
Pennsylvania
Keystone Exams
Algebra I
Item and Scoring Sampler
Pennsylvania Department of Education Bureau of Curriculum, Assessment and Instruction—August 2022
2022–2023

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INFORMATION ABOUT ALGEBRA I
Introduction .................................................................1
General Introduction .......................................................1
About the Keystone Exams .....................................................1
Alignment ...............................................................2
Depth of Knowledge .......................................................2
Exam Format .............................................................2
Item and Scoring Sampler Format ................................................3
Algebra I Exam Directions ......................................................4
General Description of Scoring Guidelines for Algebra I ...............................6
Formula Sheet ...............................................................7
ALGEBRA I MODULE 1
Multiple-Choice Items .........................................................8
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................24
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................38
Algebra I Module 1—Summary Data .............................................54
ALGEBRA I MODULE 2
Multiple-Choice Items ........................................................56
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................74
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................90
Algebra I Module 2—Summary Data ............................................104

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
1
INFORMATION ABOUT ALGEBRA I
INTRODUCTION
General Introduction
The Pennsylvania Department of Education (PDE) provides districts and schools with tools to assist
in delivering focused instructional programs aligned to the Pennsylvania Core Standards. These
tools include the standards, assessment anchor documents, Keystone Exams Test Definition,
Classroom Diagnostic Tool, Standards Aligned System, and content-based item and scoring
samplers. This 2022 Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler is a useful tool for Pennsylvania educators
in preparing students for the Keystone Exams by providing samples of test item types and scored
student responses. The Item Sampler is not designed to be used as a pretest, a curriculum, or any
other benchmark for operational testing.
This Item and Scoring Sampler contains released operational multiple-choice and constructed-
response items that have appeared on previously administered Keystone Exams. These items will
not appear on any future Keystone Exams. Released items provide an idea of the types of items that
have appeared on operational exams and that will appear on future operational Keystone Exams.
Each item has been through a rigorous review process to ensure alignment with the Assessment
Anchors and Eligible Content (AAEC). This sampler includes items that measure a variety of
Assessment Anchor or Eligible Content statements, but it does not include sample items for all
Assessment Anchor or Eligible Content statements.
The items in this sampler may be used
1
as samples of item types that students will encounter in
operational testing. Classroom teachers may find it beneficial to have students respond to the
constructed-response items in this sampler. Educators can then use the sampler as a guide to score
the responses either independently or together with colleagues.
This Item and Scoring Sampler is available in Braille format. For more information regarding Braille,
call (717) 901-2238.
ABOUT THE KEYSTONE EXAMS
The Keystone Exams are end-of-course assessments currently designed to assess proficiencies
in Algebra I, Biology, and Literature. For detailed information about how the Keystone Exams are
being integrated into the Pennsylvania graduation requirements, please contact the Pennsylvania
Department of Education or visit the PDE website at http://www.education.pa.gov.
1
The permission to copy and/or use these materials does not extend to commercial purposes.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
2
INFORMATION ABOUT ALGEBRA I
Alignment
The Algebra I Keystone Exam consists of questions grouped into two modules:
Module 1—Operations and Linear Equations & Inequalities and Module 2—Linear Functions and
Data Organizations. Each module corresponds to specific content, aligned to statements and
specifications included in the course-specific Assessment Anchor documents. The AlgebraI content
included in the Keystone Algebra I multiple-choice items will align with the Assessment Anchors as
defined by the Eligible Content statements. The process skills, directives, and action statements will
also specifically align with the Assessment Anchors as defined by the Eligible Content statements.
The content included in AlgebraI constructed-response items aligns with content included in
the Eligible Content statements. The process skills, directives, and action statements included in
the performance demands of the AlgebraI constructed-response items align with specifications
included in the Assessment Anchor statements, the Anchor Descriptor statements, and/or the
Eligible Content statements. In other words, the verbs or action statements used in the constructed-
response items or stems can come from the Eligible Content, Anchor Descriptor, or Assessment
Anchor statements.
Depth of Knowledge
Webb’s Depth of Knowledge (DOK) was created by Dr. Norman Webb of the Wisconsin Center for
Education Research. Webb’s definition of DOK is the cognitive expectation demanded by standards,
curricular activities, and assessment tasks. Webb’s DOK includes four levels, from the lowest (recall)
level to the highest (extended thinking) level.
Depth of Knowledge
Level 1 Recall
Level 2 Basic Application of Skill/Concept
Level 3 Strategic Thinking
Level 4 Extended Thinking
Each Keystone item has been through a rigorous review process and is assigned a DOK level. For
additional information about DOK, please visit the PDE website at http://static.pdesas.org/content/
documents/Keystone_Exams_Understanding_Depth_of_Knowledge_and_Cognitive_Complexity.pdf.
Exam Format
The Keystone Exams are delivered in a paper-and-pencil format as well as in a computer-based
online format. The multiple-choice items require students to select the best answer from four
possible answer options and record their answers in the spaces provided. The correct answer for
each multiple-choice item is worth one point. The constructed-response items require students
to develop and write (or construct) their responses. Constructed-response items in AlgebraI are
scored using item-specific scoring guidelines based on a 0–4-point scale. Each multiple-choice item
is designed to take about one to one-and-a-half minutes to complete. Each constructed-response
item is designed to take about ten minutes to complete. The estimated time to respond to a test
question is the same for both test formats. During an actual exam administration, students are given
additional time as necessary to complete the exam.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
3
INFORMATION ABOUT ALGEBRA I
ITEM AND SCORING SAMPLER FORMAT
This sampler includes the test directions, scoring guidelines, and formula sheet that appear in
the Keystone Exams. Each sample multiple-choice item is followed by a table that includes the
alignment, the answer key, the DOK, the percentage
2
of students who chose each answer option,
and a brief answer option analysis or rationale. Each constructed-response item is followed by a
table that includes the alignment, the DOK, and the mean student score. Additionally, each of the
included item-specific scoring guidelines is combined with sample student responses representing
each score point to form a practical item-specific scoring guide. The General Description of Scoring
Guidelines for AlgebraI used to develop the item-specific scoring guidelines should be used if any
additional item-specific scoring guidelines are created for use within local instructional programs.
The student responses in this item and scoring sampler are actual student responses; however, the
handwriting has been changed to protect the students’ identities and to make the item and scoring
sampler accessible to as many people as possible.
Example Multiple-Choice Item Information Table
Item Information
Alignment Assigned AAEC
Answer Key Correct Answer
Depth of Knowledge Assigned DOK
p-value A Percentage of students who selected option A
p-value B Percentage of students who selected option B
p-value C Percentage of students who selected option C
p-value D Percentage of students who selected option D
Option Annotations Brief answer option analysis or rationale
Example Constructed-Response Item Information Table
Alignment
Assigned
AAEC
Depth of
Knowledge
Assigned
DOK
Mean Score
Average
Score
2
All p-value percentages listed in the item information tables have been rounded.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
4
INFORMATION ABOUT ALGEBRA I
ALGEBRA I EXAM DIRECTIONS
Directions:
Below are the exam directions available to students. These directions may be used to help students
navigate through the exam.
Formulas that you may need to solve questions in this module are found on page 7 of this test
booklet. You may refer to the formula page at any time during the exam.
You may use a calculator on this module. When performing operations with π (pi), you may use either
calculator π or the number 3.14 as an approximation of π.
There are two types of questions in each module.
Multiple-Choice Questions:
These questions will ask you to select an answer from among four choices.
• First read the question and solve the problem on scratch paper. Then choose the correct
answer.
• Only one of the answers provided is correct.
• If none of the choices matches your answer, go back and check your work for
possible errors.
• Record your answer in the Algebra I answer booklet.
Constructed-Response Questions:
These questions will require you to write your response.
• These questions have more than one part. Be sure to read the directions carefully.
• You cannot receive the highest score for a constructed-response question without
completing all the tasks in the question.
• If the question asks you to show your work or explain your reasoning, be sure to show
your work or explain your reasoning. However, not all questions will require that you
show your work or explain your reasoning. If the question does not require that you
show your work or explain your reasoning, you may use the space provided for your
work or reasoning, but the work or reasoning will not be scored.
• All responses must be written in the appropriate location within the response box in
the Algebra I answer booklet. Some answers may require graphing, plotting, labeling,
drawing, or shading. If you use scratch paper to write your draft, be sure to transfer your
final response to the Algebra I answer booklet.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
5
INFORMATION ABOUT ALGEBRA I
If you finish early, you may check your work in Module 1 [or Module 2] only.
• Do not look ahead at the questions in Module 2 [or back at the questions in Module 1] of
your exam materials.
• After you have checked your work, close your exam materials.
You may refer to this page at any time during this portion of the exam.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
6
INFORMATION ABOUT ALGEBRA I
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF SCORING GUIDELINES FOR ALGEBRA I
4 Points
• The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of the mathematical concepts and
procedures required by the task.
• The response provides correct answer(s) with clear and complete mathematical procedures
shown and a correct explanation, as required by the task. The response may contain a minor
“blemish” or omission in work or explanation that does not detract from demonstrating a
thorough understanding.
3 Points
• The response demonstrates a general understanding of the mathematical concepts and
procedures required by the task.
• The response and explanation (as required by the task) are mostly complete and correct. The
response may have minor errors or omissions that do not detract from demonstrating a
general understanding.
2 Points
• The response demonstrates a partial understanding of the mathematical concepts and
procedures required by the task.
• The response is somewhat correct with partial understanding of the required mathematical
concepts and/or procedures demonstrated and/or explained. The response may contain some
work that is incomplete or unclear.
1 Point
• The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of the mathematical concepts and
procedures required by the task.
0 Points
• The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any
understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures required by the task.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
7
INFORMATION ABOUT ALGEBRA I
FORMULA SHEET
Formulas that you may need to solve questions on this exam are found below.
You may use calculator π or the number 3.14 as an approximation of π.
A = lw
l
w
V = lwh
Arithmetic Properties
Additive Inverse: a + (
ˉ
a) = 0
Multiplicative Inverse: a ·
= 1
Commutative Property: a + b = b + a
a · b = b · a
Associative Property: (a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
(a · b) · c = a · (b · c)
Identity Property: a + 0 = a
a · 1 = a
Distributive Property: a · (b + c) = a · b + a · c
Multiplicative Property of Zero: a · 0 = 0
Additive Property of Equality:
If a = b, then a + c = b + c
Multiplicative Property of Equality:
If a = b, then a · c = b · c
1
a
Linear Equations
Slope: m =
Point-Slope Formula: (y – y
1
) = m(x – x
1
)
Slope-Intercept Formula: y = mx + b
Standard Equation of a Line: Ax + By = C
y
2
– y
1
x
2
– x
1
FORMULA SHEETALGEBRA I

