first
True value of “Apps without
boarders?”
Solid development platform
Build on a language with
millions of developers
Without limitations of Java
ME
Net Books?
Still far away
Android doesn’t support X-
Server
Tech demo already complete.

ON THE HORIZON

LiMo
“LiMo believes that the growth of the mobile
industry depends on the existence of a broadly
accepted operating system.”
SDKs
Native
Java
Web
Major Players:
Verizon
Motorola
Docomo
Vodafone

PALM webOS / MOJO
Blurs the line between phone and web sources
Native
Application
Cloud
“Palm has extended the standard web
development environment through a JavaScript
framework that gives standardized UI widgets,
and access to selected device hardware and
services.”
Video

QUESTIONS
Can the development space ever be consolidated?
How big a roll does a centralized distribution
mechanism play?
Does the safety of the App Store warrant having to
pay $99 to develop something?

REFERENCES
iphone vs. Symbian vs. Android vs. Limo vs. Ovi : We cannot compare an
ecosystem with an operating system
http://opengardensblog.futuretext.com/archives/2008/06/iphone_vs_symbi_1.html
Developing Secure Mobile Applications for Android
http://www.isecpartners.com/files/iSEC_Securing_Android_Apps.pdf
Architectural manifesto: How to Choose a mobile platform
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/architecture/library/wi-arch23.html
AdMob Mobile Metrics Report
http://metrics.admob.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/04/admob-mobile-metrics-
march-09.pdf
What is Android
http://developer.android.com/guide/basics/what-is-android.html
Overview of LiMo
http://www.limofoundation.org/images/stories/pdf/090211%20limo%20overview
%20v3.pdf

REFERENCES
iPhone Application Programming Guide: The Core Application
http://developer.apple.com/iphone/library/documentation/iPhone/Conceptual/iPhoneOSProgrammingGuide/
ApplicationEnvironment/ApplicationEnvironment.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40007072-CH7-SW1
Using Symbian OS: Getting Started
http://developer.symbian.com/main/documentation/books/books_files/pdf/Getting_Started_final.pdf
Smartphone NUmbers
http://www.boygeniusreport.com/2009/04/19/samsungs-says-smartphones-will-make-up-29-percent-of-the-market-
in-2012/
UIQ Symbian
http://www.sonyericsson.com/cws/companyandpress/pressreleases/pressrelease/pressreleaseoverview/
key.PressResource.Foundation_second_update_release_FINAL-20080909
Obj-C memory
http://www.macdevcenter.com/pub/a/mac/2001/07/27/cocoa.html?page=3
Dalvik
http://www.betaversion.org/~stefano/linotype/news/110/
Android Tech Demo
http://venturebeat.com/2009/01/01/android-netbooks-on-their-way-likely-by-2010/
