
Maryland Early Learning Standards
Birth – 8 Years


Appendix | 3
Maryland State Department of Education
Division of Early Childhood Development
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Executive Summary ........................................................................4
Language & Literacy Domain. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-53
Mathematics Domain .................................................................. 55-77
Social Studies Domain ................................................................. 78-90
Science Domain ......................................................................91-102
Health Domain ......................................................................103-110
Physical Education Domain ............................................................111-116
Fine Arts Domain ....................................................................117-132
Social Foundations Domain .............................................................133-167

4 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Early learning standards define the key aspects of development and learning that are the foundation for a child’s school
and life-long success. By outlining the expectations for what children should know and be able to do at different ages
of early childhood, these standards represent the developmental and learning goals that early childhood administrators
and educators strive to meet for the children they serve. While the progress of children toward the standards will vary
depending on a variety of factors, the standards act as a guide for the pedagogical and programmatic decisions of early
childhood programs and providers. Decisions related to curriculum, assessment, professional development and family
engagement, among others, should be made with child progress toward the standards in mind.
For early childhood programs in Maryland, expectations are defined by a set of early learning standards that came from
two sources: These are Healthy Beginnings: Supporting Development and Learning from Birth through Three Years of Age
and the Maryland College and Career-Ready Standards for Pre-K - 12.
Healthy Beginnings was developed by the Maryland Department of Education and provides early learning standards for
children birth through three-years-old. The document is intended for use by families or early childhood practitioners
living or working with infants or very young children (i.e., end of age four). The Maryland College and Career-Ready
Standards were developed by the Maryland Department of Education to align to the K-12 Common Core standards that
were adopted in 2010. The Maryland Early Learning Standards document includes the prekindergarten to grade 2 portion
of the Maryland College and Career-Ready Standards.
In 2003, to help providers navigate the different standards, the Maryland Department of Education created a standards
alignment document. The document was developed to illustrate that there was in fact strong commonality among the
standards, and created a common frame of reference so providers could work collaboratively with families to meet
expectations regardless of the funding stream or program setting. Since the creation of that document, however, new
versions of two of the standards documents have been published. Healthy Beginnings replaced the Maryland Guidelines
for Healthy Child Development and Care for Young Children, and the Maryland College and Career- Ready Standards
replaced the Common Core Frameworks and the State Curriculum.
The full document provides an updated alignment based on the most recent versions of these early learning standards. The
goal of this Executive Summary document is to provide examples from the standards in each of the content areas.
The areas include: Language and Literacy, Mathematics, Social Studies, Science, Health, Physical Education, Fine Arts and
Social Foundations.

Appendix | 5
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Literature
Standard: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual
evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., repeat
repetitive phrases
from a story).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about a
story).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
make guesses about
what a story is
about).
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL1: With
modeling and
prompting, answer
questions about
details in a text.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL1: With
prompting and
support, ask and
answer questions
about key details in
a text
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL1: Ask and
answer questions
about key details in
a text.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL1: Ask and
answer such
questions as who,
what, where, when,
and how to
demonstrate
understanding in a
text.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g., repeat
repetitive p
h
rases
f
r
o
m a story
)
.
1 Year
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about a
story
)
.
gp g
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
make guesses about
w
h
at a story is
about
)
.
pp
3
Year
s
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L1: Wit
h
modeling and
prompting, answer
questions about
d
etails in a text.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L1: Wit
h
prompting and
support, ask and
answer questions
about key details in
a
t
ex
t
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L1
:
A
sk an
d
answer questions
about key details in
a
t
ex
t.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Key Ideas &
Gra
d
e
2
D
etail
s
R
L1: Ask an
d
answer suc
h
questions as w
h
o,
w
h
at, w
h
ere, w
h
en,
and how to
d
emonstrate
u
nderstanding in a
t
ex
t.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Literatur
e
S
tan
d
ar
d:
R
ead closely to determine what the text says explicitly an
d
to ma
k
e logical inferences from it; cite specific textual
evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text.
gp g

6 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Literature
Standard: Determine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and
ideas.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about
details in a story).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and/or answer
questions about a
story while it is
being read).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
point out familiar
concepts by looking
at pictures in a
text).
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL2: With
modeling and
support, retell
familiar
stories/poems.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL2: With
prompting and
support, retell
familiar stories,
including key
details.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL2: Retell stories,
including key
details, and
demonstrate
understanding of
their central
message or lesson.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL2: Recount
stories, including
fables and folktales
from diverse
cultures, and
determine their
central message,
lesson, or moral.
1 Year
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about
d
etails in a story
)
.
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and
/
or answer
questions about a
story w
h
ile it is
b
eing read).
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
point
o
ut familiar
concepts by looking
at pictures in a
text
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L2: Wit
h
modeling and
support, retell
f
amiliar
stories
/
poems.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L2: Wit
h
prompting and
support, retell
f
amiliar stories,
including ke
y
d
etails.
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L2
:
R
etell stories,
including ke
y
d
etails, and
d
emonstrate
u
nderstanding of
t
h
eir
c
entral
message or lesson.
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L2
:
R
e
c
ount
stories, including
f
a
b
les and folktales
f
rom diverse
cultures, and
d
etermine their
c
en
t
ral message,
lesson, or moral.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Literatur
e
S
tan
d
ar
d:
D
etermine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and
i
d
eas.

Appendix | 7
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Literature
Standard: Analyze how and why individuals, events, and ideas develop and interact over the course of text.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., begin
to identify simple
pictures or familiar
people).
Demonstrate
vocabulary and
comprehension by
listening with
interest and
displaying
understanding (e.g.,
perform an action
shown in a book).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
begin to understand
that stories can be
acted out).
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL3: With
modeling and
support, identify
characters, settings
and major events in
a story.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL3: With
prompting and
support, identify
characters, settings,
and major events in
a story.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL3: Describe
characters, settings,
and major events in
a story, using key
details.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RL3: Describe how
characters in a story
respond to major
events and
challenges.
D
emonstrate
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
listening wit
h
interest an
d
d
isplaying
u
nderstanding
(
e.g.,
perform an action
shown in a book
).
k
k
2
Year
s
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g.,
b
egin
to identify simple
pictures or familiar
peopl
e
)
.
1 Year
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
b
egin to understand
that stories can
b
e
acted out
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L3: Wit
h
modeling and
support, identif
y
ch
ara
c
ters, settings
and ma
j
or events in
a s
t
ory.
4
Year
s
A
. Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L3: Wit
h
prompting and
support, identif
y
c
h
aracters, settings,
and ma
j
or events in
a s
t
ory.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L3: Descri
b
e
c
h
aracters, settings,
and ma
j
or events in
a story, using
k
ey
d
etails.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
L3: Describe ho
w
c
h
aracters in a stor
y
respond to ma
j
or
events and
c
h
allenges.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Literatur
e
S
tan
d
ar
d:
A
nalyze how and why individuals, events, and ideas develop and interact over the course of text.

8 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Literature
Standard: Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative
meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
books).
Develop
vocabulary,
language usage and
some conventions
of speech (e.g.,
name an increasing
number of objects
in a book, and
describe actions).
Expand vocabulary
and language usage
(e.g., discover the
meaning of new
words from the
context or
pictures).
A. Craft &
Structure
RL4: With
modeling and
support, answer
questions about
unknown words in
stories and poems.
A. Craft &
Structure
RL4: Ask and
answer questions
about unknown
words in a text.
A. Craft &
Structure
RL4: Identify
words and phrases
in stories or poems
that suggest feelings
or appeal to the
senses.
A. Craft &
Structure
RL4: Describe how
words and phrases
(e.g., regular beats,
alliteration, rhymes,
repeated lines)
supply rhythm and
meaning in a story,
poem, or song.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases
(
e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
b
ooks
)
.
g
1 Year
D
evelop
vocabulary,
language usage and
some conventions
o
f speec
h
(
e.g.,
n
ame an increasing
n
umber of ob
j
ects
in a
b
ook, an
d
d
escribe actions
)
.
yp
2
Year
s
Expan
d
vocabular
y
and language usag
e
(
e.g., discover the
meaning of ne
w
words from the
c
on
t
ex
t
or
pictures
)
.
p
3
Year
s
A.
Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L4
:
Wit
h
modeling and
suppor
t
, answer
questions about
u
nknown words in
stories and poems.
g
4
Year
s
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L4: Ask an
d
answer questions
about unknown
words in a text.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L4: Identif
y
words and phrases
in stories or poems
that suggest feelings
o
r appeal to t
h
e
senses.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Craft &
Gra
d
e
2
S
tructur
e
R
L4: Describe ho
w
words and phrases
(
e.g., regular beats,
alliteration, r
h
ymes,
repeated lines)
supply rhythm and
meaning in a story,
poem, or song.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Literatur
e
S
tan
d
ar
d:
Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative
meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone.
yp

Appendix | 9
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Literature
Standard: Analyze the structure of texts, including how specific sentences, paragraphs, and larger portions of the text (e.g., a
section, chapter, scene, or stanza) relate to each other and the whole.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
familiar books).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to fiction and
non-fiction
materials).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to a variety of
fiction and non-
fiction materials).
A. Craft &
Structure
RL5: Gain
exposure to
common types of
literary texts (e.g.,
storybooks,
poems).
A. Craft &
Structure
RL5: Recognize
common types of
texts (e.g.,
storybooks,
poems).
A. Craft &
Structure
RL5: Explain major
differences between
books that tell
stories and books
that give
information,
drawing on a wide
reading of a range
of text types.
A. Craft &
Structure
RL5: Describe the
overall structure of
a story, including
describing how the
beginning
introduces the story
and the ending
concludes the
action.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
f
amiliar
b
ooks
)
.
p
1 Year
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to fiction an
d
no
n
-
f
i
c
tion
materials
)
.
)
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to a variety of
f
iction an
d
no
n
-
f
iction materials
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L5
:
G
ain
exposure
t
o
common types of
literary texts
(
e.g.,
storybooks,
poems
)
.
4
Year
s
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L5
:
R
ecognize
common types of
texts
(
e.g.,
storybooks,
poems
)
.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L5
:
Explain ma
j
or
d
ifferences between
b
ooks that tell
Gra
d
e
1
stories and
b
ooks
t
h
at give
information,
d
rawing on a wide
reading of a range
o
f text types.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L5
:
D
escri
b
e the
o
verall structure of
a story, including
d
escribing how the
b
eginning
introduces the stor
y
and the ending
conclu
d
es the
a
c
tion.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Literatur
e
S
tan
d
ar
d:
A
nalyze the structure of texts, including how specific sentences, paragraphs, and larger portions of the text (e.g., a
section, chapter, scene, or stanza) relate to each other and the whole.
)

10 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Literature
Standard: Assess how point of view or purpose shapes the content and style of a text.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
familiar books).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to fiction and
non-fiction
materials).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to and discuss
a variety of books).
A. Craft &
Structure
RL6: With
modeling and
support, identify
the role of author
and illustrator.
A. Craft &
Structure
RL6: With
prompting and
support, name the
author and
illustrator of a story
and define the role
of each in telling
the story.
A. Craft &
Structure
RL6: Identify who
is telling the story at
various points in a
text.
A. Craft &
Structure
RL6: Acknowledge
differences in the
points of view of
characters,
including by
speaking in a
different voice for
each character
when reading
dialogue aloud.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
f
amiliar books
)
.
1 Year
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to fiction an
d
no
n
-
f
i
c
tion
materials
)
.
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to an
d
d
iscuss
a variety of books).
3
Year
s
A.
Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L
6
:
Wit
h
modeling and
support, identif
y
the r
o
le
o
f auth
o
r
an
d
illustrator.
4
Year
s
A.
Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L
6
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, name t
h
e
author an
d
illustrator of a stor
y
an
d
d
efine the role
o
f each in telling
t
h
e story.
Kindergarte
n
A.
Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L
6
:
I
dentify who
is telling t
h
e story at
various points in a
t
ex
t.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
L
6
:
A
cknowledge
d
ifferences in the
points of view of
c
h
aracters,
including b
y
Gra
d
e
2
spea
k
ing in a
d
ifferent voice for
ea
ch
ch
ara
c
ter
when reading
d
ialogue aloud.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Literatur
e
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
ssess how point of view or purpose shapes the content and style of a text
.

Appendix | 11
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Literature
Standard: Integrate and evaluate content presented in diverse media and formats, including visually and quantitatively, as well as in
words.*
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., begin
to identify simple
pictures or familiar
people).
Recognize that
symbols have
corresponding
meaning (e.g., find
favorite cereal by
the picture on a
box).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
point out familiar
concepts by
looking at pictures
in a text).
A. Integration of
Knowledge & Ideas
RL7: With modeling
and support, tell
how the illustrations
support the story.
A. Integration of
Knowledge & Ideas
RL7: With
prompting and
support, describe
the relationship
between
illustrations and the
story in which they
appear (e.g., what
moment in a story
an illustration
depicts).
A. Integration of
Knowledge & Ideas
RL7: Use
illustrations and
details in a story to
describe its
characters, setting,
or events.
A. Integration of
Knowledge & Ideas
RL7: Use
information gained
from the
illustrations and
words in print or
digital text to
demonstrate
understanding of its
characters, setting,
or plot.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
phrases (e.g., begin
to identify simple
pictures or familiar
people).
1 Year
R
ecognize t
h
at
symbols have
corresponding
meaning (e.g., find
f
avorite cereal b
y
t
h
e picture on a
b
ox
)
.
2
Year
s
D
eve
l
o
p
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
point out familiar
concepts b
y
loo
k
ing at pictures
in a text
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Integration of
Knowledge & Idea
s
R
L
7
:
With modeling
and support, tell
h
ow t
h
e illustrations
suppor
t
t
h
e story.
4
Year
s
A
. Integration of
Knowledge & Idea
s
R
L
7
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, describe
t
h
e relations
h
ip
b
etween
illustrations an
d
the
story in w
h
ic
h
t
h
e
y
appear (e.g., w
h
at
moment in a stor
y
an illustration
d
epicts).
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Integration of
Knowledge & Idea
s
R
L
7
:
Use
illustrations an
d
d
etails in a story to
d
escri
b
e its
c
h
aracters, setting,
o
r even
t
s.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Integration of
Knowledge & Idea
s
R
L
7
:
Use
information gained
f
r
o
m the
illustrations an
d
words in print or
d
igital text to
d
emonstrate
u
nderstanding of it
s
c
h
aracters, setting,
o
r plot.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Literatur
e
S
tan
d
ar
d:
Integrate and evaluate content presented in diverse media and formats, including visually and quantitatively, as well as in
words.
*

12 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Literature
Standard: Analyze how two or more texts address similar themes or topics in order to build knowledge or to compare the
approaches the authors take.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Integration of
Knowledge & Ideas
RL9: With modeling
and support,
compare adventures
and experiences of
characters in familiar
stories.
A. Integration of
Knowledge & Ideas
RL9: With
prompting and
support, compare
and contrast the
adventures and
experiences of
characters in
familiar stories.
A. Integration of
Knowledge & Ideas
RL9: Compare and
contrast the
adventures and
experiences of
characters in
stories.
A. Integration of
Knowledge & Ideas
RL9: Compare and
contrast two or
more versions of
the same story (e.g.,
Cinderella stories)
by different authors
or from different
cultures.
pp
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
A.
Integration of
Knowledge & Idea
s
R
L
9
:
With modeling
and support,
compare adventures
and experiences of
characters in familiar
stories.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Integration of
Knowledge & Ideas
R
L
9
:
Wit
h
prompting and
suppor
t
, compare
an
d
contrast the
adventures and
experiences of
c
h
aracters in
f
amiliar stories.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Integration of
Knowledge & Ideas
R
L
9
:
Compare and
contrast t
h
e
adventures and
experiences of
c
h
aracters in
stories.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
Integration of
Knowledge & Idea
s
R
L9
R
R
:
Compare and
con
t
ras
t
t
wo or
more versions of
t
h
e same story (e.g.,
Cinderella stories
)
b
y different authors
o
r from
d
ifferent
cultures.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Literatur
e
S
tan
d
ar
d:
A
nalyze how two or more texts address similar themes or topics in order to build knowledge or to compare the
approaches the authors take.

Appendix | 13
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Literature
Standard: Read and comprehend complex literary and informational texts independently and proficiently.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about
details in a story).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and/or answer
questions about a
story while you are
reading).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
makes guesses
about what a story
is about).
A. Range of
Reading and Level
of Text Complexity
RL10: Actively
engage in group
reading activities
with purpose and
understanding.
A. Range of
Reading and Level
of Text Complexity
RL10: Actively
engage in group
reading activities
with purpose and
understanding.
A. Range of
Reading and Level
of Text Complexity
RL10: With
prompting and
support, read prose
and poetry of
appropriate
complexity for
grade 1.
A. Range of
Reading and Level
of Text Complexity
RL10: By the end
of the year, read
and comprehend
literature, including
stories and poetry,
in the grade 2-3 text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as
needed at the high
end of the range.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about
d
etails in a
story
).
y
y
1 Year
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and
/
or answer
questions about a
story w
h
ile you are
reading).
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ma
k
es guesses
about what a stor
y
is about
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
R
ange of
R
eading and Level
o
f Text Complexit
y
R
L10:
A
ctivel
y
engage in group
reading activities
with purpose and
u
n
derstanding.
4
Year
s
A.
R
ange of
R
eading and Level
o
f Text Complexit
y
R
L1
0
:
A
ctivel
y
engage in group
reading activities
with purpose and
u
nderstanding.
Kindergarte
n
A.
R
ange of
R
eading and Level
o
f Text Complexit
y
R
L1
0
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, read prose
and poetry of
appropriate
complexity for
grade 1.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
R
ange of
R
eading and Level
o
f Text Complexit
y
R
L1
0
:
By the end
o
f the year, read
and comprehend
literature, including
stories and poetry,
in the grade
2
-
3
text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as
n
ee
d
e
d
at t
h
e
h
ig
h
end of the range.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Literatur
e
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Read and comprehend complex literary and
informational texts independently and proficiently.
p
py
pyp
py

14 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Informational Text
Standard: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual
evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., point
to and name several
pictures in a book).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about a
book).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
make guesses about
what a book is
about).
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI1: With modeling
and support,
answer questions
about details in an
informational text.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI1: With
prompting and
support, ask and
answer questions
about key details in
a text.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI1: Ask and
answer questions
about key details in
a text.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI1: Ask and
answer such
questions as who,
what, where, when,
why, and how to
demonstrate
understanding of
key ideas in a text.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g., point
to and name several
pictures in a book).
1 Year
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about a
b
ook
)
.
g
pg
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
make guesses about
w
h
at a
b
ook is
about
)
.
pp
3
Year
s
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
I
1
:
With modeling
and support,
answer questions
a
b
out details in an
informational text
.
4
Year
s
A
. Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
I
1
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, ask and
answer questions
about key details in
a
t
ex
t.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
I
1
:
A
sk an
d
answer questions
about key details in
a
t
ex
t.
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
I
1
:
A
sk an
d
answer suc
h
questions as w
h
o,
w
h
at, w
h
ere, w
h
en,
why, and how to
d
emonstrate
u
n
d
er
s
tanding of
key ideas in a text.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Informational Text
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
R
ead closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual
evidence when writing or
speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text.
pg

Appendix | 15
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Informational Text
Standard: Determine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and
ideas.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about
details in a book).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and/or answer
questions about a
book while it is
being read).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
point out familiar
concepts by looking
at pictures in a
text).
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI2: With modeling
and support, recall
one or more
detail(s) related to
the main topic from
an informational
text.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI2: With
prompting and
support, identify
the main topic and
retell key details of
a text.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
Rl2: Identify the
main topic and
retell key details of
a text.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI2: Identify the
main topic of a
multiparagraph text
as well as the focus
of specific
paragraphs within
the text.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about
d
etails in a
b
ook
)
.
1 Year
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and
/
or answer
questions a
b
out a
b
ook while it is
b
eing read).
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
point out familiar
concepts by looking
at pictures in a
text
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
I
2
:
With modeling
and support, reca
l
l
o
ne
or
m
or
e
d
etail
(
s) related to
the main topic from
an inf
o
rmati
o
nal
t
ex
t.
4
Year
s
A
. Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
I
2
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, identif
y
t
h
e main topic an
d
retell key details of
a
t
ex
t.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
l
2
:
Identify the
main topic and
retel
l
key details of
a
t
ex
t.
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
I
2
:
Identify the
main topic of a
multiparagrap
h
text
as well as the focus
o
f specific
paragrap
h
s wit
h
in
t
h
e text
.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Informational Text
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
D
etermine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the k
e
y supporting details and
i
d
eas.