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
8
1
Algebra IMODULE1
ALGEBRA I MODULE 1
MULTIPLE-CHOICE ITEMS
1. An equation is shown below.
4
√
__
3 =
√
____
24x
What is the value of x?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 6
D. 8
712006712006
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.1.1.2
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 1
p-value A 70% (correct answer)
p-value B 8%
p-value C 15%
p-value D 7%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option A, by converting
4
√
__
3 to
√
___
48 , since 48 is 4
2
times 3, setting the expressions under the
radical equal to each other (48 = 24x), and then dividing both sides by
24 to get x
= 2.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by attempting to compare
the numbers without correctly interpreting the radicals. For example,
the student could arrive at option C by multiplying 4 by 3 to get 12,
squaring the 12 to get 144, and then solving 144 = 24x by dividing both
sides by 24 to get x = 6.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
9
1
Algebra IMODULE1
2. A coefficient (a) and an exponent (b) are missing in the two monomials shownbelow.
ax
3
6x
b
The least common multiple (LCM) of the two monomials is 18x
5
. Which pair of statements about
the missing coefficient and the missing exponent istrue?
A. The missing coefficient (a) must be 9 or 18.
The missing exponent (b) must be 5.
B. The missing coefficient (a) must be 9 or 18.
The missing exponent (b) can be any number 5 or less.
C. The missing coefficient (a) can be any multiple of 3.
The missing exponent (b) must be 5.
D. The missing coefficient (a) can be any multiple of 3.
The missing exponent (b) can be any number 5 or less.
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.1.2.1
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 37% (correct answer)
p-value B 19%
p-value C 22%
p-value D 22%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option A, by identifying
the factors of 18 (2, 3 & 3), recognizing the factors of 6 (2 & 3),
determining that the missing coefficient must be either 3 • 3 = 9 or
3 • 3 • 2 = 18, and recognizing that the missing exponent must be the
same as the LCM’s exponent (5) since the other exponent (3) is less
than 5.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by applying incorrect
reasoning about the GCF of monomials. For example, the student could
arrive at option D by using 3 for the missing coefficient since 3 × 6 = 18
and by not realizing that, even though the lesser of the two exponents
can be any number less than or equal to 5, the other exponent must be
equal to 5.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
10
1
Algebra IMODULE1
3. Which expression is a factor of x
2
+ 3x–40?
A. (x – 4)
B. (x – 5)
C. (x – 8)
D. (x – 10)
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.1.5.2
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 15%
p-value B 56% (correct answer)
p-value C 18%
p-value D 11%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option B, by factoring
the given expression: x
2
+ 3x – 40 = (x + 8)(x – 5). Of the given answer
options, only (x – 5) is one of the factors of the given expression.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by incorrectly factoring
the given expression. For example, a student could arrive at option C
by recognizing that 5 and 8 are factors of 40 with a difference of 3 but
incorrectly pairing the 8 with a minus sign.
Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
11
1
Algebra IMODULE1
4. Simplify:
x(x – 5) – 14
}}
x
2
– 4
; x ≠
ˉ
2, 2
A.
ˉ
5x +
7
}
2
B.
x – 7
}
x – 2
C.
x + 7
}
x + 2
D.
x – 19
}
x – 4
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.1.5.3
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 1
p-value A 31%
p-value B 39% (correct answer)
p-value C 15%
p-value D 15%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option B, by expanding
the numerator [x(x – 5) – 14 = x
2
– 5x – 14], factoring the numerator and
denominator [x
2
– 5x – 14 = (x + 2)(x – 7) and x
2
– 4 = (x + 2)(x – 2)], and
eliminating the common factor (x + 2), which leaves
x – 7
}
x – 2
.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by incorrectly factoring
the numerator or by attempting to simplify the expression before
factoring. For example, a student could arrive at option A by expanding
the numerator [x(x – 5) – 14 = x
2
– 5x – 14] but then simplifying the
resulting rational expression in parts: eliminating the x
2
terms, making
ˉ
5x its own term, and simplifying
ˉ
14
}
ˉ
4
to
7
}
2
as its own term.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
12
1
Algebra IMODULE1
5. The steps taken to correctly solve an equation are shown below, but one step is missing.
ˉ
2(x – 3) =
ˉ
6(x + 4)
ˉ
2x + 6 =
ˉ
6x – 24
?
4x =
ˉ
30
x =
ˉ
7.5
Which set of statements shows the equation that is most likely the missing step and the
property that justifies the missing step?
A. 4x–6 = 24
This step is justified by the additive property of equality.
B. 4x–6 = 24
This step is justified by the multiplicative property of equality.
C. 4x + 6 =
ˉ
24
This step is justified by the additive property of equality.
D. 4x + 6 =
ˉ
24
This step is justified by the multiplicative property of equality.
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.2.1.2
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 12%
p-value B 8%
p-value C 70% (correct answer)
p-value D 10%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option C, by adding
6x to both sides of the equation, leaving
ˉ
24 on the right side of the
equation, and identifying the property used to justify this step as the
additive property of equality.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by not considering the
minus sign or by incorrectly identifying the property being used. For
example, a student could arrive at option A by adding 6x to each side of
the equation and then switching the signs for the “+ 6” and the “
ˉ
24.”

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
13
1
Algebra IMODULE1
6. Deshawn has a box of batteries. Some of the batteries provide 1.5volts each. The rest of
the batteries provide 9volts each. The total voltage provided by all the batteries in the box is
78volts. The equation shown below models thissituation.
1.5x + 9y = 78
One solution to this equation is (10, 7). What does this solutionrepresent?
A. The box contains 10 total batteries, 7of which provide 1.5volts each.
B. The box contains 10 total batteries, 7of which provide 9volts each.
C. The box contains 10 batteries that provide 1.5volts each and 7batteries that provide
9voltseach.
D. The box contains 10 batteries that provide 9volts each and 7batteries that provide
1.5voltseach.
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.2.1.3
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 6%
p-value B 12%
p-value C 74% (correct answer)
p-value D 8%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option C, by interpreting
the x-coordinate (10) as the number of batteries that provide 1.5 volts
and the y-coordinate (7) as the number of batteries that provide 9 volts.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by incorrectly interpreting
the meaning of the coordinates. For example, a student could arrive
at option B by interpreting the x-coordinate (10) as the total number of
batteries.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
14
1
Algebra IMODULE1
7. A system of equations is shown below.
y =
1
}
2
x + 1
y =
3
}
2
x– 1
Which graph shows the system of equations with the solution or solutions of the system of
equationslabeled?
A.
5
4
3
2
1
–
1
–
2
–
3
–
4
–
5
12345
–
5
–
4
–
3
–
2
–
1
y
x
solution
solution
B.
5
4
3
2
1
–
1
–
2
–
3
–
4
–
5
12345
–
5
–
4
–
3
–
2
–
1
y
x
solution
C.
5
4
3
2
1
–
1
–
2
–
3
–
4
–
5
12345
–
5
–
4
–
3
–
2
–
1
y
x
solution
solution
D.
5
4
3
2
1
–
1
–
2
–
3
–
4
–
5
12345
–
5
–
4
–
3
–
2
–
1
y
x
solution

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
15
1
Algebra IMODULE1
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.2.2.1
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 1
p-value A 6%
p-value B 5%
p-value C 24%
p-value D 65% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option D, by identifying
the graph of the system of equations and recognizing the point of
intersection as the solution of the system.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by misidentifying the
graph of the system of equations or by considering points other than
the point of intersection as the solution of the system. For example, a
student could arrive at option C by identifying the correct graph of the
system of equations but considering the y-intercepts to be the solutions
of the system.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
16
1
Algebra IMODULE1
8. Calvin will plant lily bulbs and iris bulbs in his front garden. He will plant a total of
40flowerbulbs and 3 times as many iris bulbs as lily bulbs. The graph below shows the number
of lily bulbs(x) and the number of iris bulbs(y) Calvin willplant.
Bulbs to Be Planted
Lily Bulbs
Iris Bulbs
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
501015203025 35 40 45 50
y
x
Which statement describes the point of intersection on the graph?
A. Calvin will plant 40 lily bulbs.
B. Calvin will plant 40 iris bulbs.
C. Calvin will plant 10 lily bulbs and 30 iris bulbs.
D. Calvin will plant 30 lily bulbs and 10 iris bulbs.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
17
1
Algebra IMODULE1
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.2.2.2
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 4%
p-value B 3%
p-value C 84% (correct answer)
p-value D 9%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option C, by identifying
the point of intersection as the solution of the system of equations and
interpreting the x-coordinate (10) as the number of lily bulbs and the
y-coordinate (30) as the number of iris bulbs.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by misinterpreting the
solution of the system of equations or by considering points other than
the point of intersection as the solution of the system. For example, a
student could arrive at option D by identifying the point of intersection
as the solution of the system of equations but switching the meanings
of the x-coordinate and y-coordinate.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
18
1
Algebra IMODULE1
9. Which graph represents the solution set of the inequality |2x – 1|<7?
A.
−
10
−
8
−
6104
−
20 268
−
4
B.
−
10
−
8
−
6104
−
20 268
−
4
C.
−
10
−
8
−
6104
−
20 268
−
4
D.
−
10
−
8
−
6104
−
20 268
−
4
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.3.1.1
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 1
p-value A 8%
p-value B 28%
p-value C 10%
p-value D 54% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option D, by rewriting
the absolute value inequality as a compound inequality (
ˉ
7<2x–1<7),
solving the compound inequality by adding 1 to all three expressions
and then dividing all three expressions by 2 to get
ˉ
3 < x < 4, and
identifying the corresponding graph by recognizing that strict
inequalities have boundaries with open circles and by recognizing that
the solution set is between
ˉ
3 and 4.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by misidentifying which
endpoints to use or by using a solution set that is not between
ˉ
3 and4.
For example, a student could arrive at option B by recognizing that
strict inequalities have boundaries with open circles but interpreting the
solution set as being less than
ˉ
3 or greater than 4.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
19
1
Algebra IMODULE1
10. An inequality is shown below.
ˉ
x + 2 >
ˉ
3(x + 2)
Which graph represents the solution set of the inequality?
A.
−
8
−
6
−
4
−
20
B.
−
8
−
6
−
4
−
20
C.
−
8
−
6
−
4
−
20
D.
−
8
−
6
−
4
−
20
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.3.1.2
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 1
p-value A 24%
p-value B 62% (correct answer)
p-value C 6%
p-value D 8%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option B, by rewriting
the right side of the inequality by distributing the
ˉ
3 to get
ˉ
3x – 6,
solving the inequality by adding 3x to both sides, subtracting 2
from both sides, and then dividing both sides by 2 to get x >
ˉ
4,
and identifying the corresponding graph by recognizing that a strict
inequality has a boundary with an open circle and by recognizing that
the solution set is greater than
ˉ
4.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by misidentifying which
endpoint to use or by using a solution set that is not greater than
ˉ
4.
For example, a student could arrive at option A by recognizing that a
strict inequality has a boundary with an open circle but interpreting the
solution set as being less than
ˉ
4.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
20
1
Algebra IMODULE1
11. Sam arrives at an amusement park with $61 that he can spend at the amusement park. The
entrance fee at the amusement park is $20. It costs $3 to play a game and $4 for each ride. He
plays 6games and goes on xrides. The inequality shown below represents this situation.
38 + 4x≤ 61
The solution of the inequality is x≤ 5.75. Based on the solution, which statement must betrue?
A. Sam went on at most 5 rides.
B. Sam went on at most 6 rides.
C. Sam went on more than 6 rides.
D. Sam went on fewer than 5 rides.
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.3.1.3
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 71% (correct answer)
p-value B 12%
p-value C 6%
p-value D 11%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option A, by recognizing
that the inequality represents a solution set of all values less than or
equal to 5.75, understanding that the solution set within the context can
be only whole numbers, and interpreting this to mean the largest value
in the solution set is 5.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by incorrectly interpreting
the meaning of the inequality or misunderstanding the limits of the
solution set. For example, a student could arrive at option B by
interpreting the inequality symbol to mean “at most” but then rounding
5.75 up to 6 without considering that 6 is outside the given solution set.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
21
1
Algebra IMODULE1
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
22
1
Algebra IMODULE1
12. April is purchasing bottles of orange juice and bottles of apple juice from the store. She will buy
no more than 6 bottles of juice and will spend no more than $10.00. Each bottle of orange juice
costs $3.75, and each bottle of apple juice costs $1.25. The graph shown below represents
thissituation.
Bottles of Juice Purchased
Bottles of Orange Juice
Bottles of Apple Juice
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
12345678
y
x
Which statement describes all possible solutions where x = 2?
A. April will purchase 2 bottles of orange juice and 4bottles of applejuice.
B. April will purchase 2 bottles of orange juice and nomore than 2 bottles of applejuice.
C. April will purchase at least 2 bottles of orange juice and at least 2 bottles of applejuice.
D. April will purchase at least 2 bottles of orange juice and at most 4 bottles of applejuice.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
23
1
Algebra IMODULE1
Item Information
Alignment A1.1.3.2.2
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 10%
p-value B 61% (correct answer)
p-value C 18%
p-value D 11%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option B, by interpreting
the graph to determine that the values of y (the number of bottles of
apple juice) can be no more than 2 when x (the number of bottles of
orange juice) is 2.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by not considering the
limits of the solution set or by misinterpreting what is meant by x=2.
For example, a student could arrive at option C by describing the
solution set for x ≥ 2 and for y ≥ 2 without considering that all the points
in this set of values, other than (2, 2), are outside the given solution set.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
24
1
Algebra IMODULE1
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
13. Small baskets of tomatoes are sold at a vegetable stand for $3 per basket. Large
baskets of tomatoes are sold at the stand for $5 per basket. Only whole numbers of
baskets may be purchased.
A customer purchases a total of 8 baskets of tomatoes and pays $36.
A. Write and solve a system of equations that models the number of small baskets (x) and the
number of large baskets (y) that the customer purchases. Show or explain all your work.
Go to the next page to finish question 13.
GO ON

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
25
1
Algebra IMODULE1
13. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Another customer claims that he can purchase a total of 10 baskets of tomatoes
and pay $45.
B. Use a system of equations that describes this other customer’s purchase to
explain why the claim is incorrect.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
26
1
Algebra IMODULE1
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
#13 Item Information
Alignment A1.1.2
Depth of
Knowledge
2 Mean Score 1.58
Assessment Anchor this item will be reported under:
A1.1.2—Linear Equations
Specific Anchor Descriptor addressed by this item:
A1.1.2.2—Write, solve, and/or graph systems of linear equations using various methods.
Scoring Guide
Score Description
4
The student demonstrates a thorough understanding of linear equations by correctly
solving problems with clear and complete procedures and explanations when required.
3
The student demonstrates a general understanding of linear equations by solving
problems and providing procedures and explanations with only minor errors or
omissions.
2
The student demonstrates a partial understanding of linear equations by providing a
portion of the correct problem solving, procedures, and explanations.
1
The student demonstrates a minimal understanding of linear equations.
0
The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any
understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures as required by the task.
Response may show only information copied from the question.
Top-Scoring Student Response and Training Notes
Score Description
4
Student earns 4 points.
3
Student earns 3.0–3.5 points.
2
Student earns 2.0–2.5 points.
1
Student earns 0.5–1.5 points.
OR
Student demonstrates minimal understanding of linear equations.
0
Response is incorrect or contains some correct work that is irrelevant to the skill or
concept being measured.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
27
1
Algebra IMODULE1
Top-Scoring Response
Part A (3 points):
1
__
2
point for each correct equation
1
__
2
point for each correct value of the solution
OR
1
__
2
point for embedded solution
1 point for complete support
OR
1
__
2
point for correct but incomplete support
What?
Why?
x + y = 8
3x + 5y = 36
AND
Sample Work:
x + y = 8
3x + 5y = 36
x = 8 – y
3x + 5y = 36
x = 2 (small baskets)
y = 6 (large baskets)
3(8 – y) + 5y = 36
24 – 3y + 5y = 36 x + 6 = 8
2y
= 12
→
x = 2
y = 6
OR
Sample Explanation:
First, I set up my system of equations.
x + y = 8
3x + 5y = 36
I then multiplied the first row by 5 and the second row by
–
1
so I could add them together and cancel out the y-terms. This
gave me 2x = 4, so x = 2. I substituted this value into the first
equation and solved it for y to get y = 6.
OR equivalent
→

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
28
1
Algebra IMODULE1
Part B (1 point):
1 point for correct and complete explanation
OR
1
}
2
point for correct but incomplete explanation
What?
Why?
Sample Explanation:
The system of equations that describes this other customer’s purchase is
shown.
x + y = 10
3x + 5y = 45
The solution of this system of equations exists, but neither x nor y is a whole
number, so the customer cannot purchase 10 baskets of tomatoes for $45.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
29
1
Algebra IMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 4 points
PARTS A AND B
Question 13
Page 1
The student provided two correct equations for the system of equations (3x + 5y = 36 and x + y = 8). The student
also provided a correct solution process by showing x + y = 8 solved for x (x=8–y), substituting that expression
for x into the first equation [3(8 – y) + 5y = 36], solving for y (y = 6), substituting the value of y into the equation
x+y=8 (x + 6 = 8), and then solving for x (x = 2). Although not required, the student described what the solution
represents (The customer bought 2small baskets of tomatoes and 6large baskets of tomatoes). [3points]
The student provided a correct and complete explanation as to why the solution of the system of equations
(y=7.5 and x = 2.5) demonstrates that the claim is incorrect (only whole numbers of bushels may be
purchased); the student using “bushels” instead of “baskets” is considered a blemish and does not detract from
demonstrating a thorough understanding. [1 point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
30
1
Algebra IMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 3 points
13. Small baskets of tomatoes are sold at a vegetable stand for $3 per basket. Large
baskets of tomatoes are sold at the stand for $5 per basket. Only whole numbers of
baskets may be purchased.
A customer purchases a total of 8 baskets of tomatoes and pays $36.
A. Write and solve a system of equations that models the number of small
baskets (x) and the number of large baskets (y) that the customer purchases.
Show or explain all your work.
Go to the next page to finish question 13.
GO ON
The student provided only one of two correct equations for the system of equations ($3x + $5y = $36). The student
also provided correct but incomplete support by showing only a “check” of the correct solution (3 × 2 = 6, 5 × 6 = 30,
and 30 + 6 = 36) without showing how the values were determined. The student provided the correct solution (2 small
baskets and 6 large baskets). [2 points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
31
1
Algebra IMODULE1
13. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Another customer claims that he can purchase a total of 10 baskets of tomatoes
and pay $45.
B. Use a system of equations that describes this other customer’s purchase to
explain why the claim is incorrect.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
The student provided a correct and complete explanation as to why the claim is incorrect by first exhausting all
possible whole-number solutions (if you plug in any pair of numbers adding up to (10) . . . you couldn’t get 45) and
then by describing why the actual solution does not work (you would have to plug in decimals, but you could only use
whole numbers). [1 point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
32
1
Algebra IMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 2 points
PARTS A AND B
Question 13
Page 1
The student provided no correct equations. The student provided correct but incomplete support by showing
only a “check” of the correct solution (5 × 6 + 3 × 2 = 36 and 6 + 2 = 8) without showing how the values were
determined. The student provided the correct solution using an ordered pair: (2,6). [1.5points]
The student provided a correct but incomplete explanation by writing a correct system of equations that
describes the purchase (x + y = 10 and 3x + 5y = 45) but without offering to explain why the claim is incorrect.
[0.5points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
33
1
Algebra IMODULE1
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
34
1
Algebra IMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 1 point
13. Small baskets of tomatoes are sold at a vegetable stand for $3 per basket. Large
baskets of tomatoes are sold at the stand for $5 per basket. Only whole numbers of
baskets may be purchased.
A customer purchases a total of 8 baskets of tomatoes and pays $36.
A. Write and solve a system of equations that models the number of small
baskets (x) and the number of large baskets (y) that the customer purchases.
Show or explain all your work.
Go to the next page to finish question 13.
GO ON
The student provided one of two correct equations for the system of equations (3x + 5y = 36). The student provided
incorrect support by solving 3x = 36 for x and 5y = 36 for y. The student provided an incorrect solution since these
values are the x-intercept (12) and the y-intercept (7.1) of the provided equation. [0.5 points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
35
1
Algebra IMODULE1
13. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Another customer claims that he can purchase a total of 10 baskets of tomatoes
and pay $45.
B. Use a system of equations that describes this other customer’s purchase to
explain why the claim is incorrect.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
The student provided an incorrect explanation by incorrectly writing one of the two equations for the system of
equations (3x = 5y = 45), solving for the x-intercept (15) and the y-intercept (9), and not offering to explain why the
claim is incorrect. [0 points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
36
1
Algebra IMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 0 points
PARTS A AND B
Question 13
Page 1
The student provided no correct equations, instead writing (x)(y) = 36. The student provided incorrect support by
substituting the prices of each small basket ($3) and each large basket ($5) into the provided equation: (3)(5) = 36.
The student provided an incorrect solution (12 small baskets and 0 large baskets) with no support to show how
this solution was determined. [0 points]
The student provided an incorrect explanation since the student determined the average price per basket (if you
take 45/10 you would get 4.5), which has no bearing on whether the claim is incorrect. [0 points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
37
1
Algebra IMODULE1
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
38
1
Algebra IMODULE1
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
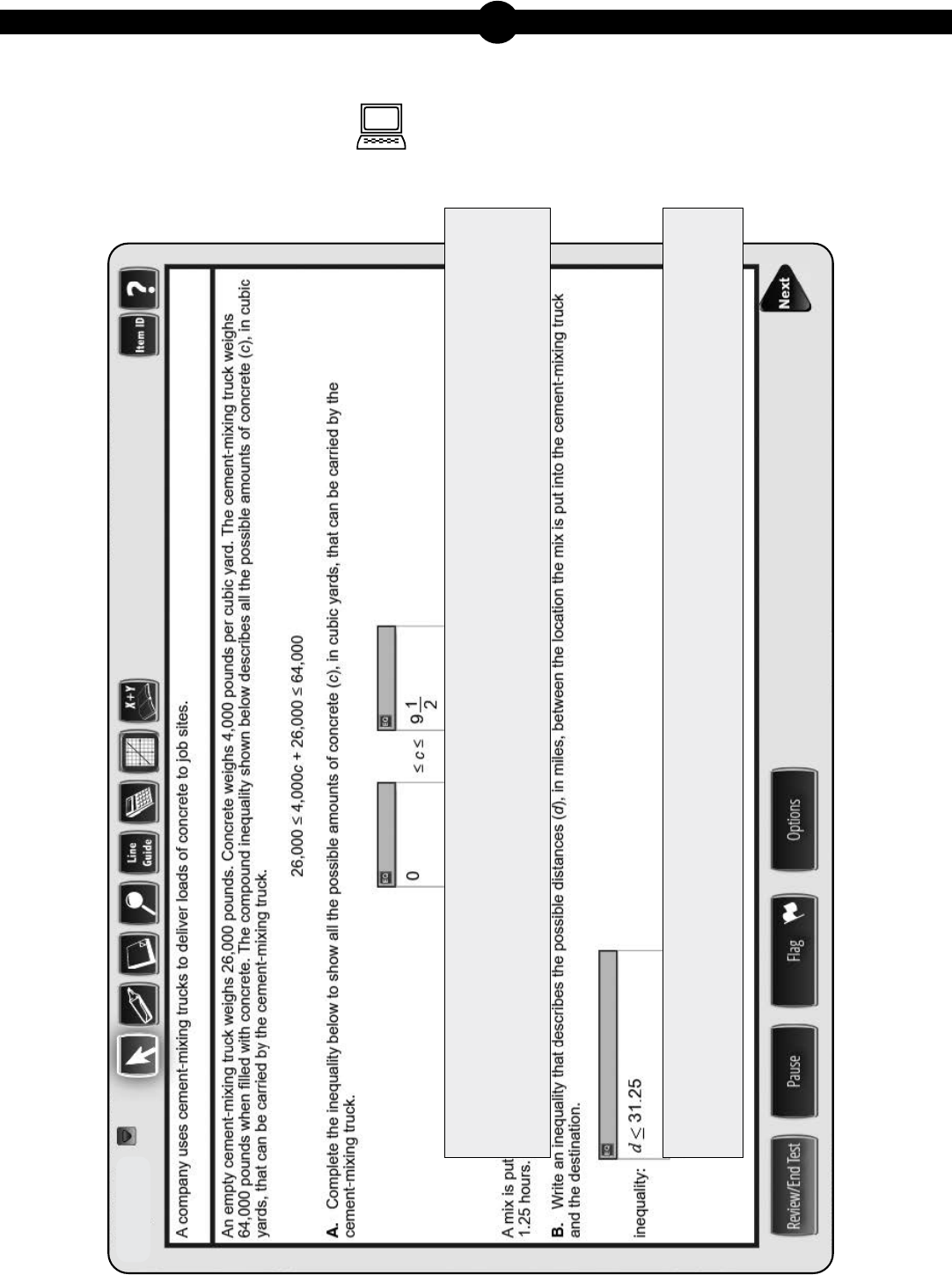
14. A company uses cement-mixing trucks to deliver loads of concrete tojobsites.
An empty cement-mixing truck weighs 26,000pounds. Concrete weighs
4,000pounds per cubic yard. The cement-mixing truck weighs 64,000pounds
when filled with concrete. The compound inequality shown below describes all the
possible amounts of concrete(c), in cubic yards, that can be carried by the
cement-mixingtruck.
26,000≤4,000c+26,000≤64,000
A. Complete the inequality below to show all the possible amounts of
concrete (c), in cubic yards, that can be carried by the cement-mixingtruck.
≤c≤
A mix is put into the cement-mixing truck to create concrete. The cement-mixing
truck must then arrive at its destination in no more than 1.25 hours. The cement-
mixing truck can average no more than 25miles perhour.
B. Write an inequality that describes the possible distances(d), in miles, between
the location the mix is put into the cement-mixing truck and the destination.
inequality:
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
39
1
Algebra IMODULE1
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
A specific job will require more than one truckload of concrete. The company will
use cement-mixing trucks that have different load capacities for carrying concrete.
The trucks they will use for this job will either have a load capacity of 6cubicyards
of concrete or a load capacity of 12cubicyards of concrete. The linear inequality
graphed below can be used to find the number of loads of concrete of each size
that will provide enough concrete to complete thejob.
Loads of Concrete Needed
Number of
6-Cubic-Yard Loads
Number of
12-Cubic-Yard Loads
012 345678
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
C. What is the minimum number of cubic yards of concrete needed to complete
thejob?
cubic yards of concrete:
D. Which ordered pair in the solution set represents the least total number of
loads of concrete needed to complete thejob?
ordered pair:( , )
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
40
1
Algebra IMODULE1
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
#14 Item Information
Alignment A1.1.3
Depth of
Knowledge
2 Mean Score 1.04
Assessment Anchor this item will be reported under:
A1.1.3—Linear Inequalities
Specific Anchor Descriptor addressed by this item:
A1.1.3.1—Write, solve, and/or graph linear inequalities using various methods.
Scoring Guide
Score
Description
4
The student demonstrates a thorough understanding of linear inequalities by correctly
solving problems with clear and complete procedures and explanations when required.
3
The student demonstrates a general understanding of linear inequalities by solving
problems and providing procedures and explanations with only minor errors or
omissions.
2
The student demonstrates a partial understanding of linear inequalities by providing a
portion of the correct problem solving, procedures, and explanations.
1
The student demonstrates a minimal understanding of linear inequalities.
0
The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any
understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures as required by the task.
Response may show only information copied from the question.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
41
1
Algebra IMODULE1
Top-Scoring Student Response and Training Notes
Score
Description
4
Student earns 4 points.
3
Student earns 3 points.
2
Student earns 2 points.
1
Student earns 1 point.
0
Response is incorrect or contains some correct work that is irrelevant to the skill or
concept being measured.
Top-Scoring Response
Part A (1 point):
1 point for correct answer
What?
Why?
0 ≤ c
≤ 9.5