16 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Informational Text
Standard: Analyze how and why individuals, events, and ideas develop and interact over the course of text.
Learning Progression: Story/Text Comprehension
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., begin
to identify simple
pictures or familiar
people).
Demonstrate
vocabulary and
comprehension by
listening with
interest and
displaying
understanding (e.g.,
perform an action
shown in a book).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
make up a story
about a book).
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI3: With modeling
and support,
connect individuals,
events, and pieces
of information in
text to life
experiences.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI3: With
prompting and
support, describe
the connection
between two
individuals, events,
ideas, or pieces of
information in a
text.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI3: Describe the
connection between
two individuals,
events, ideas, or
pieces of
information in a
text.
A. Key Ideas &
Details
RI3: Describe the
connection between
a series of historical
events, scientific
ideas or concepts,
or steps in technical
procedures in a
text.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
phrases (e.g., begin
to identify simple
pictures or familiar
people).
gg
1 Year
D
emonstrate
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
listening wit
h
interest an
d
d
isplaying
u
nderstanding (e.g.,
perform a
n
a
c
tion
shown in a book
)
.
y
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ma
k
e up a stor
y
about a book
)
.
p
3
Year
s
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
I3
:
With modeling
and support,
connect individuals,
events, and pieces
o
f inf
o
rmati
o
n in
text t
o
life
experiences.
4
Year
s
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
I3
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, describe
t
h
e
c
onne
c
tion
b
etween two
individuals, events,
ideas, or pieces of
inf
o
rmati
o
n in a
t
ex
t.
Kindergarte
n
A.
Key Ideas &
D
etail
s
R
I3
:
D
escri
b
e the
connection bet
w
een
two individuals,
events, ideas, or
pieces of
inf
o
rmati
o
n in a
t
ex
t.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Key Ideas &
Gra
d
e
2
D
etail
s
R
I3
:
D
escri
b
e the
connection between
a series of historical
events, scientific
ideas or concepts,
o
r steps in tec
h
nical
procedures in a
t
ex
t.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Informational Text
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
nalyze ho
w
and why individuals, events, and ideas develop and interact over the course of text.
Learning Progression:
Story/Text Comprehension
y

Appendix | 17
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Informational Text
Standard: Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative
meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
books).
Develop
vocabulary,
language usage and
some conventions
of speech (e.g.,
name an increasing
number of objects
in a book, and
describe actions).
Expand vocabulary
and language usage
(e.g., discover the
meaning of new
words from the
context or
pictures).
A. Craft &
Structure
RI4: With modeling
and support,
answer questions
about unknown
words in a text.
A. Craft &
Structure
RI4: With
prompting and
support, ask and
answer questions
about unknown
words in a text.
A. Craft &
Structure
RI4: Ask and
answer questions to
help determine or
clarify the meaning
of words and
phrases in a text.
A. Craft &
Structure
RI4: Determine the
meaning of words
and phrases in a
text relevant to a
grade 2 topic or
subject area.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
b
ooks
)
.
g
1 Year
yp
2
Year
s
D
evelop
vocabulary,
language usage and
some conventions
o
f speech (e.g.,
n
ame an increasing
n
umber of ob
j
ects
in a
b
ook, and
d
escribe actions
)
.
p
3
Year
s
Expan
d
vocabular
y
and language usag
e
(
e.g., discover the
meaning of ne
w
words from the
c
on
t
ex
t
or
pictures
)
.
g
4
Year
s
A
.
Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I4
:
With modeling
and support,
answer questions
about unknown
words in a text.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I4
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, ask and
answer questions
about unknown
words in a text.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I4
:
A
sk an
d
answe
r
questions to
h
elp determine or
clarify the meaning
o
f words and
p
h
rases in a text.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I4
:
D
etermine t
h
e
meaning of words
and phrases in a
text relevant to a
grade 2 topic or
sub
j
ect area.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Informational Text
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative
meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone.
yp

18 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Informational Text
Standard: Analyze the structure of texts, including how specific sentences, paragraphs, and larger portions of the text (e.g., a
section, chapter, scene, or stanza) relate to each other and the whole.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
familiar books).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to fiction and
non-fiction
materials).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to a variety of
fiction and non-
fiction materials).
A. Craft &
Structure
RI5: With modeling
and support
identify the front
cover, and back
cover of a book.
A. Craft &
Structure
RI5: Identify the
front cover, back
cover, and title page
of a book.
A. Craft &
Structure
RI5: Know and use
various text
features (e.g.
headings, tables of
contents, glossaries,
electronic menus,
icons) to locate key
facts or information
in a text.
A. Craft &
Structure
RI5: Know and use
various text
features (e.g.,
captions, bold
print, subheadings,
glossaries, indexes,
electronic menus,
icons) to locate key
facts or information
in a text efficiently.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
f
amiliar books
)
.
p
1 Year
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to fiction an
d
no
n
-
f
i
c
tion
materials
)
.
)
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to a variety of
f
iction an
d
no
n
-
f
iction materials
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I5
:
With modeling
and support
identify the front
cover, and bac
k
cover of a
b
ook.
4
Year
s
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I5
:
Identify the
f
ront cover, bac
k
cover, and title page
o
f a
b
ook.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I5
:
Know and use
various text
f
eatures (e.g.
h
eadings, tables of
contents, glossaries,
electronic menus,
icons) to locate
k
e
y
f
acts or information
in a text
.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I5: Know and use
various text
f
eatures (e.g.,
captions, bold
print, sub
h
eadings,
glossaries, indexes,
electronic menus,
icons) to locate
k
e
y
f
acts or information
Gra
d
e
2
in a text efficiently.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Informational Text
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
nalyze the structure of texts, including how specific sentences, paragraphs, and larger portions of the text (e.g., a
section, chapter, scene, or stanza) relate to each other and the whole.
)

Appendix | 19
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Informational Text
Standard: Assess how point of view or purpose shapes the content and style of a text.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
familiar books).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to fiction and
non-fiction
materials).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to and
discuss a variety of
books).
A. Craft & Structure
RI6: With modeling
and support define
the role of the
author and
illustrator/photogra
pher in presenting
the ideas or
information in a
text.
A. Craft &
Structure
RI6: Name the
author and
illustrator of a text
and define the role
of each in
presenting the ideas
or information in a
text.
A. Craft &
Structure
RI6: Distinguish
between
information
provided by
pictures or other
illustrations and
information
provided by the
words in a text.
A. Craft &
Structure
RI6: Identify the
main purpose of a
text, including what
the author wants to
answer, explain, or
describe.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g., learn
some simple words
and phrases from
f
amiliar books
)
.
1 Year
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to fiction an
d
no
n
-
f
i
c
tion
materials
)
.
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
listen to an
d
d
iscuss a variety of
b
ooks
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Craft & Structur
e
R
I
6
:
With modeling
and support define
the r
o
le
o
f the
author an
d
illustrator
/
photogra
p
h
er in presenting
the i
d
eas or
inf
o
rmati
o
n in a
t
ex
t.
4
Year
s
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I
6
:
Name t
h
e
author an
d
illustrator of a text
an
d
d
efine the role
o
f ea
c
h in
presenting the ideas
o
r inf
o
rmati
o
n in a
t
ex
t.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I
6
:
D
istinguis
h
b
etween
inf
o
rmati
o
n
provided b
y
pictures or ot
h
er
illustrations an
d
inf
o
rmati
o
n
provided by the
words in a text.
A
. Craft &
S
tructur
e
R
I
6
:
Gra
d
e
2
Identify the
main purpose of a
text, including what
t
h
e aut
h
or wants to
answer, explain, or
d
escri
b
e.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Informational Text
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
ssess how point of view or purpose shapes the content and style of a text.

20 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Informational Text
Standard: Integrate and evaluate content presented in diverse media and formats, including visually and quantitatively, as well as in
words.*
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g., begin
to identify simple
pictures or familiar
people).
Recognize that
symbols have
corresponding
meaning (e.g., find
favorite cereal by
the picture on a
box).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
point out familiar
concepts by
looking at pictures
in a text).
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI7: With modeling
and support, tell
how the
illustrations/photogr
aphs support the
text.
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI7: With
prompting and
support, describe
the relationship
between
illustrations and the
text in which they
appear (e.g., what
person, place,
thing, or idea in the
text an illustration
depicts).
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI7: Use the
illustrations and
details in a text to
describe its key
ideas.
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI7: Explain how
specific images
(e.g., a diagram
showing how a
machine works)
contribute to and
clarify a text.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
phrases (e.g., begin
to identify simple
pictures or familiar
people).
1 Year
R
ecognize t
h
at
symbols have
corresponding
meaning (e.g., find
f
avorite cereal b
y
t
h
e picture on a
b
ox
)
.
2
Year
s
D
ev
e
lop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
point out familiar
concepts b
y
loo
k
ing at pictures
in a text
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
7
:
With modeling
and support, tell
h
ow t
h
e
illustrations
/
photogr
ap
h
s support t
h
e
t
ex
t.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A
. Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
7
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, describe
t
h
e relations
h
ip
b
etween
illustrations an
d
the
text in w
h
ic
h
t
h
e
y
appear (e.g., w
h
at
person, place,
thing, or idea in the
text an illustration
d
epicts).
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
7
:
Use t
h
e
illustrations an
d
d
etails in a text to
d
escribe its ke
y
i
d
eas.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
7
:
Explain
h
o
w
specific images
(
e.g., a diagram
s
h
owing
h
ow a
machine wor
k
s
)
contri
b
ute to and
clarify a text.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Informational Text
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Integrate and evaluate content presented in diverse media and formats, including visually and quantitatively, as well as in
words.
*

Appendix | 21
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Informational Text
Standard: Delineate and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text, including the validity of the reasoning as well as the
relevance and sufficiency of the evidence.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about
details in a book).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and/or answer
questions about a
book while it is
being read).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and answer
questions about a
book).
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI8: With modeling
and support identify
the reasons an
author gives to
support points in a
text.
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI8: With
prompting and
support, identify
the reasons an
author gives to
support points in a
text.
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI8: Identify the
reasons an author
gives to support
points in a text.
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI8: Describe how
reasons support
specific points the
author makes in a
text.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about
d
etails in a
b
ook
)
.
1 Year
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and
/
or answer
questions about a
b
ook while it is
b
eing read).
y
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and answer
questions about a
b
ook
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
8
:
With modeli
n
g
and support identif
y
t
h
e reasons an
aut
h
or gives to
support points in a
t
ex
t.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
8
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, identif
y
t
h
e reasons an
aut
h
or gives to
support points in a
t
ex
t.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
8
:
Identify the
reasons an aut
h
or
gives to support
points in a text.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
8
:
D
escribe ho
w
reasons suppor
t
specific points the
author ma
k
es in a
t
ex
t.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Informational Text
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
D
elineate and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text,
i
ncluding the validity of the reasoning as well as the
relevance a
nd sufficiency of the evidence.
y

22 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Informational Text
Standard: Analyze how two or more texts address similar themes or topics in order to build knowledge or to compare the
approaches the authors take.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI9: With
prompting and
support, discuss
similarities and
differences between
two texts on the
same topic (i.e. in
illustrations or
descriptions).
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI9: With
prompting and
support, identify
basic similarities in
and differences
between two texts
on the same topic
(e.g., in
illustrations,
descriptions, or
procedures).
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI9: Identify basic
similarities in and
differences
between two texts
on the same topic
(e.g., in
illustrations,
descriptions, or
procedures).
A. Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
RI9: Compare and
contrast the most
important points
presented by two
texts on the same
topic.
pp
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
A.
Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
9
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, discuss
similarities an
d
d
ifferences between
two texts on t
h
e
same topic (i.e. in
illustrations or
d
escriptions).
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
9
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support, i
d
entif
y
b
asic similarities in
an
d
d
ifferences
b
etween two texts
o
n t
h
e same topic
(
e.g., in
illustrations,
d
escriptions, or
procedures).
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
9
:
Identify basic
similarities in an
d
d
ifferences
b
etween two texts
o
n t
h
e same topic
(
e.g., in
illustrations,
d
escriptions, or
procedures).
A.
Integration of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
R
I
9
:
Compare and
contrast t
h
e most
important points
presented by two
texts on t
h
e same
topic.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Informational Text
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
nalyze how two or more texts address similar themes or topics in order to build knowledge or to compare the
approaches the authors ta
k
e
.

Appendix | 23
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Informational Text
Standard: Read and comprehend complex literary and informational texts independently and proficiently.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about
details in a book).
Show
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and/or answer
questions about a
book while you are
reading).
Develop
comprehension by
demonstrating
understanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
makes guesses
about what a book
is about).
A. Range of
Reading and Level
of Text Complexity
RI10: Actively
engage in group
reading activities
with purpose and
understanding.
A. Range of
Reading and Level
of Text Complexity
RI10: Actively
engage in group
reading activities
with purpose and
understanding.
A. Range of
Reading and Level
of Text Complexity
RI10: With
prompting and
support, read
informational texts
appropriately
complex for grade
1.
A. Range of
Reading and Level
of Text Complexity
RI10: By the end of
the year, read and
comprehend
informational texts,
including
history/social
studies, science, and
technical texts, in
the grades 2-3 text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as
needed at the high
end of the range.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases (e.g.,
answer simple
questions about
d
etails in a
b
ook
)
.
1 Year
Sh
o
w
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ask and
/
or answer
questions a
b
out a
b
oo
k
w
h
ile you are
reading).
p
2
Year
s
D
evelop
comprehension b
y
d
emonstrating
u
nderstanding of
text during and
after reading (e.g.,
ma
k
es guesses
about what a
b
oo
k
is about
)
.
py
3
Year
s
A.
R
ange of
R
eading and Level
o
f Text Complexit
y
R
I1
0
:
A
ctivel
y
engage in group
reading activities
with purpose and
u
nderstanding.
4
Year
s
A.
R
ange of
R
eading and Level
o
f Text Complexit
y
R
I1
0
:
A
ctivel
y
engage in group
reading activities
with purpose and
u
nderstanding.
pyp
Kindergarte
n
A.
R
ange of
R
eading and Level
o
f Text Complexit
y
R
I1
0
:
Wit
h
promp
t
ing and
t
t
support, read
py
Gra
d
e
1
informational texts
appropriatel
y
complex for grade
1
.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
R
ange of
R
eading and Level
o
f Text Complexit
y
R
I1
0
:
By the end of
the year, read and
comprehend
informational texts,
including
h
istory
/
social
studies, science, and
te
ch
ni
c
al texts, in
the grades
2
-
3
text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as
n
eeded at the high
end of the range.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Informational Text
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Read and comprehend complex literary and informational texts
independently and proficiently.
p

24 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Foundational Skills
Standard: RF1 Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(e.g., explore using
markers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write).
Recognize that
symbols have
corresponding
meaning (e.g., put
toys away in
correctly labeled
bins or shelves).
Recognize that
symbols have
corresponding
meaning (e.g., sing
the alphabet song,
pointing to the
letters).
.
A. Print Concepts
RF1.a:
Demonstrate an
awareness that
words are read
from left to right,
top to bottom and
page by page.
RF1.b: Recognize
that spoken words
can be written and
read.
RF1.c: Understand
that words are
separated by spaces
in print.
RF1.d: Recognize
and name some
upper and
lowercase letters of
the alphabet.
A. Print Concepts
RF1.a: Follow
words from left to
right, top to
bottom, and page
by page.
RF1.b: Recognize
that spoken words
are represented in
written language by
specific sequences
of letters.
RF1.c: Understand
that words are
separated by spaces
in print.
RF1.d: Recognize
and name all upper
and lowercase
letters of the
alphabet.
A. Print Concepts
RF1.a: Recognize
the distinguishing
features of a
sentence (e.g., first
word, capitalization,
ending
punctuation).
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(
e.g., explore using
mar
k
ers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write
)
.
1 Year
R
ecognize t
h
at
symbols have
correspondi
n
g
meaning
(
e.g., put
toys away in
correctly labeled
b
ins or shelves
)
.
2
Year
s
R
ecognize t
h
at
symbols have
corresponding
meaning
(
e.g., sin
g
the alphabet song,
pointing to t
h
e
letters
)
.
.
gg
3
Year
s
A.
P
rint
C
oncept
s
R
F1
.
a
:
D
emonstrate an
awareness t
h
at
words are rea
d
f
rom left to right,
top to bottom and
page by page.
R
F1.
b
:
R
ecognize
that spoken words
can be written and
rea
d
.
R
F1.
c
:
Un
d
erstan
d
that words are
separated by spaces
in print.
R
F1.
d
:
R
ecognize
an
d
name some
u
pper and
lowercase letters of
t
h
e alp
h
a
b
et.
4
Year
s
A.
P
rint
C
oncept
s
R
F1
.
a
:
F
ollo
w
words from left to
rig
h
t, top to
b
ottom, and page
b
y page.
R
F1.
b
p
Kindergarte
n
:
R
ecognize
that spoken words
are represented in
written language b
y
specific sequences
o
f letters.
R
F1.
c
:
Un
d
erstan
d
that words are
separated by spaces
in print.
R
F1.
d
:
R
ecognize
and name all upper
and lowercase
letters of the
alphabet.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
P
rint
C
oncept
s
R
F1
.
a
:
R
ecognize
the distinguishing
f
eatures of a
sentence (e.g., first
word, capitalization,
ending
p
u
nctuation
)
.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Foundational Skill
s
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
RF1 Demonstrate understanding of the organization and
basic features of print.

Appendix | 25
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Foundational Skills
Standard: RF2 Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables, and sounds (phonemes).
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Recognize and react
to the sounds of
language (e.g., point
or make sounds
when looking at
books; enjoy, and
occasionally join in
simple songs).
Become aware of
the sounds of
spoken language
(e.g., sing simple
and familiar songs
with a group or
individually,
identify
environmental
sounds such as a
doorbell, fire
engine, or water
running).
Develop
phonological
awareness by
becoming aware
of the sounds of
spoken language
(e.g., begin to
supply rhyming
words in a familiar
poem or song,
draw attention to
parts of words
such as syllables
by moving or
clapping).
A. Phonological
Awareness
RF2.a: Recognize
rhyming words in
spoken language.
RF2.b: Identify and
isolate individual
words in a spoken
sentence.
RF2.c: Count,
pronounce, blend,
and segment
syllables in spoken
words.
RF2.d: Blend and
segment onsets and
rimes of single-
syllable spoken
words.
A. Phonological
Awareness
RF2.a: Recognize
and produce
rhyming words.
RF2.b: Count,
pronounce, blend,
and segment
syllables in spoken
words.
RF2.c: Blend and
segment onsets and
rimes of single-
syllable spoken
words.
RF2.d: Isolate and
pronounce the
initial, medial
vowel, and final
sounds (phonemes)
in three-phoneme
(consonant-vowel-
consonant, or
CVC) words.*
A. Phonological
Awareness
RF2.a: Distinguish
long from short
vowel sounds in
single-syllable
words.
RF2.b: Orally
produce single-
syllable words by
blending sounds
(phonemes).
RF2.c: Isolate and
pronounce initial,
medial vowel, and
final sounds
(phonemes) in
spoken single-
syllable words.
RF2.d: Segment
spoken single-
syllable words into
their complete
sequence of
individual sounds
(phonemes).
1 Year
R
ecognize and rea
ct
to the soun
d
s of
languag
e
(
e.g., point
o
r make soun
d
s
when loo
k
ing at
b
ooks; en
j
oy, and
o
ccasionally
j
oin in
simple songs)
.
2
Year
s
Become aware of
the soun
d
s of
spo
k
en languag
e
(
e.g., sing simple
and familiar songs
wit
h
a group or
individually,
identif
y
f
f
environmental
soun
d
s such as a
d
oorbell, fire
engine, or water
running
)
.
gp
3
Year
s
D
evelop
p
h
onological
awareness b
y
b
ecoming aware
o
f the soun
d
s of
spo
k
en languag
e
(
e.g., begin to
supply r
h
yming
words in a familiar
poem or song,
d
raw attention to
parts of words
such as syllables
b
y moving or
clapping
)
g
g
.
y
4
Year
s
A.
Ph
onological
A
warenes
s
R
F2
.
a
:
R
ecognize
rhyming words in
spo
k
en language.
R
F2.
b
:
Identify and
isolate individual
words in a spoken
sen
t
ence.
R
F2.
c
:
C
ount,
pronounce, blend,
and segment
syllables in spo
k
en
words.
R
F2.
d
: Blen
d
an
d
segment onsets and
rimes of singl
e
-
syllable spoken
words.
(p
Kindergarte
n
A.
Ph
onological
A
warenes
s
R
F2
.
a
:
R
ecognize
and produce
rhyming words.
R
F2.
b
:
C
ount,
pronounce, blend,
and segment
syllables in spoken
words.
R
F2.
c
:
Blen
d
an
d
segment onsets and
rimes of singl
e
-
syllable spoken
words.
R
F2.
d
:
I
solate an
d
pronounce t
h
e
initial, medial
vowel, and final
sounds (phonemes)
in t
h
re
e
-
p
h
oneme
(
consonant
-
vowe
l
-
consonan
t
, or
CVC
)
words.*
)
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Ph
onological
A
warenes
s
R
F2
.
a
:
D
istinguis
h
long from short
vowel sounds in
singl
e
-
syllable
words.
R
F2.
b
:
O
rall
y
produce singl
e
-
syllable words b
y
b
lending sounds
(
p
h
onemes).
R
F2.
c
:
Isolate an
d
pronounc
e
initial,
medial vowel, and
f
inal soun
d
s
(
p
h
onemes) in
spo
k
en singl
e
-
syllable words.
R
F2.
d
:
S
egment
spo
k
en singl
e
-
syllable words into
t
h
eir complete
sequence of
individual sounds
(
p
h
onemes).
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Foundational Skill
s
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
RF2 Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables
, and sounds (phonemes).
continued on next page