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
42
1
Algebra IMODULE1
Part B (1 point):
1 point for correct answer
What?
Why?
d
≤ 31.25 (miles)
OR
0 ≤ d ≤ 31.25
OR
0 < d ≤ 31.25
OR equivalent
Part C (1 point):
1 point for correct answer
What?
Why?
36 (cubic yards)
Part D (1 point):
1 point for correct answer
What?
Why?
(0, 3)

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
43
1
Algebra IMODULE1
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.
Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
44
1
Algebra IMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 4 points
PARTS A AND B
Question 14
Page 1 of 2
The student provided the correct compound inequality with the correct endpoints of 0 and 9
1
}
2
(
0 ≤ c ≤ 9
1
}
2
)
. While
support is not required for PartA, the student likely subtracted 26,000 from all three expressions of the given
compound inequality and then divided each of the three resulting expressions by 4,000. [1point]
The student provided a correct inequality (d≤31.25). While support is not required for PartB, the student likely
multiplied the maximum speed of the truck (25miles per hour) by the maximum time (1.25hours) the cement can be in
the truck to determine the maximum distance (25×1.25=31.25miles). [1 point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
45
1
Algebra IMODULE1
PARTS C AND D
Question 14
Page 2 of 2
The student provided the correct answer (36). While support is not required for PartC, the student likely
recognized that any point on the boundary line of the graphed linear inequality will yield the minimum
value, selected a point on the line, multiplied the x-coordinate by 6cubic yards and the y-coordinate by
12cubic yards, and then added the products. For example, by using the point (4, 1), the student could
have multiplied 4 by 6 and 1 by 12 and then added the products, resulting in 36 cubic yards of concrete
(4×6+1×12=24+12=36). [1point]
The student provided the correct ordered pair: (0, 3). While support is not required for PartD, the student
likely recognized that the coordinates should be added and identified that the smallest sum in the solution
set occurs at (0, 3), which would result in only 3 loads. [1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
46
1
Algebra IMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 3 points
14. A company uses cement-mixing trucks to deliver loads of concrete tojobsites.
An empty cement-mixing truck weighs 26,000pounds. Concrete weighs
4,000pounds per cubic yard. The cement-mixing truck weighs 64,000pounds
when filled with concrete. The compound inequality shown below describes all the
possible amounts of concrete(c), in cubic yards, that can be carried by the
cement-mixingtruck.
26,000≤4,000c+26,000≤64,000
A. Complete the inequality below to show all the possible amounts of
concrete (c), in cubic yards, that can be carried by the cement-mixingtruck.
≤c≤
A mix is put into the cement-mixing truck to create concrete. The cement-mixing
truck must then arrive at its destination in no more than 1.25 hours. The cement-
mixing truck can average no more than 25miles perhour.
B. Write an inequality that describes the possible distances(d), in miles, between
the location the mix is put into the cement-mixing truck and the destination.
inequality:
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON
The student gave the correct answer by providing a compound inequality with the correct endpoints of 0 and 9.5
(0≤c ≤9.5). The work shown is correct, though not necessary for credit. The student first subtracted 26,000 from
all three expressions of the given compound inequality and then divided each of the resulting expressions by 4,000.
[1point]
The student provided a correct inequality (0 ≤ x ≤ 31.25). The work shown is correct, though not necessary for credit.
The student started with the distance formula (d = rt) and then multiplied the maximum speed of the truck (25 miles
per hour) by the maximum time (1.25 hours) the cement can be in the truck to determine the maximum distance
(d=31.25). [1 point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
47
1
Algebra IMODULE1
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
A specific job will require more than one truckload of concrete. The company will
use cement-mixing trucks that have different load capacities for carrying concrete.
The trucks they will use for this job will either have a load capacity of 6cubicyards
of concrete or a load capacity of 12cubicyards of concrete. The linear inequality
graphed below can be used to find the number of loads of concrete of each size
that will provide enough concrete to complete thejob.
Loads of Concrete Needed
Number of
6-Cubic-Yard Loads
Number of
12-Cubic-Yard Loads
012 345678
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
C. What is the minimum number of cubic yards of concrete needed to complete
thejob?
cubic yards of concrete:
D. Which ordered pair in the solution set represents the least total number of
loads of concrete needed to complete thejob?
ordered pair:( , )
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
The student provided the correct answer (36). While support is not required for PartC, the student likely recognized
that any point on the boundary line of the graphed linear inequality will yield the minimum value, selected a point on
the line, multiplied the x-coordinate by 6 cubic yards and the y-coordinate by 12 cubic yards, and then added the
products. For example, by using the point (2, 2), the student could have multiplied 2 by 6 and 2 by 12 and then added
the products, resulting in 36 cubic yards of concrete (2×6+2×12=12+24=36). [1 point]
The student provided an incorrect ordered pair: (2, 2). No support (work or explanation) is required, so it is unclear
where an error was made. The student may have recognized that the minimum value should occur on the boundary
line of the graphed linear inequality; however, the student may not have considered that sums of the coordinates
should be compared, instead selecting a point on the graph for which the x-coordinate and the y-coordinate are the
same. [0points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
48
1
Algebra IMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 2 points
PARTS A AND B
Question 14
Page 1 of 2
The student provided an incorrect compound inequality (0 ≤ c ≤ 16). No support (work or explanation) is required,
so it is unclear where an error was made. The student may have subtracted 26,000 from the left-hand and middle
expressions of the given compound inequality but not from the right-hand expression, resulting in 0≤4,000c≤64,000,
and then divided each of the three resulting expressions by 4,000. No credit is awarded for a partially correct
compound inequality. [0points]
The student provided an incorrect inequality (d < 1.25). No support (work or explanation) is required, so it is unclear
where an error was made. The student may not have recognized that the distance can be found by multiplying the
maximum time (1.25 hours) the cement can be in the truck by the maximum speed of the truck (25 miles per hour). The
student also misinterpreted “no more than” as meaning less than (<) instead of less than or equal to (≤). [0points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
49
1
Algebra IMODULE1
PARTS C AND D
Question 14
Page 2 of 2
The student provided the correct answer (36). While support is not required for PartC, the student likely
recognized that any point on the boundary line of the graphed linear inequality will yield the minimum
value, selected a point on the line, multiplied the x-coordinate by 6cubic yards and the y-coordinate by
12cubic yards, and then added the products. For example, by using the point (6, 0), the student could
have multiplied 6 by 6 and 0 by 12 and then added the products, resulting in 36 cubic yards of concrete
(6×6+0×12=36+0=36). [1point]
The student provided a correct ordered pair: (0, 3). While support is not required for PartD, the student
likely recognized that the coordinates should be added and identified that the smallest sum in the solution
set occurs at (0, 3), which would result in only 3loads. [1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
50
1
Algebra IMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 1 point
14. A company uses cement-mixing trucks to deliver loads of concrete tojobsites.
An empty cement-mixing truck weighs 26,000pounds. Concrete weighs
4,000pounds per cubic yard. The cement-mixing truck weighs 64,000pounds
when filled with concrete. The compound inequality shown below describes all the
possible amounts of concrete(c), in cubic yards, that can be carried by the
cement-mixingtruck.
26,000≤4,000c+26,000≤64,000
A. Complete the inequality below to show all the possible amounts of
concrete (c), in cubic yards, that can be carried by the cement-mixingtruck.
≤c≤
A mix is put into the cement-mixing truck to create concrete. The cement-mixing
truck must then arrive at its destination in no more than 1.25 hours. The cement-
mixing truck can average no more than 25miles perhour.
B. Write an inequality that describes the possible distances(d), in miles, between
the location the mix is put into the cement-mixing truck and the destination.
inequality:
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON
The student provided an incorrect compound inequality (26,000 ≤ c ≤ 64,000). The student used the endpoints from
the given compound inequality without subtracting 26,000 from the endpoint values and dividing each difference
by4,000. [0points]
The student provided an incorrect inequality (25d ≤ 1.25). The student set up the inequality incorrectly by multiplying
the distance (d) by the maximum speed of the truck (25 miles per hour) instead of multiplying the maximum time
(1.25hours) the cement can be in the truck by the maximum speed of the truck. [0points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
51
1
Algebra IMODULE1
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
A specific job will require more than one truckload of concrete. The company will
use cement-mixing trucks that have different load capacities for carrying concrete.
The trucks they will use for this job will either have a load capacity of 6cubicyards
of concrete or a load capacity of 12cubicyards of concrete. The linear inequality
graphed below can be used to find the number of loads of concrete of each size
that will provide enough concrete to complete thejob.
Loads of Concrete Needed
Number of
6-Cubic-Yard Loads
Number of
12-Cubic-Yard Loads
012 345678
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
C. What is the minimum number of cubic yards of concrete needed to complete
thejob?
cubic yards of concrete:
D. Which ordered pair in the solution set represents the least total number of
loads of concrete needed to complete thejob?
ordered pair:( , )
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
The student provided an incorrect answer (3 yd
3
). No support (work or explanation) is required, so it is unclear where
an error was made. Although the student may have recognized that the minimum value should occur on the boundary
line of the graphed linear inequality and realized that the coordinates should be combined, the student may have
then added the coordinates without first multiplying each coordinate by the volume of the loads (the x-coordinate by
6 cubic yards and the y-coordinate by 12 cubic yards) and identified the smallest sum, which would occur at (0, 3),
resulting in 0 + 3 = 3. [0points]
The student provided the correct ordered pair: (0, 3). While support is not required for PartD, the student likely
recognized that the coordinates should be added and identified that the smallest sum in the solution set occurs
at(0,3), which would result in only 3 loads. [1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
52
1
Algebra IMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 0 points
PARTS A AND B
Question 14
Page 1 of 2
The student provided an incorrect compound inequality (30,000 ≤ c ≤ 62,000). No support (work or explanation) is
required, so it is unclear where an error was made. The student may have started with 26,000≤4,000c+26,000 from
the given compound inequality and then attempted to solve for c by adding 4,000 to the lower endpoint, resulting in
30,000, and then transposing the 26 of the remaining 26,000 to arrive at 62,000 for the upper endpoint. [0points]
The student provided an incorrect compound inequality (25 ≤ d ≤ 31.25). Although the 31.25 is the correct upper
endpoint, the student used the maximum speed of the truck (25 miles per hour) as the lower endpoint. No credit is
awarded for a partially correct compound inequality. [0points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
53
1
Algebra IMODULE1
PARTS C AND D
Question 14
Page 2 of 2
The student provided an incorrect answer (72) for the minimum number of cubic yards of concrete
needed to complete the job. No support (work or explanation) is required, so it is unclear where an error
was made. The student may have multiplied 6cubic yards by 12cubic yards (6×12=72). [0points]
The student provided an incorrect ordered pair: (6, 3). No support (work or explanation) is required, so it is
unclear where an error was made. The student may have identified the x-intercept (6) and the y-intercept
(3), and then used these intercepts to write an ordered pair without considering that this ordered pair
represents a point in the solution set that is not on the boundary line of the linear inequality. [0 points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
54
1
Algebra IMODULE1
ALGEBRA I MODULE 1—SUMMARY DATA
Multiple-Choice
Sample
Number Alignment Answer Key
Depth of
Knowledge
p-value
A
p-value
B
p-value
C
p-value
D
1 A1.1.1.1.2 A 1 70% 8% 15% 7%
2 A1.1.1.2.1 A 2 37% 19% 22% 22%
3 A1.1.1.5.2 B 2 15% 56% 18% 11%
4 A1.1.1.5.3 B 1 31% 39% 15% 15%
5 A1.1.2.1.2 C 2 12% 8% 70% 10%
6 A1.1.2.1.3 C 2 6% 12% 74% 8%
7 A1.1.2.2.1 D 1 6% 5% 24% 65%
8 A1.1.2.2.2 C 2 4% 3% 84% 9%
9 A1.1.3.1.1 D 1 8% 28% 10% 54%
10 A1.1.3.1.2 B 1 24% 62% 6% 8%
11 A1.1.3.1.3 A 2 71% 12% 6% 11%
12 A1.1.3.2.2 B 2 10% 61% 18% 11%
Constructed-Response
Sample
Number Alignment Points
Depth of
Knowledge Mean Score
13 A1.1.2 4 2 1.58
14 A1.1.3 4 2 1.04

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
55
1
Algebra IMODULE1
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
56
2
Algebra IMODULE2
ALGEBRA I MODULE 2
MULTIPLE-CHOICE ITEMS
1. The first six numbers in a pattern are listedbelow.
ˉ
19.2
ˉ
18.4
ˉ
17.6
ˉ
16.8
ˉ
16
ˉ
15.2
The pattern continues. Which expression could be used to determine the 100thnumber in
thepattern?
A.
ˉ
39.2(100) + 20
B.
ˉ
0.8(100)–18.4
C. 0.8(100)–20
D. 20(100)–135.2
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.1.1.1
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 8%
p-value B 30%
p-value C 54% (correct answer)
p-value D 8%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option C, by using
the pattern to determine the rate of change (0.8). Of the given answer
choices, only option C uses a rate of change of 0.8.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by incorrectly determining
the rate of change and testing only one of the values in the pattern. For
example, a student could arrive at option B by thinking the values are
going down by 0.8 without considering the effect of the negative signs
and then testing only the first value in the pattern [
ˉ
0.8(1) – 18.4 =
ˉ
19.2].

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
57
2
Algebra IMODULE2
2. The table below lists all the ordered pairs representing arelation.
x y
1 0
1 4
2 4
3 0
5 4
5 0
What is the domain of therelation?
A. {0, 4}
B. {1, 2, 3, 5}
C. {all real numbers from 0 to 4}
D. {all real numbers from 1 to 5}
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.1.1.3
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 1
p-value A 14%
p-value B 60% (correct answer)
p-value C 8%
p-value D 18%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option B, by recognizing
that the domain is the set of the x-values in a given relation and finding
the option with the same set of x-values as shown in the table.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by identifying the range
instead of the domain or by including all real number values between
the given numbers. For example, a student could arrive at option D
by thinking the domain must include all real numbers between the
minimum and maximum x-values.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
58
2
Algebra IMODULE2
3. For a local race, the prize for first place is $250 plus an additional $5 for every person who
registers for the race. The equation shown below represents the prize(y), indollars, for first
place based on the number of people(x) who register for therace.
y = 5x + 250
Which statement about the prize for first place istrue?
A. The prize for first place will always be a multiple of50.
B. The prize for first place will be $325 if 75people register for therace.
C. The prize for first place when there are 50 people registered for the race is twice as much
as when there are 25 people registered.
D. The prize for first place when there are 100 people registered for the race is twice as much
as when there are 25 people registered.
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.1.2.1
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 11%
p-value B 6%
p-value C 24%
p-value D 59% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option D, by substituting
100 and 25 into the equation for x and comparing the associated
y-values (750 and 375).
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by misinterpreting what
the values in the equation represent or by misapplying the numbers in
the answer choices. For example, a student could arrive at option C by
thinking the y-value must double when the x-value is doubled without
considering the effect of the constant term on the associated y-values.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
59
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.
2
Algebra IMODULE2
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
60
2
Algebra IMODULE2
4. The equation 3x + y = 8 describes a function of x. Which graph represents the function?
A.
x
y
481026
–
2
–
4
–
6
–
8
10
8
6
4
2
–
4
–
8
–
10
–
10
–
2
–
6
B.
x
y
481026
–
2
–
4
–
6
–
8
10
8
6
4
2
–
4
–
8
–
10
–
10
–
2
–
6
C.
x
y
481026
–
2
–
4
–
6
–
8
10
8
6
4
2
–
4
–
8
–
10
–
10
–
2
–
6
D.
x
y
481026
–
2
–
4
–
6
–
8
10
8
6
4
2
–
4
–
8
–
10
–
10
–
2
–
6

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
61
2
Algebra IMODULE2
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.1.2.2
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 1
p-value A 10%
p-value B 7%
p-value C 17%
p-value D 66% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option D, by rewriting
the equation in slope-intercept form (y =
ˉ
3x + 8) or by substituting
0s in for x and for y to find the y-intercept (y = 8) and the x
-intercept
(
3x=8→x= 2
2
}
3
)
, respectively.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by applying an incorrect
slope. For example, a student could arrive at option C by using the
coefficient of x as the slope without first rewriting the equation in
slope-intercept form.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
62
2
Algebra IMODULE2
5. Paul paints houses. He charges his customers a fixed amount to cover the expenses of using a
paint sprayer and buying brushes. He also charges an amount based on the number of gallons
of paint (x) he will need. The equation shown below represents the total amount(y), indollars,
Paul charges his customers for the materials he will need for ajob.
y = 14.5x + 80
What is represented by the number 14.5 in Paul’s equation?
A. the number of gallons of paint Paul willneed
B. the charge for each gallon of paint Paul willneed
C. the number of hours it will take to complete the paint job
D. the fixed amount charged for using a paint sprayer and buyingbrushes
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.2.1.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 26%
p-value B 63% (correct answer)
p-value C 5%
p-value D 6%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option B, by identifying
the coefficient of x as the rate of change and interpreting that to mean
the amount charged for each gallon of paint.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by switching the
meanings of two elements in the equation or by misinterpreting the rate
of change within the context. For example, a student could arrive at
option A by switching the meanings of the 14.5 and the x.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
63
2
Algebra IMODULE2
6. What is the equation of the line that passes through the points(
ˉ
2, 4) and(6, 2)?
A. y = 0.25x + 4.5
B. y = 0.25x + 0.5
C. y =
ˉ
0.25x + 14
D. y =
ˉ
0.25x + 3.5
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.2.1.3
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 1
p-value A 13%
p-value B 12%
p-value C 14%
p-value D 61% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option D, by using the
slope formula (m =
2 – 4
}
6 –
ˉ
2
=
ˉ
2
}
8
=
ˉ
0.25), applying the point-slope formula
using the slope and either of the given points [y – 2 =
ˉ
0.25(x – 6) or
y–4=
ˉ
0.25(x–
ˉ
2)], and then rewriting that equation in slope-intercept
form.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by reversing the sign
of the slope or by incorrectly finding the value of the y-intercept. For
example, a student could arrive at option C by finding the slope but
then determining the x-intercept instead of the y-intercept by starting
at the point (6, 2) and then adding 1 to the x-coordinate and
ˉ
0.25 to
the y-coordinate until the y-coordinate becomes 0, which occurs at the
point (14, 0).

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
64
2
Algebra IMODULE2
7. A line is graphed on the coordinate plane shown below.
5
4
3
2
1
–
1
–
2
–
3
–
4
–
5
12345
–
5
–
4
–
3
–
2
–
1
y
x
Which statement correctly describes the line?
A. The line has a slope of
–
2 and a y-intercept of
–
4.
B. The line has a slope of
–
2 and a y-intercept of
–
2.
C. The line has a slope of
–
1
__
2
and a y-intercept of
–
4.
D. The line has a slope of
–
1
__
2
and a y-intercept of
–
2.
819635819635

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
65
2
Algebra IMODULE2
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.2.1.4
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 1
p-value A 13%
p-value B 12%
p-value C 7%
p-value D 68% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option D, by
using twoordered pairs on the graph to determine the slope
(
m=
–
2– 0
______
0–
–
4
=
–
2
__
4
=
–
1
__
2
)
and identifying that the line crosses the y-axis at
(0,
–
2) for a y-intercept of
–
2.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by inverting the slope
formula or by using the x-intercept instead of the y-intercept. For
example, a student could arrive at option A by inverting the slope
formula as m =
–
4–0
______
0–
–
2
=
–
4
__
2
=
–
2 and by using
–
4 for the y-intercept since
the line crosses the x-axis at (
–
4, 0).

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
66
2
Algebra IMODULE2
8. Jessie lifts dumbbells as part of her exercise routine. The scatter plot below shows the
relationship between the number of pounds (x) a dumbbell weighs and the number of
repetitions(y) of a specific exercise that Jessie can perform.
0
x
y
10 15 20 25 30 35
10
5
15
20
25
30
Dumbbell Weight (pounds)
Number of Repetitions
Performed
Jessie’s Exercise Routine
Based on the scatter plot, which equation represents a line of best fit that could be used to
model the relationship between the weights of the dumbbells and the numbers of repetitions
that Jessie canperform?
A. y =
ˉ
0.8x + 30
B. y =
ˉ
1.5x + 50
C. y =
ˉ
2.8x + 73
D. y =
ˉ
3.5x + 52

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
67
2
Algebra IMODULE2
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.2.2.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 38%
p-value B 39% (correct answer)
p-value C 12%
p-value D 11%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option B, by estimating
the slope
(
m =
5 – 25
}
30 – 15
=
ˉ
20
}
15
=
ˉ
1
1
}
3
)
. Of the given answer choices, only
option B has a slope that is close to
ˉ
1
1
}
3
.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by estimating an incorrect
slope or y-intercept. For example, a student could arrive at option A
by estimating the slope using two points from the right side of the
data [e.g., (25, 10) and (30, 5), which results in m =
5 – 10
}
30 – 25
=
ˉ
5
}
5
=
ˉ
1]
without considering the effect of the two points on the left and using the
greatest value on the y-axis as the y
-intercept.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
68
2
Algebra IMODULE2
9. The list below represents the number of novels written by each of Amir’s 10favoriteauthors.
1334578101223
What is the interquartile range of the number of novels written by each of Amir’s
10favoriteauthors?
A. 3
B. 6
C. 7
D. 22
682132682132
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.3.1.1
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 1
p-value A 16%
p-value B 18%
p-value C 47% (correct answer)
p-value D 19%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option C, by determining
the first and third quartile values, which are the 3rd value (3) and
8thvalue (10) of the sorted list, and then finding the difference between
these two values (10 – 3).
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by determining an
incorrect measure of data. For example, a student could arrive at
optionD by determining the range of the data, which is the difference
between the maximum value (23) and the minimum value (1).

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
69
2
Algebra IMODULE2
10. Dion has two bunches of similar bananas. One bunch has 8bananas, and the other bunch has
9bananas. The list below shows the weight, ingrams, of each of the bananas in the bunch of8.
138118121164140115129123
Which measurement is most likely closest to the total weight of the bunch of 9bananas?
A. 932 grams
B. 1,048 grams
C. 1,179 grams
D. 1,368 grams
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.3.2.1
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 7%
p-value B 25%
p-value C 64% (correct answer)
p-value D 4%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option C, by determining
either the median value (126) or the mean value (131) of the 8 given
weights and then multiplying that value by 9, resulting in either 1,134
or 1,179. Of the answer choices, only option C is close to the derived
product.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by incorrectly determining
the measure of center or misapplying a measure of center. For example,
a student could arrive at option B by determining either the median
value (126) or the mean value (131) of the 8 given weights, multiplying
that value by 8 instead of 9, resulting in either 1,008 or 1,048, and then
selecting the answer choice that is closest to the derived product.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
70
2
Algebra IMODULE2
11. Vaughn surveyed 9 classmates. He asked each classmate for the number of days in the
previous week that he or she had eaten fruit and the number of days that he or she had
exercised. The scatter plot below shows the results of hissurvey.
Vaughn’s Survey Results
Number of Days
Fruit Eaten
Number of
Days Exercised
1
1
02
2
3
3
4
4
6
6
5
5
7
7
y
x
What is the median number of days that the 9 classmates exercised lastweek?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
817711817711

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
71
2
Algebra IMODULE2
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.3.2.2
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 4%
p-value B 12%
p-value C 75% (correct answer)
p-value D 9%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option C, by identifying
the median value of the y-coordinates (4) since the y-coordinates
represent the numbers of days exercised.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by misinterpreting what
each coordinate represents. For example, a student could arrive at
option B by identifying the median value of the x-coordinates, which
represent the numbers of days the students had eaten fruit.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
72
2
Algebra IMODULE2
12. A bookstore manager will randomly select 1 of 5 newly arrived fiction books and 1 of 4newly
arrived nonfiction books for a window display. What is the probability that the manager will
select the shortest of the newly arrived fiction books and the longest of the newly arrived
nonfictionbooks?
A. 5%
B. 10%
C. 20%
D. 45%
Item Information
Alignment A1.2.3.3.1
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 37% (correct answer)
p-value B 17%
p-value C 29%
p-value D 17%
Option Annotations A student could determine the correct answer, option A, by determining
the probability of selecting the shortest fiction book
(
1
}
5
)
, determining
the probability of selecting the longest nonfiction book
(
1
}
4
)
, and then
multiplying these probabilities together
(
1
}
5
•
1
}
4
=
1
}
20
= 0.05
)
.
A student could arrive at an incorrect answer by misapplying the
simple probabilities. For example, a student could arrive at optionC
by determining the number of combinations of books (5 • 4 = 20) and
incorrectly interpreting this as a percentage.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
73
2
Algebra IMODULE2
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
74
2
Algebra IMODULE2
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
13. Lydia delivers vegetables from a community garden. For the residents of her community, she
charges a fixed fee and a constant amount per pound of vegetables she delivers. Some of the
delivery charges based on the weight of the vegetables are shown in the tablebelow.
Lydia’s Delivery Charges
Weight
(pounds)
Delivery Charge
(dollars)
2 3.00
4 4.00
5 4.50
7 5.50
A. Based on the information in the table, how much would Lydia charge to deliver
10pounds ofvegetables?
B. Explain why including 0 in the domain of the function does not make sense in
the context of the situationdescribed.
Go to the next page to finish question 13.
GO ON

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
75
2
Algebra IMODULE2
13. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
For people who live outside of the community, Lydia adds a $5.00 gas fee to the
deliverycharge.
C. Explain why the linear function for Lydia’s delivery charges for residents in her
community and the linear function for her delivery charges for people who live
outside of the community have the same domain but differentranges.
D. Write a function to represent Lydia’s delivery charge (y), in dollars, to deliver
xpounds of vegetables to people who liveoutside the community.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
76
2
Algebra IMODULE2
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
#13 Item Information
Alignment A1.2.1
Depth of
Knowledge
2 Mean Score 1.88
Assessment Anchor this item will be reported under:
A1.2.1—Functions
Specific Anchor Descriptor addressed by this item:
A1.2.1.1—Analyze and/or use patterns or relations.
A1.2.1.2—Interpret and/or use linear functions and their equations, graphs, or tables.
Scoring Guide
Score
Description
4
The student demonstrates a thorough understanding of functions by correctly solving
problems with clear and complete procedures and explanations when required.
3
The student demonstrates a general understanding of functions by solving problems
and providing procedures and explanations with only minor errors or omissions.
2
The student demonstrates a partial understanding of functions by providing a portion of
the correct problem solving, procedures, and explanations.
1
The student demonstrates a minimal understanding of functions.
0
The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any
understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures as required by the task.
Response may show only information copied from the question.
Top-Scoring Student Response and Training Notes
Score
Description
4
Student earns 4 points.
3
Student earns 3.0–3.5 points.
2
Student earns 2.0–2.5 points.
1
Student earns 0.5–1.5 points.
OR
Student demonstrates minimal understanding of functions.
0
Response is incorrect or contains some correct work that is irrelevant to the skill or
concept being measured.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
77
2
Algebra IMODULE2
Top-Scoring Response
Part A (1 point):
1 point for correct answer
What?
Why?
$7
Part B (1 point):
1 point for correct and complete explanation
OR
1
}
2
point for correct but incomplete explanation
What?
Why?
Sample Explanation:
If 0 was in the domain, it would represent delivering 0 pounds of vegetables and
would cost $2. Nobody would pay $2 to not have anything delivered.
OR equivalent