26 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
RF2.e: Isolate and
pronounce the initial
sound in spoken
words.
RF2.f: Orally blend
and segment
individual phonemes
in two- to-three
phoneme words.
(This does not
include CVCs
ending with /l/,
/r/, or /x/)
RF2.e: Add or
substitute
individual sounds
(phonemes) in
simple, one-syllable
words to make new
words.
R
F2
.e
:
Isolate an
d
pronounce t
h
e initial
sound in spoken
words.
RF2.f
:
f
f
O
rally blend
and segment
individual phonemes
in tw
o
-
to
-
t
h
ree
phoneme words.
(
This does not
include C
VC
s
ending with
/
l
/
,
/
r
/
, or
/
x
/)
R
F2
.e
:
Add
or
su
b
stitute
individual sounds
(
p
h
onemes) in
simple, on
e
-
sy
llable
y
words to make ne
w
words.
continued from previous page

Appendix | 27
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Foundational Skills
Standard: Know and apply grade- level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Recognize and react
to the sounds of
language (e.g., point
or make sounds
when looking at
books, move
rhythmically to
familiar songs).
Recognize that
symbols have
corresponding
meaning (e.g., use
the stop sign in play
with a car set,
recognize familiar
symbols such as
hospital or library).
Recognize that
symbols have
corresponding
meaning (e.g., look
for and identify
familiar logos or
signs, find own
name card on a
carpet square and
sit there).
A. Phonics & Word
Recognition
RF3.a: Recognize
that words are
made up of letters
and their sounds.
RF3.b:
Demonstrate basic
knowledge of one-
to-one letter sound
correspondences by
producing the most
frequent sound for
some consonants.
RF3.c: Recognize
name in print as
well as some
environmental print
(symbols/words).
A. Phonics & Word
Recognition
RF3.a:
Demonstrate basic
knowledge of one-
to-one letter-sound
correspondence by
producing the
primary or many of
the most frequent
sound for each
consonant.
RF3.b: Associate
the long and short
sounds with
common spellings
(graphemes) for the
five major vowels.
RF3.c: Read
common high-
frequency words by
sight (e.g., the, of,
to, you, she, my, is,
are, do, does).
RF3.d: Distinguish
between similarly
spelled words by
A. Phonics & Word
Recognition
RF3.a: Know the
spelling-sound
correspondence for
common consonant
digraphs.
RF3.b: Decode
regularly spelled
one-syllable words.
RF3.c: Know final-
e and common
vowel team
conventions for
representing long
vowel sounds.
RF3.d: Use
knowledge that
every syllable must
A. Phonics & Word
Recognition
RF3.a: Distinguish
long and short
vowels when
reading regularly
spelled one-syllable
words.
RF3.b: Know
sound-spelling
correspondences
for additional
common vowel
teams.
RF3.c: Decode
regularly spelled
two-syllable words
with long vowels.
RF3.d: Decode
words with
common prefixes
1 Year
R
ecognize and react
to the soun
d
s of
language (e.g., point
o
r make soun
ds
when loo
k
ing at
b
ooks, move
r
h
yt
h
mically to
f
amiliar songs)
.
pp y g
2
Year
s
R
ecognize t
h
at
symbols have
corresponding
meaning
(
e.g.,
us
e
t
h
e stop sign in pla
y
wit
h
a car set,
recognize familiar
symbols such as
h
ospital or library)
.
p
3
Year
s
R
ecognize t
h
at
symbols have
corresponding
meaning
(
e.g., loo
k
f
or and identif
y
f
amiliar logos or
sig
n
s
, find own
n
ame car
d
on a
carpet square and
sit t
h
ere
)
.
y
4
Year
s
A.
P
honics & Word
R
ecognitio
n
R
F3
.
a
:
R
ecognize
that words are
made up of letters
an
d
their soun
d
s.
R
F3.
b
:
D
emonstrate
b
asic
knowledge of on
e
-
to
-
o
ne letter soun
d
correspondences b
y
producing the most
f
requent sound for
some consonan
t
s.
R
F3.
c
:
R
ecognize
n
ame in print as
well as some
environmental print
(
symbols
/
words).
g
Kindergarte
n
A
. Phonics & Word
R
ecognitio
n
R
F3
.
a
:
D
emonstrate
b
asic
knowledge of on
e
-
to
-
o
ne letter
-
soun
d
correspondence b
y
producing the
primary or many of
the most frequent
soun
d
for each
consonan
t
.
R
F3.
b
:
A
ssociate
the long and short
sounds with
common spellings
(
graphemes) for the
f
ive ma
j
or vowel
s
.
R
F3.
c
:
R
ea
d
common
h
ig
h
-
f
requency words b
y
sight (e.g., the, of,
to, you, s
h
e, my, is,
are, do, does
)
.
R
F3.
d
:
D
istinguis
h
b
etween similarl
y
spelled words b
y
A
. Phonics & Word
R
ecognitio
n
R
F3
.
a
:
Kno
w
t
h
e
spelling
-
soun
d
correspondence for
common consonan
t
d
igraph
s
.
R
F3.
b
:
D
eco
d
e
regularly spelled
o
n
e
-
syllable words.
R
F3.
c
:
Know fina
l
-
e an
d
common
vowel team
conventions for
representing long
vowel sounds.
R
F3.
d
:
Use
knowledge that
eve
ry
syllable must
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Phonics & Word
R
ecognitio
n
R
F3
.
a
:
D
istinguis
h
long and short
vowels w
h
en
reading regularl
y
spelled on
e
-
syllable
words.
R
F3.
b
:
Kno
w
soun
d
-
spelling
correspondences
f
or a
dd
itional
common vowel
t
eams.
R
F3.
c
:
D
eco
d
e
regularly spelled
t
w
o
-
syllable words
wit
h
long vowels.
R
F3.
d
:
D
eco
d
e
words wit
h
common prefixes
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Foundational Skill
s
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Know and apply grade
-
level phonics and word analysis s
kills in decoding words.
continued on next page

28 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
identifying the
sounds of the letter
that differ.
have a vowel sound
to determine the
number of syllables
in a printed word.
RF3.e: Decode
two-syllable words
following basic
patterns by
breaking the words
into syllables
RF3.f: Read words
with inflectional
endings.
RF3.g: Recognize
and read grade-
appropriate
irregularly spelled
words.
and suffixes.
RF3.e: Identify
words with
inconsistent but
common spelling-
sound
correspondences.
RF3.f: Recognize
and read grade-
appropriate
irregularly spelled
words.
identifying the
soun
d
s of the letter
that
d
iffer.
h
ave a vowel sound
to
d
etermine the
n
umber of syllables
in a printed word.
R
F3
.e
:
D
eco
d
e
t
w
o
-
syllable words
f
ollowing basic
patterns b
y
b
reaking the words
into syllable
s
RF3.f
:
f
f
R
ead words
with inflectional
endings.
R
F3.g
:
R
ecognize
an
d
read grad
e
-
appropriate
irregularly spelled
words.
an
d
suffixes.
R
F3
.e
:
Identif
y
words with
inconsistent
b
ut
common spelling
-
soun
d
correspondences.
RF3.f
:
f
f
R
ecognize
and read grad
e
-
appr
o
pr
iate
irregularly spelled
words.
continued from previous page

Appendix | 29
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Reading Foundational Skills
Standard: Engage with a variety of texts with purpose and understanding. Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support
comprehension.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases to express
himself (e.g., listen
quietly to the story,
and ask for it to be
read again; learn
some simple words
and phrases from
rhymes that are
heard repeatedly).
Begin to develop
fluency by imitative
reading (e.g., ask
for the same
favorite book over
and over again,
recite a familiar
nursery rhyme,
poem or finger play
with expression).
Begin to develop
fluency by imitative
reading (e.g., listen
to models of fluent
reading, ask to
reread a favorite
story, remembering
the funny ending
and telling it as you
start to read).
A. Fluency
RF4: Engage with a
variety of texts (e.g.,
a variety of
structures and/or
genres) with
purpose and
understanding.
A. Fluency
RF4: Read
emergent-reader
texts with purpose
and understanding.
A. Fluency
RF4: Read with
sufficient accuracy
and fluency to
support
comprehension.
RF4.a: Read on-
level text with
purpose and
understanding.
RF4.b: Read on-
level text orally with
accuracy,
appropriate rate,
and expression on
successive readings.
RF4.c: Use context
to confirm or self-
correct word
recognition and
understanding,
rereading as
necessary.
A. Fluency
RF4: Read with
sufficient accuracy
and fluency to
support
comprehension.
RF4.a: Read on-
level text with
purpose and
understanding.
RF4.b: Read on-
level text orally with
accuracy,
appropriate rate,
and expression on
successive readings.
RF4.c: Use context
to confirm or self-
correct word
recognition and
understanding,
rereading as
necessary.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases to express
h
imself (e.g., listen
quietly to t
h
e story,
and ask for it to
b
e
rea
d
again; learn
some simple words
and phrases from
r
h
ymes t
h
at are
h
eard repeatedly).
p
1 Year
Begin to develop
f
luency by imitative
reading
(
e.g., as
k
f
or the same
f
avorite
b
ook over
and over again,
re
c
ite a familiar
n
ursery r
h
yme,
poem or finger pla
y
wit
h
expressi
o
n)
.
2
Year
s
Begin to develop
f
luency by imitative
reading
(
e.g., listen
to mo
d
els of fluent
reading, ask to
reread a favorite
story, remembering
the funny ending
and telling it as you
start to read
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
F
luenc
y
R
F4
:
Engage wit
h
a
variety of texts (e.g.,
a variety of
structures and
/
or
genres) wit
h
purpose and
u
nderstanding.
4
Year
s
A.
F
luenc
y
R
F4
:
R
ea
d
emergen
t
-
rea
d
er
texts wit
h
purpose
and understanding.
Kindergarte
n
A.
F
luenc
y
R
F4
:
R
ead with
sufficient accurac
y
and fluency to
suppor
t
compre
h
ension.
R
F4
.
a
:
R
ea
d
o
n
-
level text wit
h
purpose and
u
nderstanding.
R
F4.
b
:
R
ea
d
o
n
-
level text orally wit
h
accu
r
acy,
appropriate rate,
and expression on
successive readings.
R
F4.
c
:
Use context
to confirm or self
-
f
f
correct word
recognition and
u
n
de
rstanding,
rereading as
n
ecessa
r
y.
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
A.
F
luenc
y
R
F4
:
R
ead with
sufficient accurac
y
and fluency to
suppor
t
compre
h
ension.
R
F4
.
a
:
R
ea
d
on
-
level text wit
h
purpose and
u
nderstanding.
R
F4.
b
:
R
ea
d
o
n
-
level text orally wit
h
accu
r
acy,
appropriate rate,
an
d
expression on
successive readings.
R
F4.
c
:
Use context
to confirm or self
-
f
f
correct word
recognition and
u
n
d
erstanding,
rereading as
n
ecessa
r
y.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
R
eading Foundational Skill
s
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Engage with a variety of texts with purpose and understanding. Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support
comprehension.

30 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Writing
Standard: Write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts, using valid reasoning and relevant and
sufficient evidence.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(e.g., explore using
markers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write).
Recognize that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., pretend to
write a letter by
scribbling on a
paper and
“reading” it out
loud).
Begin to develop
writing skills by
recognizing that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., begin to
control scribbles,
perhaps telling
caregiver what they
say).
A. Text Types and
Purposes
W1: With modeling
and support, use a
combination of
drawing, dictating,
and
developmentally
appropriate writing
to share opinion
about an experience
or book.
A. Text Types and
Purposes
W1: Use a
combination of
drawing, dictating,
and writing to
compose opinion
pieces in which
they tell a reader
the topic or the
name of the book
they are writing
about and state an
opinion or
preference about
the topic or book
(e.g., My favorite
book is……….).
A. Text Types and
Purposes
W1: Write opinion
pieces in which
they introduce the
topic or name the
book they are
writing about, state
an opinion, supply
a reason for the
opinion, and
provide some sense
of closure.
A. Text Types and
Purposes
W1: Write opinion
pieces in which
they introduce the
topic or book they
are writing about,
state an opinion,
supply reasons that
support the
opinion, use linking
words (e.g.,
because, and, also)
to connect opinion
and reasons, and
provide a
concluding
statement or
section.
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(
e.g., explore using
mar
k
ers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write
)
.
1 Year
R
ecognize t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representation
s
(
e.g., pretend to
write a letter b
y
scribbling on a
paper and
“reading” it out
loud
)
.
2
Year
s
Begin to develop
writing
s
k
ill
s
by
recognizing t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(
e.g.,
b
egin to
control scribbles,
per
h
aps telling
caregiver w
h
at t
h
e
y
say
)
y
y
.
3
Year
s
A.
Text Types and
P
urpose
s
W
1
:
With modeling
and support, use a
com
b
ination of
d
rawing,
d
ictating,
an
d
d
evelopmentall
y
appropriate writing
to s
h
are opinion
about an experience
o
r
b
ook.
4
Year
s
A
. Text Types and
P
urpose
s
W
1
:
Use a
com
b
ination of
d
rawing, dictating,
and writing to
compose opinion
pieces in w
h
ic
h
they tell a reader
t
h
e topic or t
h
e
n
a
m
e of the
b
oo
k
t
h
ey are writing
a
b
out and state an
o
pinion or
preference about
the topic or boo
k
(
e.g., My favorite
b
ook is……….
)
.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Text Types and
P
urpose
s
W
1
:
Write opinion
pieces in w
h
ic
h
they introduce the
topic or name t
h
e
b
ook they are
writing about, s
t
a
t
e
an opinion, suppl
y
a reason for the
o
pinion, and
provide some sense
o
f closure.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Text Types and
P
urpose
s
W
1
:
Write opinion
pieces in w
h
ic
h
they introduce the
topic or book the
y
are writing about,
state an opinion,
supply reasons t
h
at
support t
h
e
o
pinion, use lin
k
ing
words (e.g.,
b
ecause, and, also
)
to connect opinion
and reasons, and
provide a
concluding
s
t
a
t
emen
t
or
section.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
Writing
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts, using valid reasoning and relevant and
sufficient evidence.

Appendix | 31
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Writing
Standard: Write informative/explanatory texts to examine and convey complex ideas and information clearly and accurately
through the effective selection, organization, and analysis of content.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(e.g., explore using
markers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write).
Recognize that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., paint some
lines across the
paper with broad
strokes and
movements, using a
few different
colors, and tell you
that it is a rainbow).
Begin to develop
writing skills by
recognizing that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., pretend to
take your order
while playing
restaurant by
scribbling on a pad
with a pencil).
A. Text Types and
Purposes
W2: Use a
combination of
drawing, dictating,
or developmentally
appropriate writing
to state information
on a topic.
A. Text Types and
Purposes
W2: Use a
combination of
drawing, dictating,
and writing to
compose
informative/explan
atory texts in which
they name what
they are writing
about and supply
some information
about the topic.
A. Text Types and
Purposes
W2: Write
informative/explan
atory texts in which
they name a topic,
supply some facts
about the topic,
and provide some
sense of closure.
A. Text Types and
Purposes
W2: Write
informative/explan
atory texts in which
they introduce a
topic, use facts and
definitions to
develop points, and
provide a
concluding
statement or
section.
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(
e.g., explore using
mar
k
ers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write
)
.
g
1 Year
R
ecognize t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(
e.g., paint some
lines across t
h
e
paper with br
o
a
d
strokes an
d
movements, using a
f
ew different
colors, and tell you
that it is a rainbow
)
.
g
2
Year
s
Begin to develop
writing skills b
y
recognizing t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(
e.g., pretend to
take your order
w
h
ile playing
restaurant b
y
scribbling on a pad
wit
h
a pencil).
y
3
Year
s
A.
Text Types and
P
urpose
s
W
2
:
Use a
com
b
ination of
d
rawing, dictating,
o
r developmentall
y
appropriate writing
to state information
o
n a topic.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A
. Text Types and
P
urpose
s
W
2
:
Use a
com
b
ination of
d
rawing, dictating,
and writing to
compose
informative
/
expla
n
atory texts in w
h
ic
h
t
h
ey name w
h
at
t
h
ey are writing
about and suppl
y
some information
about the topic.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Text Types and
P
urpose
s
W
2
:
Write
informative
/
expla
n
atory texts in w
h
ic
h
t
h
ey name a t
o
pic,
supply some facts
about the topic,
and provide some
sense of closure.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Text Types and
P
urpose
s
W
2
:
Write
informative
/
expla
n
atory texts in w
h
ic
h
they introduce a
topic, use facts and
d
efinitions to
d
evelop points, and
provide a
concluding
s
t
a
t
emen
t
or
section.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
Writing
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Write informative
/
explanatory texts to examine and conve
y
complex ideas and information clearly and accuratel
y
through the effective selection, organization, and analysis of content.
g

32 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Writing
Standard: Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, well-chosen details, and
well-structured event sequences.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(e.g., explore using
markers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write).
Recognize that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., intentionally
make a mark on a
piece of paper).
Begin to develop
writing skills by
recognizing that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., make a picture
of self with lines
coming out of the
bottom and sides
of a circle).
A. Text Types &
Purposes
W3: With modeling
and support, use a
combination of
drawing, dictating,
or developmentally
appropriate writing
to communicate a
personal story about
a single event and
tell about the event
in a meaningful
sequence.
A. Text Types &
Purposes
W3: Use
combination of
drawing, dictating,
or writing to
narrate a single
event or several
loosely linked
events, tell about
the events in the
order in which they
occurred, and
provide a reaction
to what happened.
A. Text Types &
Purposes
W3: Write
narratives in which
they recount two or
more appropriately
sequenced events,
include some
details regarding
what happened, use
temporal words to
signal event order,
and provide some
sense of closure.
A. Text Types &
Purposes
W3: Write
narratives in which
they recount a well-
elaborated event or
short sequence of
events, include
details to describe
actions, thoughts,
and feelings, use
temporal words to
signal event order,
and provide a sense
of closure.
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(
e.g., explore using
mar
k
ers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write
)
.
1 Year
R
ecognize t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(
e.g., intentionall
y
ma
k
e a mar
k
o
n a
piece of paper).
2
Year
s
Begin to develop
writing skills b
y
recognizing t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(
e.g., ma
k
e a picture
o
f self with lines
coming out of the
b
ottom and sides
o
f a circle
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
T
ext
T
ypes &
P
urpose
s
W3
:
With modeling
and support, use a
com
b
ination of
d
rawing, dictating,
o
r developmentall
y
appropriate writing
to
c
ommuni
c
ate a
personal story about
a single event and
tell a
b
out the event
in a meaningful
sequence.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A
. Text Types &
P
u
rposes
W3
:
Use
com
b
ination of
d
rawing, dictating,
o
r writing to
n
arrate a single
event or several
loosely linked
events, tell about
t
h
e events in t
h
e
o
rder in which the
y
o
ccurred, and
provide a reaction
to what happened.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
T
ext
T
ypes &
P
urpose
s
W3
:
W
rite
n
arratives in w
h
ic
h
t
h
ey recount two or
more appropriatel
y
sequenced events,
inclu
d
e some
d
etails regarding
what happened, use
temporal words to
signal event order,
and provide some
sense of closure.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
T
ext
T
ypes &
P
urpose
s
W3
:
Write
n
arratives in w
h
ic
h
t
h
ey recount a wel
l
-
ela
b
orated event or
short sequence of
events, include
d
etails to descri
b
e
actions, t
h
oug
h
ts,
and feelings, use
temporal words to
signal event order,
and provide a sense
o
f closure.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
Writing
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, wel
l
-
chosen details, and
wel
l
-
structured event sequences.