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
78
2
Algebra IMODULE2
Part C (1 point):
1 point for correct and complete explanation
OR
1
}
2
point for correct but incomplete explanation
Note: Student does not need to provide an example for full credit (not requested in the
prompt).
What?
Why?
Sample Explanation:
The linear functions would have the same domain because the set of possible weights
of vegetables Lydia can deliver does not change. The linear functions would have
different ranges because the delivery charge for people who live outside the community
has an additional $5 gas fee. For example, $3 exists in the range for the delivery
charges for residents in her community but does not exist in the range for the delivery
charges for people who live outside of the community, because of the $5 gas fee.
OR equivalent
Part D (1 point):
1 point for correct answer
OR
1
}
2
point for an equation with either the correct slope or correct y-intercept
OR
1
}
2
point for a correct expression (i.e., 0.5x + 7 or equivalent)
What?
Why?
y
= 0.5x + 7
OR equivalent

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
79
2
Algebra IMODULE2
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
80
2
Algebra IMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 4 points
13. Lydia delivers vegetables from a community garden. For the residents of her community, she
charges a fixed fee and a constant amount per pound of vegetables she delivers. Some of the
delivery charges based on the weight of the vegetables are shown in the tablebelow.
Lydia’s Delivery Charges
Weight
(pounds)
Delivery Charge
(dollars)
2 3.00
4 4.00
5 4.50
7 5.50
A. Based on the information in the table, how much would Lydia charge to deliver
10pounds ofvegetables?
B. Explain why including 0 in the domain of the function does not make sense in
the context of the situationdescribed.
Go to the next page to finish question 13.
GO ON
The student provided the correct answer ($7). The work shown is
correct, though not necessary for credit. The student included the
recognition that each pound of vegetables delivered is $0.50 and
the delivery charge is an additional $2. From here, the student likely
determined the charge for the delivery of 10 pounds of vegetables by
multiplying 0.50 by10 and adding 2, resulting in a delivery charge of
$7. [1point]
The student provided a correct and complete explanation (If there are
0 pounds of vegetables then there is no need to pay for it). [1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
81
2
Algebra IMODULE2
13. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
For people who live outside of the community, Lydia adds a $5.00 gas fee to the
deliverycharge.
C. Explain why the linear function for Lydia’s delivery charges for residents in her
community and the linear function for her delivery charges for people who live
outside of the community have the same domain but differentranges.
D. Write a function to represent Lydia’s delivery charge (y), in dollars, to deliver
xpounds of vegetables to people who liveoutside the community.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
The student provided a correct and complete explanation (They have the same domain because Lydia still charges
50cents per pound for the vegetables. They have different ranges because the people outside of the community have
to pay for a $5 gas fee . . . causing the amount of money to go up) by recognizing that the domain represents the
pounds of vegetables delivered and the ranges are different due to the gas fee. [1point]
The student provided a correct function (y = 0.5x + 7). While support is not required for Part D, the student likely
recognized that the constant amount per pound would remain at $0.50 (0.5x) and that the original $2 fixed fee would
increase by $5 to $7 (+ 7). [1 point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
82
2
Algebra IMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 3 points
PARTS A AND B
Question 13
Page 1 of 2
The student provided an incorrect answer ($6.00). No support
(work or explanation) is required, so it is unclear where an error
was made. The student may have determined the delivery charge
for 8pounds of vegetables (0.50•8+2=6). [0points]
The student provided a correct and complete explanation (it
is obvoius 0 of something costs zero dollars), realizing that
someone receiving nothing should pay nothing. [1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
83
2
Algebra IMODULE2
PARTS C AND D
Question 13
Page 2 of 2
The student provided a correct and complete explanation (The
pounds of vegtables (domain) are still available while the cost
(range) are increased by five dollars because of the out of city gas
fee). [1 point]
The student provided a correct function (y = x × 0.50 + 7). While
support is not required for PartD, the student likely recognized
that the constant amount per pound would remain at $0.50
(x×0.50) and that the original $2fixed fee would increase by $5
to $7 (+7). [1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
84
2
Algebra IMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 2 points
13. Lydia delivers vegetables from a community garden. For the residents of her community, she
charges a fixed fee and a constant amount per pound of vegetables she delivers. Some of the
delivery charges based on the weight of the vegetables are shown in the tablebelow.
Lydia’s Delivery Charges
Weight
(pounds)
Delivery Charge
(dollars)
2 3.00
4 4.00
5 4.50
7 5.50
A. Based on the information in the table, how much would Lydia charge to deliver
10pounds ofvegetables?
B. Explain why including 0 in the domain of the function does not make sense in
the context of the situationdescribed.
Go to the next page to finish question 13.
GO ON
The student provided an incorrect answer ($11.50). The student provided work, although it is not required or assessed. Based
on the work provided, the student correctly determined that the slope (m) is
1
}
2
. In the redrawn table, the student correctly
showed that the domain increases by 3 (+3) from 7 to 10 but incorrectly increased the range by 6 (+6) from 5.5 toy, resulting
in y = 11.50. The student may have determined the incorrect amount of increase for the range by dividing the amount of
increase for the domain by
1
}
2
instead of multiplying it by
1
}
2
. [0points]
The student provided a correct and complete explanation (if the domain is zero then that means there is zero pounds.
When there is zero pounds it obviously wouldn’t cost any money). [1 point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
85
2
Algebra IMODULE2
13. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
For people who live outside of the community, Lydia adds a $5.00 gas fee to the
deliverycharge.
C. Explain why the linear function for Lydia’s delivery charges for residents in her
community and the linear function for her delivery charges for people who live
outside of the community have the same domain but differentranges.
D. Write a function to represent Lydia’s delivery charge (y), in dollars, to deliver
xpounds of vegetables to people who liveoutside the community.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
The student provided a correct and complete explanation (adding $5 to the charge doesn’t affect how many pounds
someone buys. But since you are adding $5 to the delivery charge, the ranges will increase). [1 point]
The student provided an incorrect function
(
y =
1
}
2
x + 5
)
with a correct slope
(
1
}
2
)
. The student provided work,
although it is not required or assessed. Based on the work provided, the student omitted the original $2 fixed fee that
all customers pay and instead used only the $5 gas fee for people who live outside the community. [0.5points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
86
2
Algebra IMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 1 point
PARTS A AND B
Question 13
Page 1 of 2
The student provided an incorrect answer (5). No support (work or explanation) is
required, so it is unclear where an error was made. The student may have forgotten
to add on the fixed fee of $2 after determining that the cost per pound of vegetables
is $0.50 and multiplying that amount by 10 (for 10pounds of vegetables) for a total
of $5. [0points]
The student provided a correct and complete explanation (if you include the zero
pounds there would be no charge so it would not make sense in the equation).
[1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
87
2
Algebra IMODULE2
PARTS C AND D
Question 13
Page 2 of 2
The student provided an incorrect explanation (Because the domain all have to be
different). This is incorrect because the domain stays the same and the ranges are
different due to the $5 gas fee for people outside of the community. [0points]
The student provided an incorrect function (y = 5x + 5). No support (work or
explanation) is required, so it is unclear where an error was made. The student may
have used the $5 gas fee for both the slope and the initial value without considering
the original function for the residents in Lydia’s community. [0points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
88
2
Algebra IMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 0 points
13. Lydia delivers vegetables from a community garden. For the residents of her community, she
charges a fixed fee and a constant amount per pound of vegetables she delivers. Some of the
delivery charges based on the weight of the vegetables are shown in the tablebelow.
Lydia’s Delivery Charges
Weight
(pounds)
Delivery Charge
(dollars)
2 3.00
4 4.00
5 4.50
7 5.50
A. Based on the information in the table, how much would Lydia charge to deliver
10pounds ofvegetables?
B. Explain why including 0 in the domain of the function does not make sense in
the context of the situationdescribed.
Go to the next page to finish question 13.
GO ON
The student provided an incorrect answer ($7.50). No support (work or explanation) is required, so it is unclear where
an error was made. [0 points]
The student provided an incorrect explanation (Including 0 in the domain . . . does not make sense because the
weight would be in the domain and the delivery charge would be in the range). While the domain is the weight and the
range is the delivery charge, this explanation does not describe why including 0 in the domain would not make sense
(because 0 would represent 0 pounds of vegetables and would cost $2, which no one would pay). [0 points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
89
2
Algebra IMODULE2
13. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
For people who live outside of the community, Lydia adds a $5.00 gas fee to the
deliverycharge.
C. Explain why the linear function for Lydia’s delivery charges for residents in her
community and the linear function for her delivery charges for people who live
outside of the community have the same domain but differentranges.
D. Write a function to represent Lydia’s delivery charge (y), in dollars, to deliver
xpounds of vegetables to people who liveoutside the community.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
The student provided an incorrect explanation (The functions would have the same domain because for every
twopounds Lydia goes up, she adds a $1 charge). This does not clearly state that the weight of the vegetables
doesn’t change and that the range would change due to the gas fee for those outside of the community. [0points]
The student provided an incorrect function (y = x + 5). No support (work or explanation) is required, so it is unclear
where an error was made. For the slope, the student may have used the adds a $1 charge from the explanation
provided in PartC without considering that for every two pounds would cause the slope to become $0.50
($1÷2=$0.50). For the initial value, the student may have omitted the original $2 fixed fee that all customers pay and
instead used only the $5 gas fee for people who live outside the community. [0points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
90
2
Algebra IMODULE2
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
14. Lucy randomly surveyed 25 students in her school about the number of bottles of water they
consumed in the last week. She recorded the results in the bar graph shown below.
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0123456
Bottles of Water
Number of Students
Bottles of Water Consumed Last Week
A. What is the mode of the responses from Lucy’ssurvey?
mode:
B. How many bottles of water, in all, did the 25 students Lucy surveyed consume
lastweek?
bottles of water
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
91
2
Algebra IMODULE2
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
There are 236 students in Lucy’s school.
C. Based on her graph, how many of the 236students should Lucy expect to
have consumed either 0bottles or 1bottle of water last week?
students
Lucy determines that the interquartile range of the 25 responses isq.
D. Write an expression to represent the interquartile range of the responses Lucy
should expect to get, based on her graph, if she surveys all 236students in
herschool.
expression:
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
92
2
Algebra IMODULE2
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
#14 Item Information
Alignment A1.2.3
Depth of
Knowledge
2 Mean Score 1.52
Assessment Anchor this item will be reported under:
A1.2.3—Data Analysis
Specific Anchor Descriptor addressed by this item:
A1.2.3.1—Use measures of dispersion to describe a set of data.
A1.2.3.2—Use data displays in problem-solving settings and/or to make predictions.
Scoring Guide
Score
Description
4
The student demonstrates a thorough understanding of data analysis by correctly
solving problems with clear and complete procedures and explanations when required.
3
The student demonstrates a general understanding of data analysis by solving
problems and providing procedures and explanations with only minor errors or
omissions.
2
The student demonstrates a partial understanding of data analysis by providing a
portion of the correct problem solving, procedures, and explanations.
1
The student demonstrates a minimal understanding of data analysis.
0
The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any
understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures as required by the task.
Response may show only information copied from the question.
Top-Scoring Student Response and Training Notes
Score
Description
4
Student earns 4 points.
3
Student earns 3 points.
2
Student earns 2 points.
1
Student earns 1 point.
0
Response is incorrect or contains some correct work that is irrelevant to the skill or
concept being measured.

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
93
2
Algebra IMODULE2
Top-Scoring Response
Part A (1 point):
1 point for correct answer
What?
Why?
0
Part B (1 point):
1 point for correct answer
What?
Why?
35 (bottles of water)
Part C (1 point):
1 point for correct answer
What?
Why?
151 (students)
OR
152 (students)
OR
151.04 (students)
Part D (1 point):
1 point for correct answer
What?
Why?
q
OR
2
OR equivalent expression

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
94
2
Algebra IMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 4 points
PARTS A AND B
Question 14
Page 1 of 2
The student provided the correct answer for the mode (0). While
support is not required for PartA, the student likely looked at
the bar graph and identified the number of bottles with the most
responses (that is, the tallest bar), which is 0 bottles of water.
[1point]
The student provided the correct answer (35). While support is not required for PartB,
the student likely multiplied the height of each bar by the number of bottles for that bar
and then added the products (0 • 11 + 1 • 5 + 2 • 4 + 3 • 2 + 4 • 1 + 5 • 0 + 6 • 2=
0+5+8+6+4+0+12=35). [1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
95
2
Algebra IMODULE2
PARTS C AND D
Question 14
Page 2 of 2
The student provided a correct answer (151). While support is not required for PartC,
the student likely divided the number of students who drank either 0bottles or
1bottle of water (16) by the number of students surveyed (25) to determine the ratio of
students who drank either 0bottles or 1bottle of water (0.64) and then multiplied the
ratio (0.64) by the number of students in the school (236), resulting in 151.04, which
rounds to 151students. [1point]
The student provided a correct expression of the new interquartile range (2-0). While
support is not required for PartD, the student likely identified that the Q1value (the
average of the 6th and 7th values of the data set) is in the “0bottles” bar, identified
that the Q3value (the average of the 19th and 20th values of the data set) is in the
“2bottles” bar, and then set up the interquartile range expression using Q3–Q1.
[1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
96
2
Algebra IMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 3 points
14. Lucy randomly surveyed 25 students in her school about the number of bottles of water they
consumed in the last week. She recorded the results in the bar graph shown below.
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0123456
Bottles of Water
Number of Students
Bottles of Water Consumed Last Week
A. What is the mode of the responses from Lucy’ssurvey?
mode:
B. How many bottles of water, in all, did the 25 students Lucy surveyed consume
lastweek?
bottles of water
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON
The student provided an incorrect answer (11). The student provided work, although it is not required or assessed. Based
on the work provided, the student correctly determined the height of each bar and identified the bar with the greatest
height; however, the student then used the height of the bar (11) instead of the number of bottles (0) as the mode. [0points]
The student provided the correct answer (35). The work shown is correct, though not necessary for credit. For each bar, the
student multiplied the height of the bar by the number of bottles for that bar, omitting the 0-bottle bar and the 5-bottle bar
(both of which would result in 0 bottles consumed), and then added the products. [1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
97
2
Algebra IMODULE2
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
There are 236 students in Lucy’s school.
C. Based on her graph, how many of the 236students should Lucy expect to
have consumed either 0bottles or 1bottle of water last week?
students
Lucy determines that the interquartile range of the 25 responses isq.
D. Write an expression to represent the interquartile range of the responses Lucy
should expect to get, based on her graph, if she surveys all 236students in
herschool.
expression:
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
The student provided a correct answer (151). The work shown is correct, though not necessary for credit. The student
counted the number of students who drank either 0bottles or 1bottle of water, divided that number (16) by the number
of students surveyed (25) to determine the ratio of students who drank either 0bottles or 1bottle of water (0.64), and
then multiplied the number of students in the school (236) by the ratio (0.64), resulting in 151.04, which rounds down to
151students. [1point]
The student provided a correct expression of the new interquartile range (q). The work shown is correct, though not
necessary for credit. The student determined that simply multiplying the numbers used to calculate the interquartile range
by a constant amount would not change the interquartile range itself (that is, q would remain q). The student did this by first
calculating the ratio of each response from the original survey of 25students and then multiplying these ratios by the total
number of students (236), which showed that the interquartile range would not change if Lucy surveyed the whole school.
[1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
98
2
Algebra IMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 2 points
PARTS A AND B
Question 14
Page 1 of 2
The student provided an incorrect answer (11). The
student provided additional information, although it
is not required or assessed. Based on the additional
information provided, the student correctly identified
the bar with the greatest height but used the height of
the bar (11students) instead of the number of bottles
(0) as the mode. [0points]
The student provided the correct answer (35). While support is not required for PartB,
the student likely multiplied the height of each bar by the number of bottles for that bar
and then added the products (0 • 11 + 1 • 5 + 2 • 4 + 3 • 2 + 4 • 1 + 5 • 0 + 6 • 2 =
0 + 5 + 8 + 6 + 4 + 0 + 12 =35). [1point]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
99
2
Algebra IMODULE2
PARTS C AND D
Question 14
Page 2 of 2
The student provided a correct answer (151). While support is not required for
PartC, the student likely divided the number of students who drank either 0bottles
or 1bottle of water (16) by the number of students surveyed (25) to determine the
ratio of students who drank either 0bottles or 1bottle of water (0.64) and then
multiplied the ratio (0.64) by the number of students in the school (236), resulting in
151.04, which rounds to 151students. [1point]
The student provided an incorrect answer (Of 236, 104 have had 0bottles during the
week). No support (work or explanation) is required, so it is unclear where an error
was made. The student may have considered only the ratio of students who drank
0bottles of water
(
11
}
25
=0.44
)
and then multiplied the number of students in the
school (236) by the ratio (0.44), resulting in 103.84, which rounds to 104students.
[0points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
100
2
Algebra IMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 1 point
14. Lucy randomly surveyed 25 students in her school about the number of bottles of water they
consumed in the last week. She recorded the results in the bar graph shown below.
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0123456
Bottles of Water
Number of Students
Bottles of Water Consumed Last Week
A. What is the mode of the responses from Lucy’ssurvey?
mode:
B. How many bottles of water, in all, did the 25 students Lucy surveyed consume
lastweek?
bottles of water
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON
The student provided an incorrect answer (2). No support (work or explanation) is required, so it is unclear where an
error was made. The student may have identified the most common bar height, since the 3-bottle bar and the 6-bottle
bar each had a height of 2 students. [0 points]
The student provided an incorrect answer (14). No support (work or explanation) is required, so it is unclear where an
error was made. The student may have determined the number of students who consumed at least 1 bottle of water
(5 + 4 + 2 + 1 + 2 = 14). [0 points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
101
2
Algebra IMODULE2
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
There are 236 students in Lucy’s school.
C. Based on her graph, how many of the 236students should Lucy expect to
have consumed either 0bottles or 1bottle of water last week?
students
Lucy determines that the interquartile range of the 25 responses isq.
D. Write an expression to represent the interquartile range of the responses Lucy
should expect to get, based on her graph, if she surveys all 236students in
herschool.
expression:
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
The student provided a correct answer (151). While support is not required for PartC, the student likely divided the
number of students who drank either 0bottles or 1bottle of water (16) by the number of students surveyed (25) to
determine the ratio of students who drank either 0bottles or 1bottle of water (0.64) and then multiplied the ratio (0.64)
by the number of students in the school (236), resulting in 151.04, which rounds to 151students. [1point]
The student provided an incorrect answer (9.44q). The student provided work, although it is not required or assessed.
Based on the work provided, the student determined that the number of students surveyed (25) should be multiplied
by 9.44 to get the total number of students in the school (236); using this information, the student then multiplied the
interquartile range of the 25responses(q) by 9.44 to incorrectly determine the interquartile range of all 236students.
[0points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
102
2
Algebra IMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 0 points
PARTS A AND B
Question 14
Page 1 of 2
The student provided an incorrect answer (11).
No support (work or explanation) is required, so it
is unclear where an error was made. The student
may have correctly identified the bar with the
greatest height but then used the height of the bar
(11students) instead of the number of bottles (0) as
the mode. [0points]
The student provided an incorrect answer (14). No support (work or explanation)
is required, so it is unclear where an error was made. The student may have
determined the number of students who consumed at least 1 bottle of water
(5+4+2+1+2=14). [0points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
103
2
Algebra IMODULE2
PARTS C AND D
Question 14
Page 2 of 2
The student provided an incorrect answer (200). No support (work or explanation) is required,
so it is unclear where an error was made. The student may have subtracted the number of
students surveyed (25) and the number of students who drank 0bottles of water (11) from the
number of students in the school (236). [0points]
The student provided an incorrect answer (q = 236 – 14), which was in the form of an equation
instead of an expression. Based on the equation, the student subtracted the number of
students who consumed at least 1bottle of water (14) from the total number of students in
the school (236). No credit is awarded for an equation with oneside consisting of a correct
expression (q). [0points]

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
104
2
Algebra IMODULE2
ALGEBRA I MODULE 2—SUMMARY DATA
Multiple-Choice
Sample
Number Alignment Answer Key
Depth of
Knowledge
p-value
A
p-value
B
p-value
C
p-value
D
1 A1.2.1.1.1 C 2 8% 30% 54% 8%
2 A1.2.1.1.3 B 1 14% 60% 8% 18%
3 A1.2.1.2.1 D 2 11% 6% 24% 59%
4 A1.2.1.2.2 D 1 10% 7% 17% 66%
5 A1.2.2.1.1 B 2 26% 63% 5% 6%
6 A1.2.2.1.3 D 1 13% 12% 14% 61%
7 A1.2.2.1.4 D 1 13% 12% 7% 68%
8 A1.2.2.2.1 B 2 38% 39% 12% 11%
9 A1.2.3.1.1 C 1 16% 18% 47% 19%
10 A1.2.3.2.1 C 2 7% 25% 64% 4%
11 A1.2.3.2.2 C 2 4% 12% 75% 9%
12 A1.2.3.3.1 A 2 37% 17% 29% 17%
Constructed-Response
Sample
Number Alignment Points
Depth of
Knowledge Mean Score
13 A1.2.1 4 2 1.88
14 A1.2.3 4 2 1.52

Keystone Algebra I Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
105
2
Algebra IMODULE2
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.

Copyright © 2022 by the Pennsylvania Department of Education. The materials contained in
this publication may be duplicated by Pennsylvania educators for local classroom use. This
permission does not extend to the duplication of materials for commercial use.
Keystone Exams
Algebra I
Item and Scoring Sampler 2022