Appendix | 33
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Writing
Standard: Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Production and
Distribution of
Writing
W5: With modeling,
guidance, and
support from adults,
review drawing,
dictation or
developmentally
appropriate writing.
A. Production and
Distribution of
Writing
W5: With guidance
and support from
adults, respond to
questions and
suggestions from
peers and add
details to
strengthen writing
as needed.
A. Production and
Distribution of
Writing
W5: With guidance
and support from
adults, focus on a
topic, respond to
questions and
suggestions from
peers, and add
details to
strengthen writing
as needed.
A. Production and
Distribution of
Writing
W5: With guidance
and support from
adults and peers,
focus on a topic
and strengthen
writing as needed.
1 Year
pg
2
Year
s
gy
3
Year
s
yp g g
4
Year
s
A.
P
ro
d
uction an
d
D
istri
b
ution of
Writing
W5
:
With modeling,
guidance, and
support from adults,
review drawing,
d
ictation or
d
evelopmentall
y
appropriate writing.
gg
Kindergarte
n
A
. Pro
d
uction an
d
D
istri
b
ution of
Writing
W5
:
With guidance
and support from
adults, respond to
questions and
suggestions from
peers and add
d
etails to
s
t
rengt
h
en writing
as nee
d
e
d
.
yg pp
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Pro
d
uction an
d
D
istri
b
ution of
Writing
W5
:
With guidance
and support from
adults, focus on a
topic, respond to
questions and
suggestions from
peers, and add
d
etails to
strengt
h
en writing
as nee
d
e
d
.
A
. Pro
d
uction an
d
D
istri
b
u
ti
o
n
o
f
Writing
W5
:
With guidance
and support from
adults and peers,
f
ocus on a topic
and strengthen
writing as needed.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
Writing
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach.
yg pp

34 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Writing
Standard: Use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing and to interact and collaborate with others.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(e.g., explore using
markers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write).
Recognize that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., make a picture
of with lines
coming out of the
bottom and sides
of a circle and tell
you that it is him).
Begin to develop
writing skills by
recognizing that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., show a friend
his picture on a
wall).
A. Production and
Distribution of
Writing
W6: With
prompting and
support from adults,
explore a variety of
digital tools to
express ideas.
A. Production and
Distribution of
Writing
W6: With guidance
and support from
adults, explore a
variety of digital
tools to produce
and publish writing
including
collaboration with
peers.
A. Production and
Distribution of
Writing
W6: With guidance
and support from
adults, use a variety
of digital tools to
produce and
publish writing,
including in
collaboration with
peers.
A. Production and
Distribution of
Writing
W6: With guidance
and support from
adults, use a variety
of digital tools to
produce and
publish writing,
including in
collaboration with
peers.
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(
e.g., explore using
mar
k
ers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write
)
.
1 Year
R
ecognize t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(
e.g., ma
k
e a picture
o
f with lines
coming out of the
b
ottom and sides
o
f a circle an
d
tell
you t
h
at it is
h
im).
gy g
2
Year
s
Begin to develop
writing skills b
y
recognizing t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writ
ing are
tt
meaningful
representations
(
e.g., show a friend
h
is picture on a
wall
)
.
gp
3
Year
s
A.
P
ro
d
uction an
d
D
istri
b
ution of
Writing
W
6
:
Wit
h
prompting and
support from adults,
explore a variety of
d
igital tools to
express ideas.
p
4
Year
s
A.
P
ro
d
uction an
d
D
istri
b
ution of
W
riting
W
6
:
With guidance
and support from
adults, explore a
variety of digital
tools to produce
and publish writing
including
collaboration with
peers.
g
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A.
P
ro
d
uction an
d
D
istri
b
ution of
Writing
W
6
:
With guidance
and support from
adults, use a variet
y
o
f
d
igital tools to
produce and
publish writing,
including in
collaboration with
peers.
A.
P
ro
d
uction an
d
D
istri
b
ution of
Writing
W
6
:
With guidance
and support from
adults, use a variet
y
o
f digital tools to
produce and
publish writing,
including in
collaboration with
peers.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
Writing
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing
and to interact and collaborate with others.
gy g
gp
p
g

Appendix | 35
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Writing
Standard: Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects based on focused questions, demonstrating understanding of
the subject under investigation.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Research to Build
and Present
Knowledge
W7: Participate in
shared research and
shared writing
projects.
A. Research to
Build and Present
Knowledge
W7: Participate in
shared research and
writing projects
(e.g., explore a
number of books
by a favorite author
and express
opinions about
them).
A. Research to
Build and Present
Knowledge
W7: Participate in
shared research and
writing projects
(e.g., explore a
number of “how-
to” books on a
given topic and use
them to write a
sequence of
instructions.
A. Research to
Build and Present
Knowledge
W7: Participate in
shared research and
writing projects
(e.g., read a number
of books on a
single topic to
produce a report;
record science
observations).
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
A.
R
esearch to Buil
d
an
d
Present
Knowledg
e
W7
:
P
articipate in
share
d
research an
d
shared writing
pro
j
ect
s
.
Kindergarte
n
A.
R
esearc
h
to
Buil
d
an
d
Present
Knowledg
e
W7
:
P
articipate in
share
d
research an
d
writing pro
j
ects
(
e
.
g
., explore a
n
um
b
er of
b
ooks
b
y a favorite author
and express
o
pinions about
t
h
em
)
.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
R
esearc
h
to
Buil
d
an
d
Present
Knowledg
e
W7
:
P
articipate in
share
d
research an
d
writing pro
j
ects
(
e.g., explore a
n
umber of “ho
w
-
to”
b
ooks on a
given topic and use
th
em to write a
sequence of
instruction
s
.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
R
esearc
h
to
Buil
d
an
d
Present
Knowledg
e
W7
:
P
articipate in
share
d
research an
d
writing pro
j
ects
(
e.g., read a number
o
f
b
ooks on a
single topic to
produce a report;
recor
d
science
o
bservations
)
.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
Writing
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Conduct short as well as more sustained research pro
j
ects based on focused questions, demonstrating understanding of
the sub
j
ect under investigation.

36 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Writing
Standard: Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources, assess the credibility and accuracy of each source,
and integrate the information while avoiding plagiarism.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Research to Build
and Present
Knowledge
W8: With modeling
and support from
adult, recall
information from
experiences or
information from
provided sources to
answer a question.
A. Research to
Build and Present
Knowledge
W8: With guidance
and support from
adults, recall
information from
experiences or
gather information
from provided
sources to answer a
question.
A. Research to
Build and Present
Knowledge
W8: With guidance
and support from
adults, recall
information from
experiences or
gather information
from provided
sources to answer a
question.
A. Research to
Build and Present
Knowledge
W8: Recall
information from
experiences or
gather information
from provided
sources to answer a
question.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
A.
R
esearch to Buil
d
an
d
Present
Knowledg
e
W
8
:
With modeling
and support from
adult, recall
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
experiences or
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
provided sources to
answer a question
.
Kindergarte
n
A.
R
esearc
h
to
Buil
d
an
d
Present
Knowledg
e
W
8
:
With guidance
and support from
adults, recall
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
experiences or
gather information
f
rom provided
sources
t
o answer a
question
.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
R
esearc
h
to
Buil
d
an
d
Present
Knowledg
e
W
8
:
With guidance
and support from
adults, recall
inf
o
rmati
o
n
f
r
o
m
experiences or
gather information
f
rom provided
sources
t
o answer a
question.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
R
esearc
h
to
Buil
d
an
d
Present
Knowledg
e
W
8
:
R
e
c
all
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
experiences or
gather information
f
rom provided
sources
t
o answer a
questio
n
.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
Writing
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources, assess the credibility and accuracy of each source,
and integrate the information while avoiding plagiaris
m
.

Appendix | 37
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Speaking & Listening
Standard: Prepare for and participate effectively in a range of conversations and collaborations with diverse partners, building on
others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly and persuasively.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Communicate using
consistent sounds,
words, and gestures
(e.g., use single
words such as “no”
and “bye”
appropriately, shake
head yes when
asked, “Are you
ready to go
outside?”).
Enter into a
conversation (e.g.,
repeat what has just
been said, or make
up a story to be
part of the
conversation;
interrupt or talk
over other people’s
conversation).
Have more
meaningful
conversations with
peers and adults
(e.g., offer own
information in a
group story or
discussion about a
visit by the
firefighters, talk to
a friend or
caregiver, an
imaginary friend, or
the dolls and toys
that he is playing
with).
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL1: Participate in
collaborative
conversations with
diverse partners
about pre-
kindergarten topics
and texts with peers
and adults in small
and larger groups.
SL1.a: Follow
agreed-upon rules
for discussions (e.g.,
listening to others
and taking turns,
speaking about the
topics and texts
under discussion).
SL1.b: During
scaffolded
conversations,
continue a
conversation
through multiple
exchanges.
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL 1: Participate in
collaborative
conversations with
diverse partners
about Kindergarten
topics and texts
with peers and
adults in small and
larger groups.
SL1.a: Follow
agreed-upon rules
for discussions
(e.g., listening to
others and taking
turns speaking
about the topics
and texts under
discussion).
SL1.b: Continue a
conversation
through multiple
exchanges.
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL1: Participate in
collaborative
conversations with
diverse partners
about grade 1
topics and texts
with peers and
adults in small and
larger groups.
SL1.a: Follow
agreed-upon rules
for discussions
(e.g., listening to
others with care,
speaking one at a
time about the
topics and texts
under discussion).
SL1.b: Build on
others’ talk in
conversations by
responding to the
comments of
others through
multiple exchanges.
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL1: Participate in
collaborative
conversations with
diverse partners
about grade 2
topics and texts
with peers and
adults in small and
larger groups.
SL1.a: Follow
agreed-upon rules
for discussions
(e.g., gaining the
floor in respectful
ways, listening to
others with care,
speaking one at a
time about the
topics and texts
under discussion).
SL1.b: Build on
others’ talk in
conversation by
linking their
comments to the
remarks of others.
C
ommunicate using
consistent sounds,
words, and gesture
s
(
e.g.,
u
se single
words such as “n
o
”
and “bye”
appropriately, sha
k
e
h
ead yes when
asked, “Are you
ready to go
o
utside?”
)
.
1 Year
Enter int
o
a
conversatio
n
(
e.g.,
repeat w
h
at
h
as
j
ust
b
een said, or make
u
p a story to be
part of the
conversation;
interrupt or tal
k
o
ver ot
h
er people’s
conversation
)
.
pg
2
Year
s
H
ave more
meaningful
conversations wit
h
peers and adult
s
(
e.g.,
o
ffer own
inf
o
rmati
o
n in a
group s
t
or
y
or
d
iscussion a
b
out a
visit by the
f
irefighters, tal
k
t
o
a frien
d
or
caregiver, an
imaginary friend, or
the dolls and toys
t
h
at
h
e is playing
wit
h)
.
yp
3
Year
s
y
4
Year
s
A.
Compre
h
ension
and Colla
b
oration
S
L
1
:
P
articipate in
colla
b
orative
conversations wit
h
d
iverse par
t
ners
about pr
e
-
kindergarten topics
and texts with peers
an
d
a
d
ults in small
and larger groups.
S
L1.a
:
F
ollo
w
agree
d
-
u
pon rules
f
or discussions (e.g.,
listening to ot
h
ers
and taking turns,
speaking about the
topics and texts
u
nder discussion
)
.
S
L1.
b
:
D
uring
scaffol
d
e
d
conversations,
c
ontinue a
conversation
t
h
roug
h
multiple
exc
h
an
g
e
s
.
Kindergarte
n
A.
Compre
h
ension
and Colla
b
oration
S
L
1
:
P
articipate in
colla
b
orative
conversations wit
h
d
iverse partners
about Kindergarten
topics and texts
with peers and
a
d
ults in small an
d
larger groups.
S
L1.a
:
F
ollo
w
agree
d
-
u
pon rules
f
or
d
iscussions
(
e.g., listening to
o
thers and taking
turns spea
k
in
g
about the topics
an
d
texts un
d
er
d
iscussion
)
.
S
L1.
b
:
Co
ntinue a
conversation
t
h
roug
h
multiple
exc
h
ange
s
.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Compre
h
ension
a
n
d Colla
b
oratio
n
S
L
1
:
P
articipate in
colla
b
orative
conversations wit
h
d
iverse partners
about grade 1
topics and texts
with peers and
a
d
ults in small an
d
larger groups.
S
L1.a
:
F
ollo
w
agree
d
-
u
pon rules
f
or
d
iscussions
(
e.g., listening to
o
t
h
ers wit
h
care,
spea
k
ing one at a
time a
b
out the
topics and texts
u
nder discussion
)
.
S
L1.
b
:
Buil
d
on
o
thers’ tal
k
in
conversations b
y
responding to the
comments of
o
t
h
ers t
h
roug
h
multi
p
le exc
h
an
g
es.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
Compre
h
ension
and Colla
b
oratio
n
S
L
1
:
P
articipate in
colla
b
orative
conversations wit
h
d
iverse partners
about grade 2
topics and texts
with peers and
a
d
ults in small an
d
larger groups.
S
L1.a
:
F
ollo
w
agree
d
-
u
pon rules
f
or
d
iscus
s
ions
(
e.g., gaining t
h
e
f
loor in respectful
ways, listening to
o
t
h
ers wit
h
care,
spea
k
ing one at a
time a
b
out the
topics and texts
u
nder discussion
)
.
S
L1.
b
:
Buil
d
on
o
thers’ tal
k
in
conversation b
y
lin
k
ing their
comments to t
h
e
remar
k
s of others.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage
&
Literac
y
S
tran
d:
S
pea
k
ing & Listening
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
P
repare for and participate effectively in a range of conversations and collaborations with diverse partners, building on
others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly and persuasively.
continued on next page

38 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
SL1.c: Ask
questions to clear
up any confusion
about the topics
and texts under
discussion.
SL1.c: Ask for
clarification and
further explanation
as needed about the
topics and texts
under discussion.
S
L1.c
:
A
s
k
questions to clear
u
p any confusion
about the topics
an
d
texts un
d
er
d
iscussion.
S
L1.c
:
A
sk for
clarification an
d
f
urther explanation
as needed a
b
out the
topics and texts
u
n
d
er
d
iscussion.
continued from previous page

Appendix | 39
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Speaking & Listening
Standard: Integrate and evaluate information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Show more interest
in speech (e.g.,
respond to one step
direction such as
“Come to
mommy,” point to
the cat in a book
when you say,
“Where is the
cat?”).
Use words and
some common
rules of speech to
express ideas and
thoughts (e.g., ask
questions about the
story as well as
naming objects).
Demonstrate active
listening skills (e.g.,
ask questions about
what has been
heard).
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL2: Confirm
understanding of
text read aloud or
information
presented orally or
through other media
by asking and
answering questions
about key details
with modeling and
support.
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL2: Confirm
understanding of
text read aloud or
information
presented orally or
through other
media by asking
and answering
questions about key
details and
requesting
clarification if
something is not
understood.
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL2: Ask and
answer questions
about key details in
a text read aloud or
presented orally or
through other
media.
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL2: Recount or
describe key ideas
or details from a
text read aloud or
information
presented orally or
through other
media.
Sh
ow more interest
in speec
h
(
e.g.,
respond to one step
d
irection such as
“
Co
me t
o
mommy,
”
point to
the cat in a
b
oo
k
w
h
en you say,
“W
h
ere is t
h
e
c
at?
”
)
.
g
1 Year
Use words and
some common
rules of speech to
express ideas and
thoughts (e.g., as
k
questions about the
story as well as
n
aming ob
j
ects)
.
2
Year
s
D
emonstrate active
listening s
k
ills (e.g.,
ask questions about
what has been
h
eard
)
.
p
3
Year
s
A.
Compre
h
ension
an
d
Colla
b
oratio
n
S
L
2
:
Co
nfirm
u
nderstanding of
text rea
d
alou
d
or
inf
o
rmati
o
n
presented orally or
through other media
b
y asking and
answering questions
about key details
with modeling and
suppor
t
.
4
Year
s
A.
Compre
h
ension
and Colla
b
oration
S
L
2
:
Co
nfirm
u
nderstanding of
text rea
d
alou
d
or
inf
o
rmati
o
n
presented orally or
t
h
roug
h
ot
h
er
media by asking
and answering
questions about ke
y
d
etails an
d
requesting
c
larifi
c
ation if
somet
h
ing is not
u
n
d
erstoo
d
.
Kindergarte
n
gyq
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Compre
h
ension
and Colla
b
oration
S
L
2
:
A
sk an
d
answer questions
a
b
out key details in
a text rea
d
alou
d
or
presented orally or
t
h
roug
h
ot
h
er
me
d
ia
.
yy
Gra
d
e
2
A.
Compre
h
ension
and Colla
b
oratio
n
S
L
2
:
R
e
c
ount or
d
escribe key ideas
o
r
d
etails from a
text rea
d
alou
d
or
inf
o
rmati
o
n
presented orally or
t
h
roug
h
ot
h
er
me
d
ia
.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
S
pea
k
ing & Listening
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Integrate and evaluate information presented in diverse media and formats,
including visually, quantitatively, and orally
.
gyq

40 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Speaking & Listening
Standard: Evaluate a speaker’s point of view, reasoning, and use of evidence and rhetoric.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Communicate using
consistent sounds,
words, and gestures
(e.g., try to mimic
words when
prompted, begin to
put two words
together in a
phrase).
Demonstrate active
listening strategies
(e.g., listen for
short periods of
time, begin to ask
questions).
Show
understanding and
respond to simple
directions and
requests (e.g., begin
to ask “how” and
“why” questions).
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL3: Ask and
answer questions in
order to seek help,
get information, or
clarify something
that is not
understood.
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL3: Ask and
answer questions in
order to seek help,
get information, or
clarify something
that is not
understood.
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL3: Ask and
answer questions
about what a
speaker says in
order to gather
additional
information or
clarify something
that is not
understood.
A. Comprehension
and Collaboration
SL3: Ask and
answer questions
about what a
speaker says in
order to clarify
comprehension,
gather additional
information, or
deepen
understanding of a
topic or issue.
C
ommunicate using
consistent sounds,
words, and gesture
s
(
e.g., try to mimic
words when
prompted, begin to
put two words
toget
h
er in a
p
h
ras
e
)
.
1 Year
D
emonstrate active
listening strategies
(
e.g., listen for
short periods of
time, begin to as
k
questions
)
.
2
Year
s
Sh
o
w
u
nderstanding and
respond to simple
d
irections an
d
r
eque
s
ts (e.g., begin
to ask “how” and
“w
h
y” questions)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Compre
h
ension
and Colla
b
oration
S
L3
:
A
sk an
d
answer questions in
o
rder to seek help,
get information, or
clarify something
t
h
at is not
u
n
d
erstoo
d
.
4
Year
s
A.
Compre
h
ension
and Colla
b
oration
S
L3
:
A
sk an
d
answer questions in
o
rder to seek help,
get information, or
clarify something
t
h
at is not
u
n
d
erstoo
d
.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Compre
h
ension
and Colla
b
oration
S
L3
:
A
sk an
d
answer questions
about what a
spea
k
er says in
o
rder to gather
a
dd
itional
inf
o
rmati
o
n
o
r
clarify something
t
h
at is not
u
n
d
erstoo
d
.
A.
Compre
h
ension
and Colla
b
oratio
n
S
L3
:
A
sk an
d
answer questions
about what a
spea
k
er says in
o
rder to clarif
y
compre
h
ension,
gather additional
information, or
d
eepen
u
nderstanding of a
topic or issue.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
ang
u
age & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
S
pea
k
ing & Listening
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Evaluate a s
p
eaker’s
p
oint of view, reasonin
g
, and use of evidence and rhetoric.

Appendix | 41
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Speaking & Listening
Standard: Present information, findings, and supporting evidence such that listeners can follow the line of reasoning and the
organization, development, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Communicate
using consistent
sounds, words, and
gestures (e.g., start
to put words
together in phrases
such as “ma-ma bye
bye”).
Use words and
some common
rules of speech to
express ideas and
thoughts (e.g., use
descriptive
language to tell you
what he wants).
Demonstrate active
listening skills (e.g.,
retell, and relate to
what has been
heard).
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL4: Describe
familiar people,
places, things, and
events with
modeling and
support.
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL4: Describe
familiar people,
places, things, and
events and, with
prompting and
support, provide
additional detail.
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL4: Describe
people, places,
things, and events
with relevant
details, expressing
ideas and feelings
clearly.
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL4: Tell a story or
recount an
experience with
appropriate facts
and relevant
descriptive details,
speaking audibly in
coherent sentences.
C
ommuni
c
ate
u
sing consistent
sounds, words, and
gestures
(
e.g., start
to put words
toget
h
er in p
h
rases
suc
h
as “ma
-
ma bye
b
ye”).
g
1 Year
Use words and
some common
rules of speech to
express ideas and
t
ho
u
g
h
ts (e.g., use
d
escriptive
language to tell you
w
h
at
h
e wants
)
.
py
2
Year
s
D
emonstrate active
listening s
k
ills (e.g.,
retell, and relate to
what has been
h
eard
)
.
pp p
3
Year
s
pp
4
Year
s
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L4
:
D
escri
b
e
f
amiliar people,
places, things, and
events wit
h
modeling and
suppor
t
.
Kindergarte
n
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L4
:
D
escri
b
e
f
amiliar people,
places, things, and
events and, with
prompting and
support, provide
a
dd
itional
d
etail.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L4
:
D
escri
b
e
people, places,
t
h
ing
s
, and events
wit
h
relevant
d
etails, expressing
ideas and feelings
clearly.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L4
:
T
ell a story or
re
c
oun
t
an
experience wit
h
appropriate facts
and relevant
d
escriptive details,
speaking audibly in
co
h
erent sentence
s
.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage &
L
iterac
y
S
tran
d:
S
pea
k
ing & Listening
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
P
resent information, findings, and supporting evidence such that listeners can follow the line of reasoning and the
organization, development, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience.

42 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Speaking & Listening
Standard: Make strategic use of digital media and visual displays of data to express information and enhance understanding of
presentations.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases to express
himself (e.g., begin
to participate in
songs and rhymes
by smiling,
clapping, or making
noise.
Recognize that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., paint some
lines across the
paper with broad
strokes and
movements, using a
few different
colors, and tell you
that it is a rainbow).
Use writing utensils
for scribble and
drawings (e.g.,
begin to draw
representations of
people and
objects).
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL5: Add drawings
or visual displays to
descriptions as
desired to provide
additional detail.
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL5: Add drawings
or visual displays to
descriptions as
desired to provide
additional detail.
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL5: Add drawings
or other visual
displays to
descriptions when
appropriate to
clarify ideas,
thoughts, and
feelings.
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL5: Create audio
recordings of
stories or poems;
add drawings or
other visual displays
to stories or
recounts of
experiences when
appropriate to
clarify ideas,
thoughts, and
feelings.
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases to express
h
imself (e.g., begin
to participate in
songs and rhymes
b
y smiling,
clapping, or ma
k
ing
n
ois
e
.
p
1 Year
R
ecognize t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(
e.g., paint some
lines across t
h
e
paper with broad
strokes an
d
movements, using a
f
ew different
colors, and tell you
that it is a rainbow
)
.
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
Use writing utensils
f
or scri
bb
le and
d
rawings (e.g.,
b
egin to dra
w
representations of
p
eople and
o
b
j
ects).
4
Year
s
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L5
:
A
dd drawings
o
r visual displays to
d
escriptions as
d
esired to provide
a
dd
itional
d
etai
l
.
Kindergarte
n
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L5
:
A
dd drawings
o
r visual displays to
d
escriptions as
d
esired to provide
a
dd
itional
d
etail.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L5
:
A
dd drawings
o
r ot
h
er visual
d
isplays to
d
escriptions when
appropriate to
clarify ideas,
thoughts, and
f
eelings.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L5
:
Create au
d
io
re
cordings of
stories or poems;
add drawings or
o
ther visual displays
to stories or
recounts of
experiences w
h
en
appropriate to
clarify ideas,
thoughts, and
f
eelings.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
S
pea
k
ing & Listening
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
M
ake strategic use of digital media and visual displays of data to express information and enhance understanding of
p
resentations.

Appendix | 43
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Speaking & Listening
Standard: Adapt speech to a variety of contexts and communicative tasks, demonstrating command of formal English when
indicated or appropriate.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Communicate using
consistent sounds,
words, and gestures
(e.g., get upset
when adults don’t
understand what he
says, begin to put
two words together
into a phrase).
Use words and
some common
rules of speech to
express ideas and
thoughts (e.g.,
speak clearly
enough to be
understood without
mumbling or
running sounds
together).
Use more
conventions of
speech when
speaking (e.g., not
pronounce all of
his words correctly,
but be easily
understood most of
the time).
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL6: With modeling
and support, speak
audibly and express
thoughts, feelings,
and ideas clearly.
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL6: Speak audibly
and express
thoughts, feelings,
and ideas clearly.
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL6: Produce
complete sentences
when appropriate
to task and
situation. (See
grade 1 Language
standards 1 and 3
on page 27 for
specific
expectations).
A. Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
SL6: Produce
complete sentences
when appropriate
to task and
situation in order to
provide requested
detail or
clarification. (See
grade 2 Language
standards 1 and 3
on pages 27 and 28
for specific
expectations).
C
ommunicate using
consistent sounds,
words, and gesture
s
(
e.g., ge
t
upse
t
when adults don’t
u
nderstand what he
s
ay
s
, begin to put
two words together
into a p
h
ras
e
)
.
pp p
1 Year
Use words and
some common
rules of speech to
express ideas and
t
h
oug
h
t
s
(
e.g.,
spea
k
clearl
y
enough to be
u
nderstood without
mumbling or
running sounds
toget
h
er)
.
p
2
Year
s
U
s
e m
or
e
conventions of
speec
h
w
h
en
spea
k
ing (e.g., not
pronounce all of
h
is words correctly,
b
ut be easil
y
u
n
d
erstoo
d
most of
t
h
e time
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L
6
:
With modeling
and support, spea
k
audibly and express
thoughts, feelings,
and ideas clearly.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L
6
:
S
peak audibl
y
and express
thoughts, feelings,
and ideas clearly.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L
6
:
P
ro
d
uce
complete sentences
w
h
en appropriate
to task an
d
situation.
(
See
grade 1
L
anguage
stan
d
ar
d
s 1 an
d
3
o
n page
2
7
f
or
f
f
specific
expectation
s
)
.
A.
P
resentation of
Knowledge and
I
d
ea
s
S
L
6
:
P
ro
d
uce
complete sentences
w
h
en appropriate
to task an
d
situation in or
d
er to
provide requested
d
etail or
clarification.
(
See
grade 2 Language
s
t
an
d
ar
d
s 1 an
d
3
o
n pages
2
7
an
d
2
8
fo
r specific
expectation
s
)
.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
S
pea
k
ing & Listening
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
dapt speech to a variety of contexts and communicative tasks, demonstrating command of formal English when
indicated or appropriate.

44 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Language
Standard: Demonstrate command of the conventions of Standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Start to understand
and use common
rules of speech
(e.g., use simple
gestures such as
shaking head for
“no” or waving
“bye bye”).
Use words and
some common
rules of speech to
express ideas and
thoughts (e.g., use
the words I, we, he,
and she in
sentences, use
some uncommon
plurals such as
“foots” instead of
“feet”).
Use more
conventions of
speech when
speaking (e.g., use
‘s’ at the end of
plurals and ‘ed’ for
past tense, use
plurals, pronouns
and possessive
words such as
“my” and “his”).
A. Conventions of
Standard English
L1: Demonstrate
beginning
understanding of the
conventions of
standard English
grammar and usage
when engaged in
literacy activities
(e.g. Interactive
Read Alouds, shared
reading, shared
writing,
developmentally
appropriate writing,
oral language
activities, etc.).
L1.a: Print upper
and lowercase letters
in first name.
L1.b: Use frequently
occurring nouns and
verbs.
L1.c: Develop
understanding of
A. Conventions of
Standard English
L1: Demonstrate
command of the
conventions of
standard English
grammar and usage
when writing or
speaking.
L1.a: Print many
upper and
lowercase letters.
L1.b: Use
frequently
occurring nouns
and verbs.
L1.c: Form regular
plural nouns orally
A. Conventions of
Standard English
L1: Demonstrate
command of the
conventions of
standard English
grammar and usage
when writing or
speaking.
L1.a: Print all
upper- and
lowercase letters.
L1.b: Use common,
proper, and
possessive nouns.
L1.c: Use singular
and plural nouns
A. Conventions of
Standard English
L1Demonstrate
command of the
conventions of
standard English
grammar and usage
when writing or
speaking.
L1.a: Use collective
nouns (e.g., group).
L1.b: Form and use
frequently
occurring irregular
plural nouns (e.g.,
feet, children, teeth,
mice, fish).
L1.c: Use reflexive
pronouns (e.g.,
S
tart to un
d
erstan
d
an
d
use common
rules of speech
(
e.g., use simple
gestures suc
h
as
shaking head for
“no
”
or waving
“bye bye”).
1 Year
Use words and
some common
rules of speech to
express ideas and
t
h
oug
h
ts (e.g., use
t
h
e wor
d
s I, we, he,
an
d
she in
sen
t
ences, use
some uncommon
plurals suc
h
as
“foots” instea
d
of
“feet”
)
.
2
Year
s
Use more
conventions of
speec
h
w
h
en
spea
k
ing (e.g., use
‘s’ at the en
d
of
plurals and ‘ed’ for
pas
t
t
ense, use
plurals, pronouns
and possessive
words such as
“my” and “his”).
3
Year
s
A.
Conventions of
S
tandard Englis
h
L1
:
D
emonstrate
b
eginning
u
nderstanding of the
conventions of
standard English
grammar and usage
when engaged in
literacy activities
(
e.g. Interactive
R
ead Alouds, shared
reading, shared
writing,
d
evelo
p
mentall
y
appropriate writing,
o
ral language
activities, etc.
)
.
L
1
.
a
:
P
rint upper
and lowercase letters
in first name.
L
1.
b
:
Use frequentl
y
o
ccurring nouns and
ver
bs
.
L
1.
c
:
D
evelop
u
nderstanding of
4
Year
s
A.
Conventions of
S
tandard Englis
h
L
1
:
D
emonstrat
e
comman
d
of the
conventions of
standard English
grammar and usage
w
h
en writing or
spea
k
ing
.
L
1
.
a
:
P
rint man
y
u
pper and
lowercase letters.
L
1.
b
:
Use
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring nouns
and ver
b
s.
L
1.
c
:
F
orm regular
plural nouns orall
y
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Conventions of
S
tandard Englis
h
L1
:
D
emonstrate
comman
d
of the
conventions of
standard English
grammar and usage
w
h
en writing or
spea
k
ing.
L
1
.
a
:
P
rint all
u
pper
-
an
d
lowercase letter
s
.
L
1.
b
:
Use common,
proper, and
possessive nouns.
L
1.
c
:
Use singular
and plural nouns
A.
Conventions of
S
tandard Englis
h
L1
D
emonstrate
comman
d
of the
conventions of
standard English
g
r
amma
r
and usage
w
h
en writing or
spea
k
ing.
L
1
.
a
:
Use collective
n
ouns (e.g., group
)
.
L
1.
b
:
Gra
d
e
2
F
orm an
d
use
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring irregular
plural nouns (e.g.,
f
eet, children, teeth,
mice, fish
)
.
L
1.
c
:
Use reflexive
pronouns
(
e.g.,
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
L
anguag
e
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
D
emonstrate command of the conventions of Standard En
g
lish
g
rammar and usa
g
e when writin
g
or s
p
eakin
g
.

Appendix | 45
M
singular and plural
nouns (e.g., dog
means one dog;
dogs means more
than one dog).
L1.d: Understand
and begin to use
question words (e.g.,
interrogatives such
as who, what, where,
when, why, how).
L1.e: Gain exposure
to the most
frequently occurring
prepositions (e.g.,
to, from, in, out, on,
off, for, of, by,
with).
L1.f: Produce
complete sentences
in shared language
activities.
by adding /s/ or
/es/ (e.g., dog,
dogs; wish, wishes).
L1.d: Understand
and use question
words
(interrogatives)
(e.g., who, what
where, when, why,
how).
L1.e: Use the most
frequently
occurring
prepositions (e.g.,
to, from, in, out,
on, off, for, of, by,
with).
L1.f: Produce and
expand complete
sentences in shared
language activities.
with matching
verbs in basic
sentences (e.g., He
hops, we hop).
L1.d: Use personal,
possessive, and
indefinite pronouns
(e.g., I, me, my;
they them their;
anyone,
everything).
L1.e: Use verbs to
convey a sense of
past, present, and
future (e.g.,
Yesterday I walked
home; today I walk
home; tomorrow I
will walk home).
L1.f: Use frequently
occurring
adjectives.
myself, ourselves).
L1.d: Form and use
the past tense of
frequently
occurring irregular
verbs (e.g., sat, hid,
told).
L1.e: Use adjectives
and adverbs, and
choose between
them depending on
what is to be
modified.
L1.f: Produce,
expand, and
rearrange complete
simple and
compound
sentences (e.g., The
boy watched the
movie; The little
boy watched the
movie; The action
movie was watched
by the little boy).
singular and plural
n
ouns (e.g., dog
means one dog;
d
ogs means more
than one dog).
L
1.
d
:
Un
d
erstan
d
and begin to use
question words (e.g.,
interrogatives suc
h
as w
h
o, w
h
at, w
h
ere,
w
h
en, w
h
y,
h
ow).
L
1
.e
:
Gain exposure
to t
h
e mo
s
t
f
requently occurring
prepositions (e.g.,
to, from, in, out, on,
o
ff, for, of, by,
wit
h)
.
L1.f
:
f
f
P
ro
d
uce
complete sentences
in shared language
activities.
b
y adding
/
s
/
or
/
es
/
(e.g., dog,
d
ogs; wish, wishes).
L
1.
d
:
Un
d
erstan
d
and use question
words
(
interrogatives
)
(
e.g., w
h
o, w
h
at
w
h
ere, w
h
en, w
h
y,
h
ow
)
.
L
1
.e
:
Use t
h
e most
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring
prepositions (e.g.,
to, from, in, out,
o
n, off, for, of, by,
wit
h)
.
L1.f
:
f
f
P
ro
d
uce an
d
expand complete
sentences in share
d
language activities.
wit
h
matc
h
ing
ver
b
s in
b
asic
sentences
(
e.g., He
h
ops,
w
e
h
op).
L
1.
d
:
Use personal,
possessive, and
indefinite pronouns
(
e.g., I, me, my;
t
h
ey t
h
em t
h
eir;
anyone,
everyt
h
ing).
L
1
.e
:
Use ver
b
s to
convey a sense of
past, present, and
f
uture (e.g.,
Yesterday I walked
h
ome;
t
o
day I wal
k
h
ome;
t
o
morrow I
will wal
k
home
)
.
L1.f
:
f
f
Use frequentl
y
o
ccurring
ad
j
ectives.
myself, ourselves).
L
1.
d
:
F
orm an
d
use
the past tense of
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring irregular
verbs (e.g., sat, hid,
told
)
.
L
1
.e
:
Use ad
j
ectives
and adverbs, and
choose between
them depending on
what is to be
mo
d
ifie
d
.
L1.f
:
f
f
P
roduce,
expand, and
rearrange complete
simple and
compound
sentences (e.g., T
h
e
b
oy watched the
movie; T
h
e little
b
oy watched the
movie; T
h
e action
movie was watched
b
y the little boy).
continued on next page
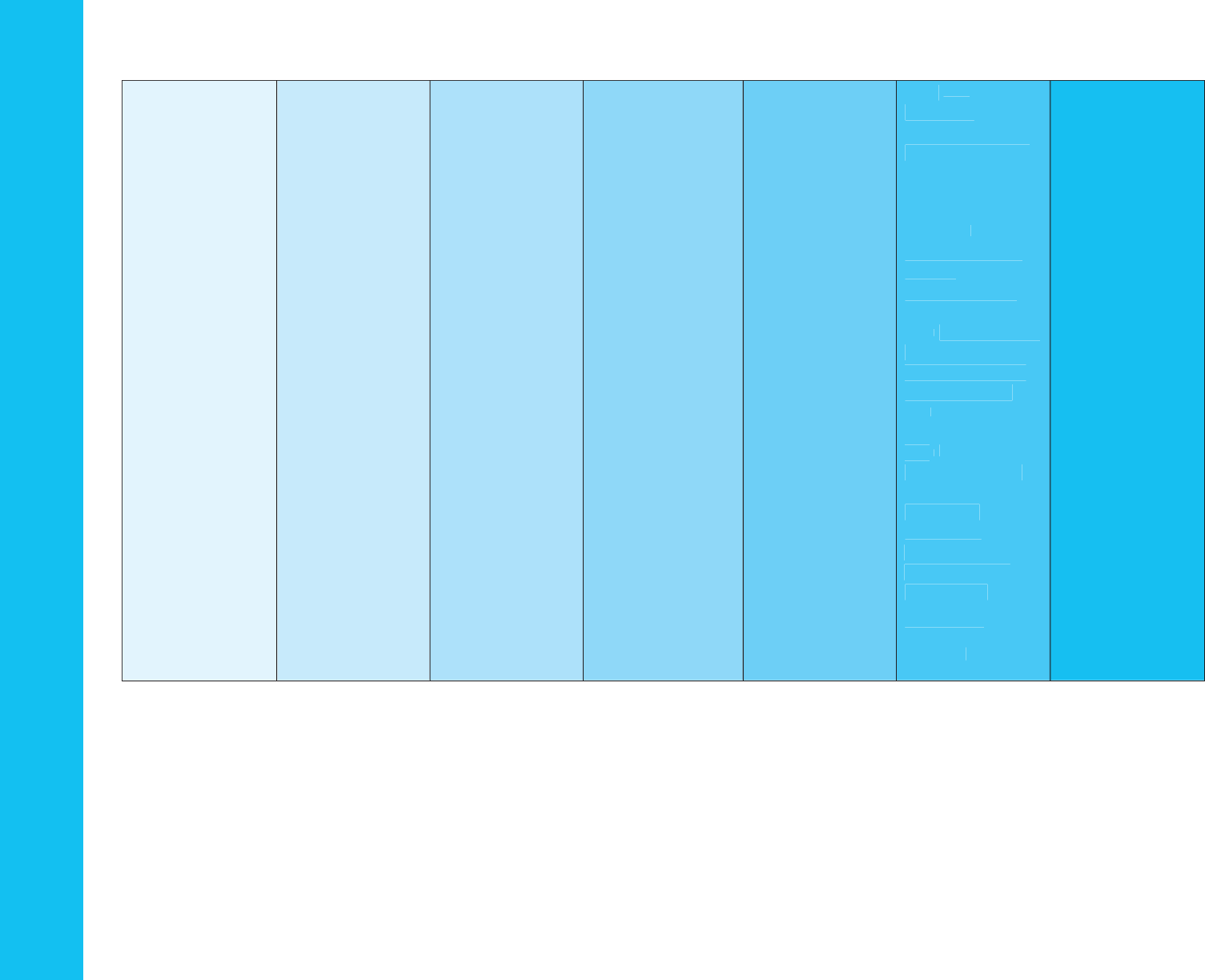
46 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
L1.g: Use
frequently
occurring
conjunctions (e.g.,
and, but, or, so
because).
L1.h: Use
determiners (e.g.,
articles,
demonstratives).
L1.i: Use frequently
occurring
prepositions (e.g.,
during, beyond,
toward).
L1.j: Produce and
expand complete
simple and
compound
declarative,
interrogative,
imperative, and
exclamatory
sentence in
response to
prompts.
L
1.g: Use
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring
con
j
unctions (e.g.,
and, but, or, so
b
ecause
)
.
L
1
.h
:
Use
d
eterminers (e.g.,
articles,
d
emonstratives
)
.
L
1
.
i
:
Use frequentl
y
o
ccurring
prepositions (e.g.,
d
uring, beyond,
t
o
w
ard
)
.
L
1.
j
:
P
ro
d
uce an
d
expand complete
simple and
compound
d
eclarative,
interrogative,
imperative, and
exclamator
y
sentence in
response
t
o
promp
t
s.
continued from previous page

Appendix | 47
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Language
Standard: Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(e.g., explore using
markers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write).
Recognize that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., pretend to
write a letter by
scribbling on a
paper and
“reading” it out
loud).
Begin to develop
writing skills by
recognizing that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., begin to
control scribbles,
perhaps telling
caregiver what they
say).
L2 Gain exposure to
conventions of
standard English
capitalization,
punctuation, and
spelling during
shared reading and
writing experiences.
L2.a Recognize that
their name begins
with a capital letter.
L2.b Demonstrate
awareness of name
and function of end
punctuation (e.g.,
period, question
mark and
exclamation point).
L2.c Use letter-like
shapes, symbols,
letters, and words to
convey meaning.
L2.d Develop fine
motor skills
necessary to control
L2 Demonstrate
command of the
conventions of
standard English
capitalization,
punctuation, and
spelling when
writing.
L2.a Capitalize the
first word in a
sentence and the
pronoun I.
L2.b Recognize and
name end
punctuation.
L2.c Write a letter
or letters for most
consonant and
short-vowel sounds
(phonemes).
L2.d Spell simple
words phonetically,
drawing on
L2 Demonstrate
command of the
conventions of
standard English
capitalization,
punctuation, and
spelling when
writing.
L2.a Capitalize
dates and names of
people.
L2.b Use end
punctuation for
sentences.
L2.c Use commas
in dates and to
separate single
words in a series.
L2.d Use
conventional
spelling for words
Demonstrate
command of the
conventions of
standard English
capitalization,
punctuation, and
spelling when
writing.
L2.a Capitalize
holidays, product
names, and
geographic names.
L2.b Use commas
in greetings and
closings of letters.
L2.c Use an
apostrophe to form
contractions and
frequently
occurring
possessives.
L2.d Generalize
learned spelling
patterns when
1 Year
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating
(
e.g., explore
u
sing
mar
k
ers, crayons,
chalk to draw and
write
)
.
2
Year
s
R
ecognize t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(
e.g., pretend to
write a letter b
y
scribbling on a
paper and
“reading” it out
loud
)
.
3
Year
s
Begin to develop
writing skills b
y
recogni
z
ing t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(
e.g., begin to
control scribbles,
per
h
aps telling
caregiver w
h
at t
h
e
y
say
)
.
g
4
Year
s
L
2 Gain exposure to
conventions of
standard English
capitalization,
punctuation, and
spelling during
shared reading and
writing experiences.
L
2.a Recognize t
h
at
their name begins
wit
h
a capital letter.
L
2.
b
Demonstrate
awareness of name
an
d
function of en
d
punctuation (e.g.,
period, question
mark an
d
exclamation point).
L
2.c Use letter
-
li
k
e
s
h
apes,
s
ymbols,
letters, and words to
convey meaning.
L
2.d Develop fine
motor s
k
ills
n
ecessary to control
pp
Kindergarte
n
L
2
D
emonstrate
comman
d
of the
conventions of
standard English
capitalization,
punctuation, and
spelling w
h
en
writing.
L
2.a
C
a
p
italize t
h
e
f
irst word in a
sentence an
d
the
pronoun I.
L
2.b Recognize and
n
ame en
d
punctuation.
L
2.c Write a letter
o
r letters for most
consonant an
d
s
h
ort
-
vowel sounds
(
p
h
onemes).
L
2.d Spell simple
words phonetically,
d
rawing on
pg
Gra
d
e
1
L
2
D
emonstrate
comman
d
of the
conventions of
standard English
capitalization,
punctuation, and
spelling w
h
en
writing.
L
2.a Capitalize
d
ates an
d
names of
people.
L
2.
b
Use end
punctuation for
sen
t
ences.
L
2.c Use commas
in
d
ates an
d
to
separate single
words in a series.
L
2.
d
Use
conventional
spelling for words
gg
Gra
d
e
2
D
emonstrate
comman
d
of the
conventions of
standard English
capitalization,
punctuation, and
spelling w
h
en
writing.
L
2.a Capitalize
h
olidays, product
n
ames, and
geograp
h
ic names.
L
2.
b
Use commas
in greetings and
closings of letters.
L
2.c Use an
apostrophe to form
contractions an
d
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring
possessives.
L
2.
d
Generalize
learned spelling
patterns w
h
en
g
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
L
anguag
e
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing.
pg
continued on next page

48 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
and sustain
handwriting.
knowledge of
sound-letter
relationships.
L2.e Produce
handwriting that is
legible to the
audience.
with common
spelling patterns
and for frequently
occurring irregular
words
L2.e Spell untaught
words phonetically,
drawing on
phonemic
awareness and
spelling
conventions.
writing words (e.g.,
cage badge; boy
boil).
L2.e Consult
reference materials,
including beginning
dictionaries, as
needed to check
and correct
spellings.
an
d
sustain
h
andwriting.
knowledge of
soun
d
-
letter
relations
h
ips.
L
2.e Pro
d
uce
h
andwriting that is
legible to the
au
d
ience.
wit
h
common
spelling patterns
and for frequentl
y
o
ccurring irregular
word
s
L
2.e Spell untaug
h
t
wor
d
s p
h
onetically,
d
rawing on
p
h
onemic
awareness and
spelling
conventions.
writing words (e.g.,
cage badge; bo
y
b
oil
)
.
L
2.e Consult
reference materials,
i
ncluding beginning
d
ictionaries, as
n
ee
d
e
d
to chec
k
an
d
correct
s
p
ellin
g
s.
continued from previous page

Appendix | 49
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Language
Standard: Apply knowledge of language to understand how language functions in different contexts, to make effective choices for
meaning or style, and to comprehend more fully when reading or listening.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
L3: (Begins in
grade 2.)
L3: (Begins in grade
2.)
L3: (Begins in
grade 2.)
L3: (Begins in
grade 2.)
A. Knowledge of
Language
L3: Use knowledge
of language and its
conventions when
writing, speaking,
reading, or
listening.
L3.a: Compare
formal and
informal uses of
English.
gy
1 Year
p
2
Year
s
y
3
Year
s
L
3
:
(
Begins in
grade 2.)
gg
4
Year
s
L
3
:
(
Begins in grade
2
.
)
Kindergarte
n
L
3
:
(
Begins in
grade 2.)
Gra
d
e
1
L
3
:
(
Begins in
grade 2.)
Gra
d
e
2
A.
Knowledge of
L
anguag
e
L
3
:
Use knowledge
o
f language and its
conventions w
h
en
writing, spea
k
ing,
reading, or
listening.
L
3
.
a
:
C
ompare
f
ormal an
d
informal uses of
Englis
h
.
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
L
anguag
e
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
pply knowledge of language to understand how language functions in different contexts, to make effective choices for
meaning or style, and to comprehend more fully when reading or listening.

50 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Language
Standard: Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases by using context clues, analyzing
meaningful word parts, and consulting general and specialized reference materials, as appropriate.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases to express
himself (e.g., learn
new words and
phrases from those
frequently used by
the adults and
children around
him).
Develop
vocabulary,
language usage and
some conventions
of speech (e.g.,
name an increasing
number of objects
in the books read,
and describe
actions, repeat
words heard in the
environment).
Expand vocabulary
and language usage
(e.g., use words to
describe the
purpose and
function of objects,
learn the names of
new objects).
A. Vocabulary
Acquisition and Use
L4: Determine or
clarify the meaning
of unknown words
and phrases based
on pre-kindergarten
reading and content.
A. Vocabulary
Acquisition and
Use
L4: Determine or
clarify the meaning
of unknown and
multiple meaning
words and phrases
based on
kindergarten
reading and
content.
L4.a: Identify new
meanings for
familiar words and
apply them
accurately (e.g.,
knowing duck is a
verb and learning
the verb to duck).
L4.b: Use the most
frequently
occurring
inflections and
affixes (e.g., -ed, -s,
re-, un-, pre-, -ful, -
less) as a clue to the
meaning of an
A. Vocabulary
Acquisition and
Use
L4: Determiner or
clarify the meaning
of unknown and
multiple-meaning
words and phrases
based on grade 1
reading and
context, choosing
flexibly from an
array of strategies.
L4.a: Use sentence-
level context as a
clue to the meaning
of a word or
phrase.
L4.b: Use
frequently
occurring affixes as
a clue to the
meaning of a word.
A. Vocabulary
Acquisition and
Use
L4: Determine or
clarify the meaning
of unknown and
multiple-meaning
words and phrases
based on grade 2
reading and
content, choosing
flexibly from an
array of strategies.
L4.a: Use sentence-
level context as a
clue to the meaning
of a word or
phrase.
L4.b: Determine
the meaning of the
new word formed
when a known
prefix is added to a
known word (e.g.,
happy/unhappy,
tell/retell).
1 Year
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases to express
h
imself
(
e.g., learn
n
ew words and
phrases from those
f
requently used b
y
the a
d
ults an
d
chil
d
ren aroun
d
h
im
)
.
2
Year
s
D
evelop
vocabulary,
language usage and
some conventions
o
f speec
h
(
e.g.,
n
ame an increasing
n
umber of ob
j
ects
in the books read,
and descri
b
e
actions, repea
t
words heard in the
environment
)
.
3
Year
s
Expand vocabular
y
and language usage
(
e.g., use words to
d
escri
b
e the
purpose and
fu
n
ction of ob
j
ects,
learn the names of
n
ew ob
j
ects).
4
Yea
rs
A.
V
ocabular
y
A
cquisition and Us
e
L
4
:
D
etermine
o
r
clarify the meaning
o
f unknown words
and phrases based
o
n pr
e
-
kindergarten
reading and content.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Vocabular
y
A
cquisition and
Use
L
4
:
D
etermine
o
r
clarify the meaning
o
f unknown and
multiple meaning
words and phrases
b
ased on
kindergarten
reading and
c
on
t
en
t
.
L
4
.
a
:
Identify ne
w
meanings for
f
amiliar words and
apply t
h
em
accurately (e.g.,
knowing duck is a
verb and learnin
g
the verb to duck
)
.
L
4.
b
:
Use t
h
e most
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring
inflections an
d
affixes (e.g.,
-
ed,
-
s
,
re
-
, un
-
, pr
e
-
,
-
f
ul,
-
less
)
as a clue to t
h
e
meaning of an
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Vocabular
y
A
cquisition and
Use
L
4
:
D
eterminer
o
r
clarify the meaning
o
f unknown and
multipl
e
-
meaning
words and phrases
b
ased on grade 1
reading and
context, c
h
oosing
f
lexibly from an
array of strategies.
L
4
.
a
:
Use sentenc
e
-
level context as a
clue to t
h
e meaning
o
f a word or
p
h
rase.
L
4
.b
:
Use
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring affixes as
a
c
lue to t
h
e
meaning of a word.
A
. Vocabular
y
A
cquisition and
Use
L
4
:
D
etermine
o
r
clarify the meaning
o
f unknown and
multipl
e
-
meaning
words and phrases
b
ased on grade 2
reading and
content, c
h
oosing
f
lexibly from an
array of strategies.
L
4
.
a
:
Use sentenc
e
-
level context as a
clue to t
h
e meaning
o
f a word or
p
h
rase.
L
4.
b
:
D
etermine
the meaning of the
n
ew word formed
when a
k
nown
prefix is added to a
known word (e.g.,
h
appy
/
unhappy,
tell
/
retell
)
.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
L
anguag
e
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
D
etermine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multipl
e
-
meaning words and phrases by using context clues, analyzing
meaningful word parts, and consulting general and specialized reference materials, as appropriate.
continued on next page

Appendix | 51
M
unknown word.
L4.c: Identify
frequently
occurring root
words (e.g., look)
and their
inflectional forms
(e.g., looks, looked,
looking).
L4.c: Use a known
root word as a clue
to the meaning of
an unknown word
with the same root
(e.g., addition,
additional).
L4.d: Use
knowledge of the
meaning of
individual words to
predict the meaning
of compound
words (e.g.,
birdhouse,
lighthouse,
housefly; bookshelf,
notebook,
bookmark).
L4.e: Use glossaries
and beginning
dictionaries, both
print and digital, to
determine or clarify
the meaning of
words and phrases.
u
nknown word.
L
4.
c
:
Identif
y
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring root
words (e.g., look)
an
d
their
inflectional forms
(
e.g., looks, looked,
loo
k
ing).
L
4.
c
:
Use a
k
nown
root word as a clue
to the meaning of
an unknown word
wit
h
t
h
e same root
(
e.g., addition,
additional
)
.
L
4
.
d
:
Use
knowledge of the
meaning of
individual words to
predict the meaning
o
f compound
words (e.g.,
b
irdhouse,
lig
h
t
h
ouse,
h
ousefly; bookshelf,
n
otebook,
b
ookmark
)
.
L
4
.e
:
Use glossaries
and beginning
d
ictionaries, both
print and digital, to
d
etermine or clarif
y
the meaning of
words and phrases.
continued from previous page

52 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Language
Standard: Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
L5: With modeling
and support from
adults, explore word
relationships and
nuances in word
meanings.
L5.a: With modeling
and support, sort
common objects
into categories (e.g.,
shapes, foods) to
gain a sense of the
concepts the
categories represent.
L5.b: With modeling
and support,
demonstrate
understanding of
frequently occurring
verbs and adjectives
by relating them to
their opposites
(antonyms).
L5.c: Identify real-
life connections
between words and
their use (e.g., note
objects in classroom
that are small).
L5: With guidance
and support from
adults, explore
word relationships
and nuances in
word meanings.
L5.a: Sort common
objects into
categories (e.g.,
shapes, foods) to
gain a sense of the
concepts the
categories
represent.
L5.b: Demonstrate
understanding of
frequently
occurring verbs and
adjectives by
relating them to
their opposites
(antonyms).
L5.c: Identify real-
life connections
between words and
their use (e.g., note
places at school
that are colorful).
L5: With guidance
and support from
adults, demonstrate
understanding of
word relationships
and nuances in
word meanings.
L5.a: Sort words
into categories (e.g.,
colors, clothing) to
gain a sense of the
concepts the
categories
represent.
L5.b: Define words
by category and by
one or more key
attributes (e.g., a
duck is a bird that
swims; a tiger is a
large cat with
stripes).
L5.c: Identify real-
life connections
between words and
their use (e.g., note
places at home that
are cozy).
L5: Demonstrate
understanding of
word relationships
and nuances in
word meanings.
L5.a: Identify real-
life connections
between words and
their use (e.g.,
describe foods that
are spicy or juicy).
L5.b: Distinguish
shades of meaning
among closely
related verbs (e.g.,
toss, throw, hurl)
and closely related
adjectives (e.g.,
thin, slender,
skinny, scrawny).
L
5
:
With modeling
and support from
adults, explore word
relationships and
n
uances in word
meanings.
L
5.a
:
With modeling
and support, sort
common ob
j
ects
into categories (e.g.,
shapes, foods) to
gain a sense of the
concepts t
h
e
categories represent.
L
5.
b
:
With modeling
and support,
d
emonstrate
u
nderstanding of
f
requently occurring
verbs and ad
j
ectives
b
y relating t
h
em to
t
h
eir opposites
(
antonyms
)
.
L
5.c
:
Identify rea
l
-
life connections
b
etween words and
t
h
eir use (e.g., note
o
b
j
ects in classroom
t
h
at are small
)
.
g
L
5
:
With guidance
and support from
adults, explore
word relationships
an
d
nuances in
word meaning
s
.
L
5.a
:
S
ort common
o
b
j
ects into
categories (e.g.,
shapes, foods) to
gain a sense of the
concepts t
h
e
categories
represen
t
.
L
5.
b
:
D
emonstrate
u
nderstanding of
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring verbs and
ad
j
ectives b
y
relating t
h
em to
t
h
eir opposites
(
antonyms
)
.
L
5.c
:
Identify rea
l
-
life connections
b
etween words and
t
h
eir use (e.g., note
places at sc
h
ool
that are colorful
)
.
L
5
:
With guidance
and support from
adults, demonstrate
u
nderstanding of
word relationships
an
d
nuances in
word meanings.
L
5.a
:
S
ort words
into categories (e.g.,
colors, clot
h
ing) to
gain a sense of the
concepts t
h
e
categories
represen
t
.
L
5.
b
:
D
efine words
b
y category and b
y
o
ne or more
k
e
y
attributes (e.g., a
d
uck is a
b
ird that
swims; a tiger is a
large cat wit
h
stripes
)
.
L
5.c
:
Identify rea
l
-
life connections
b
etween words and
t
h
eir use (e.g., note
places at
h
ome t
h
at
are cozy
)
.
L
5
:
D
emonstrate
u
n
d
erstan
d
i
n
g of
word relationships
an
d
nuances in
word meanings.
L
5.a
:
Identify rea
l
-
life connections
b
etween words and
t
h
eir use (e.g.,
d
escri
b
e foods that
are spicy or
j
uicy
)
.
L
5.
b
:
D
istinguis
h
shades of meaning
among closel
y
related verbs (e.g.,
toss, t
h
row,
h
url
)
and closely related
ad
j
ectives (e.g.,
thin, slender,
s
k
inny, scrawny).
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
L
anguag
e
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
D
emonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
Kinder
g
arte
n
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
continued on next page
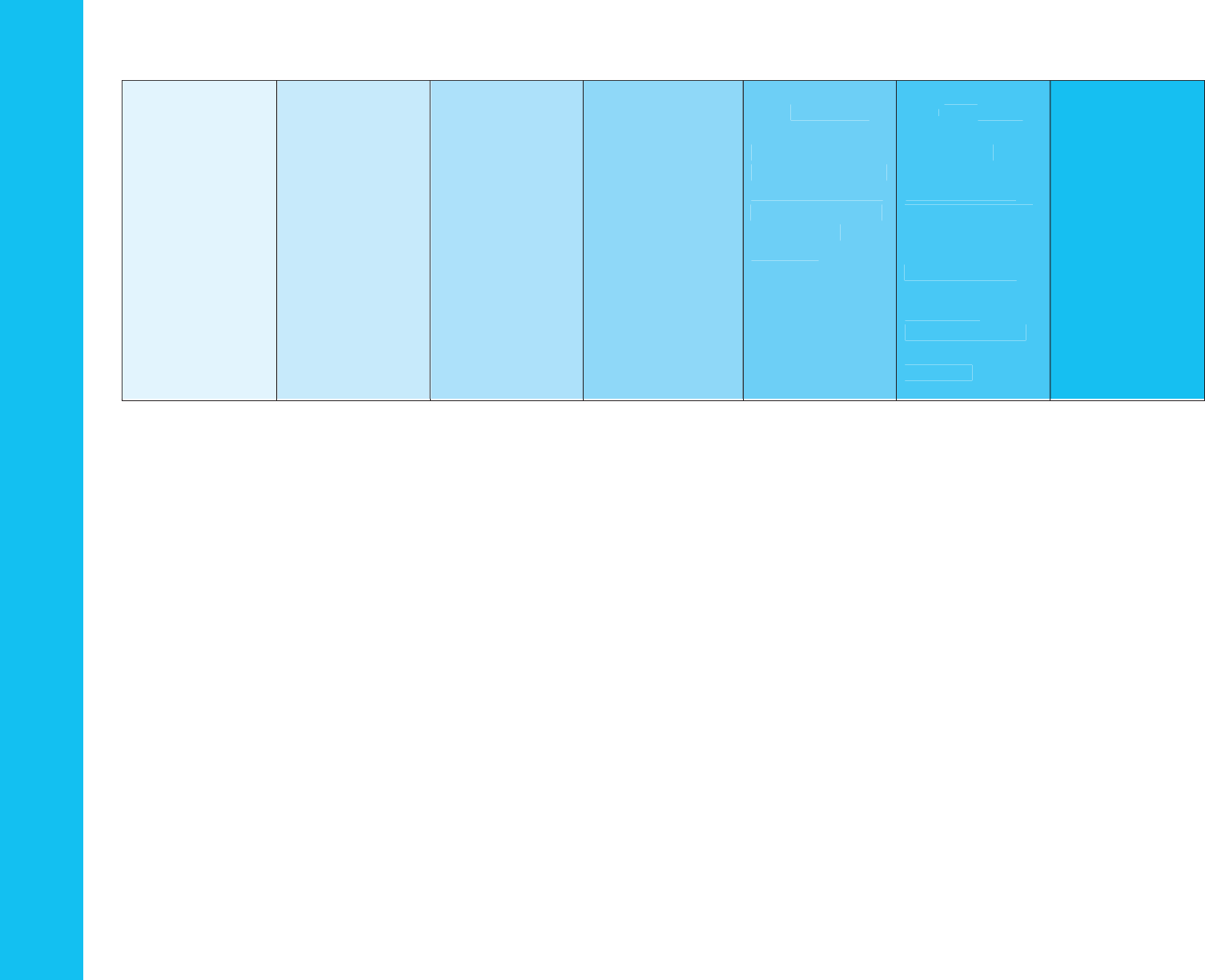

Appendix | 53
M
L5.d: Distinguish
shades of meaning
among verbs
describing the same
general action (e.g.,
walk, strut, prance)
by acting out
meanings.
L5.d: Distinguish
shades of meaning
among verbs
differing in manner
(e.g., look, peek,
glance, stare, glare,
scowl) and
adjectives differing
in intensity (e.g.,
large, gigantic) by
defining or
choosing them or
by acting out the
meanings.
L
5.
d
:
D
istinguis
h
shades of meaning
among verbs
d
escribing the same
general action (e.g.,
wal
k
, strut, prance)
b
y acting out
meanings.
L
5.
d
:
D
isti
n
guis
h
shades of meaning
among verbs
d
iffering in manner
(
e.g., loo
k
, pee
k
,
glance, stare, glare,
scowl
)
and
ad
j
ectives differing
in intensity (e.g.,
large, gigantic) b
y
d
efining or
c
h
oosing t
h
em or
b
y acting out the
meanings.
continued from previous page

54 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Language & Literacy
Strand: Language
Standard: Acquire and use accurately a range of general academic and domain-specific words and phrases sufficient for reading,
writing, speaking, and listening at the college and career readiness level; demonstrate independence in gathering vocabulary
knowledge when encountering an unknown term important to comprehension or expression.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Demonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension by
using words and
phrases to express
himself (e.g., learn
new words and
phrases from those
frequently used by
the adults and
children around
him).
Develop
vocabulary,
language usage and
some conventions
of speech (e.g.,
name an increasing
number of objects
in the books read,
and describe
actions, repeat
words heard in the
environment).
Expand vocabulary
and language usage
(e.g., use words to
describe the
purpose and
function of objects,
learn the names of
new objects).
L6: Use words and
phrases acquired
through
conversation, being
read to, and
responding to text.
L6: Use words and
phrases acquired
through
conversation,
reading and being
read to, and
responding to text.
L6: Use words and
phrases acquired
through
conversations,
reading and being
read to, and
responding to texts,
including using
frequently
occurring
conjunctions to
signal simple
relationships (e.g.,
because).
L6: Use words and
phrases acquired
through
conversations,
reading and being
read to, and
responding to texts,
including using
adjectives and
adverbs to describe
(e.g., When other
kids are happy that
makes me happy).
D
emonstrate
increasing
vocabulary and
comprehension b
y
u
sing words and
p
h
rases to express
h
imself (e.g., learn
n
ew words and
phrases from those
f
requently used b
y
the a
d
ults an
d
chil
d
ren aroun
d
h
im
)
.
g
1 Year
D
evelop
vocabulary,
language usag
e
an
d
some conventions
o
f speech (e.g.,
n
ame an increasing
n
umber of ob
j
ects
in the books read,
and descri
b
e
actions, repeat
words heard in the
environment
)
.
g
2
Year
s
Expand vocabular
y
and language usage
(
e.g., use words to
d
escri
b
e the
purpose and
f
unction of ob
j
ec
t
s,
learn the names of
n
ew ob
j
ects).
p
3
Year
s
L6
:
Use words and
phrases acquired
t
h
roug
h
conversation, being
read to, and
responding to text.
p
4
Year
s
p
Kindergarte
n
L6
:
Use words and
phrases acquired
t
h
roug
h
conversation,
reading and being
read to, and
responding to text.
Gra
d
e
1
L6
:
Use w
o
r
d
s an
d
phrases acquired
t
h
roug
h
conversations,
reading and being
read to, and
responding to texts,
including using
f
requentl
y
o
ccurring
con
j
unctions to
signal simple
relations
h
ips (e.g.,
b
ecause
)
.
L6
:
Use words and
phrases acquired
t
h
roug
h
conversations,
reading and being
read to, and
responding to texts,
including using
ad
j
ectives and
Gra
d
e
2
adver
b
s to descri
b
e
(
e.g., W
h
en ot
h
er
kids are happy that
ma
k
es me happy).
D
o
main
:
L
anguage & Literac
y
S
tran
d:
L
anguag
e
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
cquire and use accurately a range of general academic and domai
n
-
specific words and phrases sufficient for reading,
writing, speaking, and listening at the college and career readiness level; demonstrate independence in gathering vocabular
y
knowledge when encountering an unknown term important to comprehension or expression.

Appendix | 55
M
Domain: Mathematics
Strand: Counting and Cardinality
Standard: Know number names and the count sequence.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Show beginning
interest in quantity
and number
relationships (e.g.,
will give two
crackers when
asked, “Can I have
two crackers?”).
Show beginning
interest in numerals
and counting (e.g.,
recognize and
name the numerals
in a counting
book).
A. Know Number
Names and the
Count Sequence
PK.CC.1: Count
verbally to ten by
ones.
PK.CC.2: Recognize
the concept of just
after or just before a
given number in the
counting sequence
up to ten.
PK.CC.3: Identify
written numerals 0-
10.
A. Know Number
Names and the
Count Sequence
K.CC.1: Count to
100 by ones and by
tens.
K.CC.2 Count
forward beginning
from a given
number within the
known sequence
(instead of having
to begin at one).
K.CC.3: Write
numbers from zero
to twenty.
Represent a
number of objects
with a written
numeral 0-20 (with
0 representing a
count of no
objects).
1 Year
S
how beginning
interest in quantit
y
and number
relations
h
ip
s
(
e.g.,
will give two
crac
k
ers when
asked, “Can I have
two crac
k
ers?”
)
.
2
Year
s
S
how beginning
interest in numera
l
s
an
d
counting
(
e.g.,
recognize and
n
ame t
h
e numerals
in a counting
b
ook
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Know Number
Names and the
Count Sequenc
e
P
K
.
CC.1
:
Co
unt
verbally to
t
en
by
o
nes.
P
K
.
CC.2
:
R
ecognize
the concept of
j
ust
after or
j
ust before a
given number in the
counting sequence
u
p
t
o
t
e
n
.
P
K
.
CC.
3
:
I
dentif
y
written numera
l
s
0
-
1
0
.
4
Year
s
A.
Know Number
Names and the
Count Sequenc
e
K
.CC.1
:
Co
unt t
o
100 by ones and b
y
t
ens.
K
.CC.
2
Co
unt
f
orward b
e
ginnin
g
f
rom a given
n
umber within the
k
nown sequence
(
instead of havin
g
to begin at
o
n
e
)
.
K
.CC.
3
:
Kindergarten
Write
n
umbers from
z
er
o
to
t
wen
ty
.
R
epresent a
n
umber of ob
j
ects
wit
h
a written
n
umeral
0
-
2
0
(
wit
h
0 representing a
c
ount of no
o
b
j
ects).
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
M
at
h
ematic
s
S
tran
d:
Counting and Cardinalit
y
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Know number names and the coun
t
sequence.

56 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Mathematics
Strand: Counting and Cardinality
Standard: Count to tell the number of objects.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Show beginning
interest in quantity
and number
relationships (e.g.,
complain that a
friend has more
orange slices than
he does).
Show beginning
interest in numerals
and counting (e.g.,
proudly show that
he can count three
objects, count the
name cards to see if
there is room for
him in a given play
center where only
four children may
play at a time).
A. Count to Tell the
Number of Objects
PK.CC4:
Understand the
relationship between
numbers and
quantities to five,
then to ten; connect
counting to
cardinality.
PK.CC.4a: When
counting objects, say
the number names
in the standard
order, pairing each
object with one and
only one number
name.
PK.CC.4b:
Recognize that the
last number name
said tells the number
of objects counted.
A. Count to Tell
the Number of
Objects
K.CC.4:
Understand the
relationship
between numbers
and quantities;
connect counting
to cardinality.
K.CC.4a: When
counting objects,
say the number
names in the
standard order,
pairing each object
with one and only
one number name
and each number
name with one and
only one object.
K.CC.4b:
Understand that
the last number
name said tells the
number of objects
counted. The
number of objects
is the same
1 Year
S
how beginning
interest in quantit
y
and num
b
er
relations
h
ips (e.g.,
complain t
h
at a
f
rien
d
has m
or
e
o
range slices t
h
an
h
e does
)
.
2
Year
s
S
how beginning
interest in numerals
and counting
(
e.g.,
proudly show that
h
e
c
an
c
ount t
h
ree
o
b
j
ects, count the
n
ame car
d
s to see if
there is room for
h
im in a given pla
y
center w
h
ere onl
y
f
our children ma
y
play at a time)
.
j
3
Year
s
A.
Co
unt t
o
Tell t
h
e
Number of O
bj
ec
ts
P
K
.CC
4:
Un
d
erstan
d
the
relationship between
n
um
b
ers and
quantities to
f
iv
e
,
t
h
en t
o
t
e
n
; connec
t
counting to
cardinality.
P
K.CC.4a: W
h
en
counting ob
j
ects, sa
y
the num
b
er names
in the stan
d
ar
d
o
rder, pairing each
o
b
j
ect with one and
o
nly one number
n
ame
.
P
K.CC.4
b
:
R
ecognize t
h
at t
h
e
last num
b
er name
said tells the num
b
er
o
f ob
j
ects counted.
4
Year
s
A.
Co
unt t
o
T
ell
the Number of
O
bj
ec
ts
K
.CC.
4:
Un
d
erstan
d
the
relations
h
ip
b
etween numbers
and quantities;
connect counting
to cardinality.
K
.CC.
4a
:
W
h
en
counting ob
j
ects,
s
a
y
the num
b
er
n
ames in t
h
e
standard order,
pairing each ob
j
ect
with one and onl
y
o
ne num
b
er name
and each num
b
er
n
ame with one and
o
nly one ob
j
ect.
K.CC.4
b
:
Un
d
erstan
d
that
the last num
b
er
n
ame sai
d
tells the
Kindergarte
n
n
umber of ob
j
ects
counte
d
. The
n
umber of ob
j
ects
is t
h
e same
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
M
at
h
ematic
s
S
tran
d:
Counting and Cardinalit
y
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Count to tell the number of objects.
continued on next page

Appendix | 57
M
PK.CC.4c: Begin to
recognize that each
successive number
name refers to a
quantity that is one
larger.
PK.CC.5: Represent
a number (0-5, then
to ten) by producing
a set of objects with
concrete materials,
pictures, and/or
numerals (with 0
representing a count
of no objects).
PK.CC.6: Recognize
the number of
objects in a set
without counting
(Subitizing). (Use
regardless of their
arrangement or the
order in which they
were counted.
K.CC.4c:
Understand that
each successive
number name
refers to a quantity
that is one larger.
Understand that
each successive
number name
refers to a quantity
that is one larger.
K.CC.5: Count to
answer “how
many?” questions
about as many as
twenty things
arranged in a line, a
rectangular array,
or a circle, or as
many as ten things
in a scattered
configuration;
given a number
from 1-20, count
out that many
objects.
K.CC.6: Identify
whether the
number of objects
in one group is
greater than, less
P
K.
CC
.4
c
: Begin to
recognize t
h
at eac
h
successive num
b
er
n
ame refers to a
quantity t
h
at is one
larger.
P
K.
CC
.5
:
R
epresent
a number
(0
-
5, t
h
en
to
t
e
n
)
n
b
y producing
a set of ob
j
ects with
concrete materials,
pictures, and
/
or
n
umerals
(
wit
h
0
representing a count
o
f no ob
j
ects).
P
K
.CC.6
:
R
ecognize
the num
b
er of
o
b
j
ects in a set
wit
h
out counting
(
Subitizing). (Use
regardless of their
arrangement or t
h
e
o
rder in which the
y
were counted.
K.
CC
.4
c
:
Un
d
erstan
d
that
eac
h
successive
n
um
b
er name
refers to a quantit
y
t
h
at is one larger.
Un
d
erstan
d
that
eac
h
successive
n
um
b
er name
refers to a quantit
y
t
h
at is one larger.
K.
CC
.5
:
Co
unt t
o
answer “
h
o
w
many?
”
questions
about as many as
t
wen
ty
t
h
ings
arranged in a line, a
rectangular array,
o
r a circle, or as
many as
t
en t
h
ings
in a scattere
d
configuration;
given a number
f
r
o
m
1
-
2
0, count
o
ut t
h
at man
y
o
b
j
ects.
K
.CC.6
:
Identif
y
w
h
et
h
er t
h
e
n
umber of ob
j
ects
in one group is
greater t
h
an, less
continued from previous page

58 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
one to five objects).
A. Compare
Quantities
PK.CC.7: Explore
relationships by
comparing groups
of objects up to five
and then ten.
Identify whether the
number of objects in
one group is greater
than, less than, or
equal to the number
of objects in another
group (e.g., by using
matching and
counting strategies).
(Include groups with
up to five objects).
than, or equal to
the number of
objects in another
group (e.g., by
using matching and
counting
strategies). (Include
groups with up to
ten objects).
A. Compare
Numbers
K.CC.7: Compare
two numbers
between one and
ten presented as
written numerals.
o
ne to fiv
e
o
b
j
ects)
.
A.
C
ompare
Quantitie
s
P
K
.CC.7
:
Explore
relationships b
y
comparing groups
o
f ob
j
ects up to
f
ive
an
d
then te
n
.
Identify whether the
n
umber of ob
j
ects in
o
ne group is greater
t
h
an, less t
h
an, or
equal to t
h
e nu
m
b
er
o
f ob
j
ects in another
grou
p
(
e.g., by using
matching and
counting strategie
s
)
.
(
I
n
clu
de
groups wit
h
u
p
t
o
f
iv
e
o
b
j
ects).
t
h
an, or equal to
the num
b
er
o
f
o
b
j
ects in another
group
(
e.g., b
y
u
sing matching and
counting
strategie
s
)
.
(
Include
groups wit
h
up to
ten ob
j
ects).
A
. Compare
N
u
m
b
er
s
K
.C
C.7
:
C
ompare
two numbers
b
etween
o
n
e
an
d
t
en presented as
written numerals.

Appendix | 59
M
Domain: Mathematics
Strand: Operations & Algebraic Thinking
Standard: Understand addition as putting together and adding to, and understand subtraction as taking apart and taking from.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Show interest in
quantity, measuring
and number
relationships (e.g.,
sing “Five Little
Monkeys jumping
on the Bed” and
know that the next
number is one less
than the one
before).
A. Understand
Addition as Putting
Together and
Adding to, and
Understand
Subtraction as
Taking Apart and
Taking From
PK.OA.1: Explore
addition and
subtraction with
objects, fingers,
mental images,
drawings1, sounds
(e.g., claps), acting
out situations, or
verbal explanations
(up to five).
A. Understand
Addition as Putting
Together and
Adding to, and
Understand
Subtraction as
Taking Apart and
Taking From
K.OA.1: Represent
addition and
subtraction with
objects, fingers,
mental images,
drawings, sounds
(e.g., claps), acting
out situations, or
verbal explanations,
expressions, or
equations.
A. Represent and
Solve Problems
Involving Addition
and Subtraction
1.OA.1:
Use addition and
subtraction within
twenty to solve
word problems
involving situations
of adding to, taking
from, putting
together, taking
apart, and
comparing, with
unknowns in all
positions, e.g., by
using objects,
drawings, and
equations with a
symbol for the
unknown number
to represent the
problem.
A. Represent and
Solve Problems
Involving Addition
and Subtraction
2.OA.1: Use
addition and
subtraction within
100 to solve one-
and two-step word
problems involving
situations of adding
to, taking from,
putting together,
taking apart, and
comparing, with
unknowns in all
positions, e.g., by
using drawings, and
equations with a
symbol for the
unknown number
to represent the
problem.
A. Add and
Subtract Within
Twenty
1 Year
2
Year
s
Sh
ow interest in
quantity, measuring
and num
b
er
relations
h
ips (e.g.,
sing “Five Little
M
on
k
eys
j
umping
o
n the Be
d
” an
d
k
now that the next
n
um
b
er is one less
t
h
an t
h
e
o
ne
b
efore
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
Un
d
erstan
d
A
ddition as Putting
Together and
A
dding to, and
Un
d
erstan
d
S
u
b
traction as
Taking Apart and
Ta
k
ing Fro
m
P
K
.
OA
.1
:
Explore
a
dd
ition an
d
subtraction with
o
b
j
ects, fingers,
mental images,
d
rawings1, sounds
(
e.g., claps), acting
o
ut situations, or
verbal explanations
(
up to
f
iv
e
)
.
4
Year
s
A.
Un
d
erstan
d
A
ddition as Putting
Together and
A
dding to, and
Un
d
erstan
d
S
u
b
traction as
Taking Apart and
Ta
k
ing Fro
m
K
.
OA
.1
:
R
epresent
a
dd
ition an
d
subtraction with
o
b
j
ects, fingers,
mental images,
d
rawings, sounds
(
e.g., claps), actin
g
o
ut situations, or
verbal explanations,
expressions, or
equations.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Repres
e
n
t an
d
S
olve Pro
b
lems
Involving Addition
and Su
b
tractio
n
1
.
OA
.1
:
Use a
dd
ition an
d
subtraction within
t
wen
ty
to solve
word problems
involving situations
o
f adding to, taking
f
rom, putting
together, ta
k
ing
apart, and
comparing, wit
h
u
n
k
nowns in all
positions, e.g., b
y
u
sing ob
j
ects,
d
rawings, and
equations wit
h
a
symbol for the
u
nknown number
to represent t
h
e
pr
o
b
lem.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
R
epresent and
S
olve Pro
b
lems
Involving Addition
and Su
b
tractio
n
2
.
OA
.1
:
Use
a
dd
ition an
d
subtraction within
100 to solve on
e
-
and tw
o
-
step word
problems involving
situations of adding
to, ta
k
ing from,
putting toget
h
er,
taking apart, and
comparing, wit
h
u
n
k
nowns in all
positions, e.g., b
y
u
sing drawings, and
equations wit
h
a
sy
m
b
ol for the
u
nknown number
to represent t
h
e
problem.
A
. A
dd
an
d
Subtract W
ith
in
W
W
T
wen
ty
D
o
main
:
M
at
h
ematic
s
S
tran
d:
O
perations & Algebraic Thinking
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Understand addition as
p
uttin
g
to
g
ether and addin
g
to, and understand subtraction as takin
g
a
p
art an
d
ta
k
in
g
from.

60 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
PK.OA.2:
Decompose quantity
(less than or equal to
five) into pairs in
more than one way
(e.g., by using
objects or drawings).
PK.OA.3: For any
given quantity from
zero to five, use
objects or drawings
to find the quantity
that must be added
to make five.
K.OA.2: Solve
addition and
subtraction word
problems, and add
and subtract within
ten (e.g., by using
objects or drawings
to represent the
problem).
K.OA.3:
Decompose
numbers less than
or equal to ten into
pairs in more than
one way, e.g., by
using objects or
drawing, and
record each
decomposition by a
drawing or
equation (e.g., 5 =
2 + 3 and 5 = 4 +
1).
1.OA.2: Solve word
problems that call
for addition of
three whole
numbers whose
sum is less than or
equal to twenty
(e.g., by using
objects, drawings,
and equations with
a symbol for the
unknown number
to represent the
problem).
A. Understand and
Apply Properties of
Operations and
Relationship
Between Addition
and Subtraction
1.OA.3: Apply
properties of
operations as
strategies to add
and subtract.
(Students need not
use formal terms
for these
properties).
Examples: If 8 + 3 =
11 is known, then 3 +
8 = 11 is also known.
(Commutative property
of addition) To add 2
2.OA.2: Fluently
add and subtract
within twenty using
mental strategies.
By end of Grade 2,
know from
memory all sums of
two one-digit
numbers.
A. Work with
Equal Groups of
Objects to Gain
Foundations for
Multiplication
2.OA.3: Determine
whether a group of
objects (up to
twenty has an odd
or even number of
members, e.g., by
pairing objects or
counting them by
2s; write an
equation to express
an even number as
a sum of two equal
addends.
P
K
.
OA
.2
:
D
ecompose quantit
y
(
less t
h
an or equal to
f
iv
e
)
into pairs in
m
o
re t
h
an one wa
y
(
e.g., by using
o
b
j
ects or drawings).
P
K
.
OA
.
3
:
F
or an
y
given quantity from
z
er
o
to
f
iv
e
, u
s
e
o
b
j
ects or drawings
to find the quantit
y
that must
b
e added
t
o
ma
k
e
f
iv
e
.
K
.
OA
.
2:
S
olve
a
dd
ition an
d
subtraction word
problems, and add
and subtract within
ten
(
e.g., by using
o
b
j
ects or drawings
to represent t
h
e
problem
)
m
.
K
.
OA
.
3
:
D
ecompose
n
um
b
ers less than
o
r equal to
t
en int
o
pairs in more t
h
an
o
ne way, e.g., b
y
u
sing ob
j
ects or
d
rawing, and
recor
d
each
d
ecomposition by a
d
rawing
or
equation (e.g., 5 =
2
+ 3 an
d
5 = 4 +
1
)
.
1
.
OA
.2
:
S
olve word
problems that call
f
or a
dd
ition of
t
h
ree w
h
ole
n
umbers whose
sum is less t
h
an or
equal to
t
wen
ty
(
e.g., by using
o
b
j
ects, drawings,
and equations with
a symbol for the
u
nknown number
to represent t
h
e
problem
)
m
.
A
. Un
d
erstan
d
an
d
A
pply Properties of
O
perations a
n
d
R
elations
h
ip
Between A
dd
ition
an
d
S
ub
traction
1
.
OA
.
3
:
A
ppl
y
properties of
o
perations as
strategies to add
and su
b
tract.
(
Students need not
u
se f
o
rmal terms
f
or these
propertie
s
)
.
E
xamp
l
es: I
f
8 + 3 =
11 is known, then 3 +
8
= 11 is a
l
so
k
nown.
(
Commutative property
of
a
dd
ition) To a
dd
2
2.
OA
.2
:
F
luentl
y
add and su
b
tract
wit
h
in
t
wen
ty
u
sing
mental strategies.
By end of Grade 2,
k
now from
memory all sums of
t
wo on
e
-
d
igit
n
um
b
ers.
A
. Work with
Equal Groups of
O
b
j
ects to Gain
F
o
un
d
ations
fo
r
M
ultiplicatio
n
2.
OA
.
3
:
D
etermine
whether a group of
o
b
j
ects (up to
t
wen
ty
h
as an o
dd
o
r even num
b
er of
members, e.g., b
y
pairing ob
j
ects or
counting them b
y
2
s; write an
equation to express
an even num
b
er as
a sum of two equal
a
dd
en
d
s.

Appendix | 61
M
K.OA.4: For any
number from one
to nine, find the
number that makes
ten when added to
the given number
(e.g., by using
objects or drawings
and record the
answer with a
drawing or
equation).
K.OA.5: Fluently
add and subtract
within five.
+ 6 + 4, the second
two numbers can be
added to make a ten,
so 2 + 6 + 4 = 2 +
10, which equals 12.
(Associative property of
addition.)
1.OA.4:
Understand
subtraction as an
unknown-addend
problem. For
example, subtract 10
– 8 by finding the
number that makes 10
when added to 8.
A. Add and
Subtract Within
Twenty
1.OA.5: Relate
counting to
addition and
subtraction (e.g., by
counting on two to
add two).
1.OA.6: Add and
subtract within
twenty,
demonstrating
fluency for addition
and subtraction
within ten. Use
2.OA.4: Use
addition to find the
total number of
objects arranged in
rectangular arrays
with up to five
rows and up to five
columns; write an
equation to express
the total as a sum
of equal addends.
K
.
OA
.
4
:
F
or an
y
n
um
b
er from
o
n
e
to
n
in
e
, find the
n
um
b
er that makes
ten when added to
the given number
(
e
.
g
.
, by using
o
b
j
ects or drawings
an
d
recor
d
the
answer wit
h
a
d
rawing or
equation
)
n
.
K.OA.5
:
F
lu
e
n
tl
y
add and su
b
tract
wit
h
in
f
iv
e
.
+ 6 + 4, the secon
d
t
wo num
b
ers can
b
e
a
dd
e
d
to make a ten,
s
o 2 +
6
+ 4 = 2 +
10, which equals 12.
(Associative property o
f
a
dd
ition.
)
1
.
OA
.
4
:
U
nd
erstan
d
su
b
traction as an
u
n
k
nown
-
a
dd
en
d
problem.
F
or
e
xam
pl
e, subtract 1
0
–
8
by
f
in
d
ing the
number that ma
k
es 1
0
when a
dd
e
d
to
8
.
A.
Add
an
d
Subtract W
ith
in
W
W
T
went
y
1.OA.5
:
R
elate
counting to
a
dd
ition an
d
subtraction (e.g., b
y
counting on
t
w
o
to
a
dd
t
w
o
)
.
1
.
OA
.6
:
Add
an
d
subtract within
t
wen
ty
,
d
emonstrating
f
luency for addition
and su
b
traction
wit
h
in
t
en
.
Use
2.
OA
.
4
:
Use
a
dd
ition to fin
d
the
total num
b
er of
o
b
j
ects arranged in
rectangular a
rr
ay
s
wit
h
up to
f
iv
e
rows and up to
f
iv
e
columns; write an
equation to express
t
h
e total as a sum
o
f equal addends.
continued from previous page

62 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
strategies such as
counting on,
making ten (e.g. 8
+ 6 = 8 + 2 + 4,
which leads to 10 +
4 = 14);
decomposing a
number leading to
a ten (e.g., 13 – 4 =
13 – 3 – 1, which
leads to 10 – 1 =
9); using the
relationship
between addition
and subtraction
(e.g., knowing that
8 + 4 = 12, one
knows 12 – 8 = 4);
and creating
equivalent but
easier or known
sums (e.g., adding 6
+ 7 by creating the
known equivalent 6
+ 6 + 1 = 12 + 1,
which equals 13).
A. Work with
addition and
subtraction
equations.
1.OA.7:
Understand the
meaning of the
equal sign, and
determine if
equations involving
strategies suc
h
as
counting on,
ma
k
ing ten (e.g. 8
+
6 = 8 + 2 + 4,
which leads to 10 +
4
= 14
)
;
d
ecomposing a
n
umber leading to
a
te
n
(
e.g., 13
–
4
=
13
–
3
–
1, w
h
ic
h
lea
d
s to 10
–
1 =
9
); using t
h
e
relations
h
ip
b
etween addition
and su
b
traction
(
e.g.,
k
nowing that
8
+ 4 = 12, one
k
nows 12
–
8
= 4
)
;
and creating
equivalent but
easier or
k
nown
sums (e.g., adding 6
+
7 by creating the
k
n
o
wn equivalent 6
+
6 + 1 = 12 + 1,
w
h
ic
h
equals 13).
A.
Wor
k
with
a
dd
ition an
d
su
b
traction
equations.
1
.
OA
.7
:
Un
d
erstan
d
the
meaning of the
equal sign, and
d
etermine if
e
q
uations involvin
g
continued on next page

Appendix | 63
M
addition and
subtraction are true
or false. For
example, which of the
following equations are
true and which are
false? 6 = 6, 7 = 8 –
1, 5 + 2 = 2 + 5, 4
+ 1 = 5 + 2.
1.OA.8:
Determine the
unknown whole
number in an
addition or
subtraction
equation relating
three whole
numbers. For
example, determine the
unknown number that
makes the question
true in each of the
equations 8 + ? = 11,
5 = ? - 3, 6 + 6 = ?.
a
dd
ition an
d
su
b
traction are true
o
r false.
F
or
example, which o
f the
o
f
o
ll
owing equations are
t
rue an
d
which are
f
a
l
se? 6 = 6, 7 =
8
–
1,
5
+ 2 = 2 +
5
, 4
+ 1 =
5
+ 2
.
1
.
OA
.
8
:
D
etermine t
h
e
u
n
k
nown whole
n
um
b
er in an
a
dd
ition or
su
b
traction
equation relating
t
h
ree w
h
ole
n
um
b
ers.
F
or
e
xam
p
le,
d
etermine the
unknown nu
mber that
u
u
makes the question
t
rue in each o
f
the
e
quations 8 + ? = 11,
5
=
?
-
3, 6 + 6 = ?.
continued from previous page

64 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Mathematics
Strand: Number and Operations in Base Ten
Standard: Work with numbers to gain foundations for place value.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Work with
Numbers 0-10 to
Gain Foundations
for Place Value
PK.NBT.1:
Investigate the
relationship between
ten ones and ten.
A. Work with
Numbers 11-19 to
Gain Foundations
for Place Value
K.NBT.1:
Compose and
decompose
numbers from
elven to nineteen
into ten ones and
some further ones
(e.g., by using
objects or
drawings, and
record each
composition or
decomposition by a
drawing or
equation - such as
18 = 10 + 8);
understand that
these numbers are
composed of ten
ones and one, two,
three, four, five,
six, seven, eight, or
nine ones.
A. Extend the
Counting Sequence
1.NBT.1: Count to
120 starting at any
number less than
120. In this range,
read and write
numerals and
represent a number
of objects with a
written numeral.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
A.
Wor
k
with
Numbers
0
-
10 to
Gain Foun
d
ations
f
or Place
V
alu
e
P
K.NB
T
.
1
:
Investigate t
h
e
relationship between
ten ones an
d
ten.
4
Year
s
A.
Wor
k
with
Numbers 1
1
-
1
9
to
Gain Foun
d
ations
f
or Place
V
alu
e
K.NB
T
.
1
:
Compose and
d
ecompose
n
um
b
ers from
elve
n
to
n
ineteen
int
o
ten ones an
d
some further one
s
(
e.g., by using
o
b
j
ects or
d
rawings, and
recor
d
each
composition or
d
ecompo
s
ition by a
d
rawing or
equation
-
suc
h
as
18 = 10 + 8
)
;
u
n
d
erstan
d
that
these num
be
r
s a
r
e
composed of ten
o
nes and one, two,
three, four, five,
s
ix, seven, eig
h
t, or
n
ine ones.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Exten
d
the
Counting Sequenc
e
1.NB
T
.
1
:
Co
unt t
o
120 starting at an
y
n
um
b
er less than
120. In t
h
is range,
read and write
n
umerals an
d
represent a number
o
f
o
b
j
ects with a
written numeral.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
M
at
h
ematic
s
S
tran
d:
Number and Operations in Base T
e
n
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Work with numbers to
g
ain foundations for
p
lace value.
continued on next page

Appendix | 65
M
A. Understand
Place Value
1.NBT.2:
Understand that
the two digits of a
two-digit number
represent amounts
of tens and ones.
1.NBT.2a:
Understand the
following as a
special case: 10 can
be thought of as a
bundle of ten ones
-- called a “ten.”
1.NBT.2b:
Understand the
following as a
special case: The
numbers from 11
to 19 are composed
of a ten and one,
two, three, four,
five, six, seven,
eight, or nine ones.
A. Understand
Place Value
2.NBT.1:
Understand that the
three digits of a
three-digit number
represent amounts
of hundreds, tens,
and ones; e.g., 706
equals 7 hundreds,
0 tens, and 6 ones.
2.NBT.1a:
Understand the
following as a
special case: 100
can be thought of
as a bundle of ten
tens -- called a
“hundred.”
2.NBT.1b:
Understand the
following as a
special case: The
numbers 100, 200,
300, 400, 500, 600,
700, 800, 900 refer
to one, two, three,
four, five, six,
seven, eight, or nine
hundreds (and zero
tens and zero ones).
A.
Un
d
erstan
d
P
lace
V
alu
e
1.NB
T
.
2
:
Un
d
erstan
d
that
the two digits of a
t
w
o
-
d
igit number
represen
t
amoun
t
s
o
f tens an
d
ones.
1.NB
T
.2a
:
Un
d
erstan
d
the
f
ollowing as a
special case: 10 can
b
e thought
o
f as a
b
undle of ten ones
--
calle
d
a “ten.”
1.NBT.2b
:
Un
d
erstan
d
the
f
ollowing as a
special case: T
h
e
n
um
b
ers from 11
to 19 are composed
o
f a ten and one,
two, three, four,
f
ive, six, seven,
eig
h
t, or nine one
s
.
A.
Un
d
erstan
d
P
lace
V
alu
e
2
.NB
T
.1:
Un
d
erstan
d
that the
three digits of a
t
h
re
e
-
d
igit number
represen
t
amoun
t
s
o
f hundreds, tens,
and ones; e.g., 706
equals 7 hundreds,
0 tens, and 6 ones.
2
.NB
T
.1a
:
Un
d
erstan
d
the
f
ollowing as a
special case: 100
can be thought of
as a
b
undle of ten
t
ens
--
calle
d
a
“hun
d
re
d
.”
2
.NBT.1b
:
Un
d
erstan
d
the
f
ollowing as a
special case: T
h
e
n
umbers 100, 200,
3
00, 400, 500, 600,
7
00, 800, 900 refer
to one, two, t
h
r
ee
,
f
our, five, six,
seven, eig
h
t, or nine
h
undreds
(
and
z
er
o
tens an
d
z
er
o
o
nes
)
.
continued from previous page

66 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
1.NBT.2c:
Understand the
following as a
special case: The
numbers 10, 20, 30,
40, 50, 60, 70, 80,
90 refer to one,
two, three, four,
five, six, seven,
eight, or nine tens
(and 0 ones).
1.NBT.3: Compare
two two-digit
numbers based on
meanings of the
tens and ones
digits, recording the
results of
comparisons with
the symbols >,=,
and <.
A. Use Place Value
Understanding and
Properties of
Operations to Add
and Subtract.
1.NBT.4: Add
within 100,
including adding a
two-digit number
and a one-digit
number, and
adding a two-digit
2.NBT.2: Count
within 1000; skip-
count by 5s, 10s,
and 100s.
2.NBT.3: Read and
write numbers to
1000 using base-ten
numerals, number
names, and
expanded form.
2.NBT.4: Compare
two three-digit
numbers based on
meanings of the
hundreds, tens, and
ones digits, using >,
=, and < symbols
1.NB
T
.2c
:
Un
d
erstan
d
the
f
ollowing a
s
a
special case: T
h
e
n
umbers 10, 20, 30,
4
0, 50, 60, 70, 80,
9
0 refer to one,
two, three, four,
f
ive, six, seven,
eig
h
t, or nine tens
(
and 0 ones).
1.NB
T
.3
:
C
ompare
t
wo
t
w
o
-
d
igit
n
um
b
ers
b
ased on
meanings of the
tens an
d
ones
d
igits, recording the
resu
l
ts of
comparisons wit
h
the symbols >,=,
an
d
<.
A.
Use Place
V
alue
Understanding and
P
roperties of
O
perations to Add
an
d
S
ub
tract.
1.NB
T
.4
:
Add
wit
h
in 100,
including adding a
t
w
o
-
d
igit number
an
d
a on
e
-
d
igit
n
umber, and
adding a tw
o
-
d
igit
2
.NB
T
.
2
:
Co
unt
within 1000; s
k
i
p
-
count by 5s, 10s,
an
d
100s.
2
.NB
T
.3
:
R
ea
d
an
d
write numbers to
1000 using bas
e
-
t
en
n
umerals, number
n
ames, and
expanded form.
2.
NB
T
.4
:
C
ompare
two t
h
re
e
-
d
igit
n
um
b
ers
b
ased on
meanings of the
h
undreds, tens, and
o
nes digits, using >,
=
, and < symbols
continued on next page

Appendix | 67
M
number and a
multiple of 10,
using concrete
models or drawings
and strategies based
on place value,
properties of
operations, and/or
the relationship
between addition
and subtraction;
relate the strategy
to a written method
and explain the
reasoning used.
Understand that in
adding two-digit
numbers, one adds
tens and tens, ones
and ones, and
sometimes it is
necessary to
compose a ten.
1.NBT.5: Given a
two-digit number,
mentally find ten
more or ten less
than the number,
without having to
count; explain the
reasoning used.
to record the results
of comparisons.
A. Use Place Value
Understanding and
Properties of
Operations to Add
and Subtract
2.NBT.5: Fluently
add and subtract
within 100 using
strategies based on
place value,
properties of
operations, and/or
the relationship
between addition
n
um
b
er and a
m
ul
tiple of 10,
u
sing concrete
models or drawings
and strategies based
o
n place value,
properties of
o
perations, and
/
or
t
h
e relations
h
ip
b
etween addition
and subtraction;
relate t
h
e strateg
y
to a written method
and explain the
reasoning used.
Un
d
erstan
d
that in
adding tw
o
-
d
igit
n
umbers, one adds
tens and tens, ones
and ones, and
sometimes it is
n
ecessary
t
o
compose a
t
en.
1.NB
T
.5
:
Given a
t
w
o
-
d
igit number,
mentally find
t
e
n
m
or
e
or
t
en less
than the number,
wit
h
out
h
aving to
count; explain t
h
e
reasoning
use
d
.
to recor
d
the results
o
f comparisons.
A.
Use Place
V
alue
Understanding and
P
roperties of
O
perations to
Add
and Su
b
tract
2
.NB
T
.5
:
F
luentl
y
add and su
b
tract
wit
h
in 100 using
strategies based on
place value,
properties of
o
perations, and
/
or
t
h
e relations
h
ip
b
etween addition
continued from previous page

68 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
1.NBT.6: Subtract
multiples of ten in
the range of 10-90
from multiples of
ten in the range of
10-90 (positive or
zero differences),
using concrete
models or drawings
and strategies based
on place value,
properties of
operations, and/or
the relationship
between addition
and subtraction;
relate the strategy
to a written method
and explain the
reasoning used.
and subtraction.
2.NBT.6: Add up
to four two-digit
numbers using
strategies based on
place value,
properties of
operations.
2.NBT.7: Add and
subtract within
1000, using
concrete models or
drawings and
strategies based on
place value,
properties of
operations, and/or
the relationship
between addition
and subtraction;
relate the strategy
to a written
1.NB
T
.
6
:
S
ubtract
multiples of
t
en in
the range of 1
0
-
9
0
f
rom multiples of
t
en in the range of
1
0
-
9
0 (positive or
z
ero differences
)
,
u
sing concrete
models or drawings
and strategies based
o
n place value,
properties of
o
perations, and
/
or
t
h
e relations
h
ip
b
etween addition
and subtraction;
relate t
h
e strateg
y
to a written method
an
d
explain t
h
e
reasoning used.
and su
b
traction.
2
.NB
T
.
6
:
A
dd up
to four tw
o
-
d
igit
n
umbers using
strategies based on
place value,
properties of
o
perations.
2
.NB
T
.
7
:
Add
an
d
subtract within
1000, using
concrete mo
d
els or
d
rawings and
strategies based on
place value,
properties of
o
perations, and
/
or
t
he
relations
h
ip
b
etween addition
and subtraction;
relate t
h
e strateg
y
to a written
continued on next page

Appendix | 69
M
method.
Understand that in
adding or
subtracting three-
digit numbers, one
adds or subtracts
hundreds and
hundreds, tens and
tens, ones and ones;
and sometimes it is
necessary to
compose or
decompose tens or
hundreds
2.NBT.8: Mentally
add ten or 100 to a
given number 100-
900, and mentally
subtract ten or 100
from a given
number 100-900.
2.NBT.9: Explain
why addition and
subtraction
strategies work,
using place value
and the properties
of operations.
metho
d
.
Un
d
erstan
d
that in
adding or
subtracting thre
e
-
d
igit numbers, one
adds or su
b
tracts
h
un
d
re
d
s an
d
h
undreds, tens and
tens, ones and ones;
an
d
sometimes it is
n
ecessary
t
o
compose or
d
ecompose tens or
h
un
d
re
ds
2
.NB
T
.8
:
M
en
t
all
y
a
dd
t
en
o
r 100 to a
given number 10
0
-
9
00, and mentall
y
su
b
tract
t
e
n
o
r 100
f
rom a given
n
um
b
er 10
0
-
9
00.
2
.NB
T
.9
:
Explain
why addition and
su
b
traction
strategies wor
k
,
u
sing place value
and the properties
o
f o
p
eration
s
.
continued from previous page

70 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Mathematics
Strand: Measurement & Data
Standard: Describe and compare measureable attributes.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Show interest in
quantity and
number
relationships (e.g.,
fill large and small
containers with
sand or water).
Show interest in
quantity, measuring
and number
relationships (e.g.,
fill a balance scale
with beads, making
one side go down,
then the other, tell
a friend that he is
taller than the
tower he has built).
A. Describe and
Compare
Measureable
Attributes
PK.MD.1: Describe
measurable
attributes of objects,
such as length or
weight.
PK.MD.2: Directly
compare two objects
with a measurable
attribute in
common, using
words such as
longer/shorter;
heavier/lighter; or
taller/shorter.
A. Describe and
Compare
Measureable
Attributes
K.MD.1: Describe
measurable
attributes of
objects, such as
length or weight.
Describe several
measurable
attributes of a
single object.
K.MD.2: Directly
compare two
objects with a
measurable
attribute in
common, to see
which object has
“more of”/ “less
of” the attribute,
and describe the
difference. For
example, directly
compare the
heights of two
children and
describe one child
as taller/shorter.
A. Measure
Lengths Indirectly
and by Iterating
Length Units
1.MD.1: Order
three objects by
length; compare the
lengths of two
objects indirectly
by using a third
object.
1.MD.2: Express
the length of an
object as a whole
number of length
units, by laying
multiple copies of a
shorter object (the
length unit) end to
end; understand
that the length
measurement of an
object is the
number of same-
size length units
that span it with no
gaps or overlaps.
Limit to contexts
A. Measure and
Estimate Lengths in
Standard Units
2.MD.1: Measure
the length of an
object by selecting
and using
appropriate tools
such as rulers,
yardsticks, meter
sticks, and
measuring tapes.
2.MD.2: Measure
the length of an
object twice, using
length units of
different lengths for
the two
measurements;
describe how the
two measurements
relate to the size of
the unit chosen.
1 Year
Sh
ow interest in
quantity and
n
um
b
er
relations
h
ips (e.g.,
f
ill large and small
containers wit
h
sand or water
)
.
2
Year
s
Sh
o
w
interest in
quantity, measuring
and num
b
er
relations
h
ips (e.g.,
f
ill a
b
alance scale
with beads, making
o
ne side go down,
t
h
en t
h
e ot
h
er, tell
a frien
d
that he is
taller t
h
an t
h
e
tower he has built
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
D
escri
b
e and
C
ompare
M
easurea
b
le
A
ttri
b
ute
s
P
K
.
M
D.1
:
D
escri
b
e
measura
b
le
attributes of ob
j
ects,
suc
h
as lengt
h
or
weig
h
t.
P
K
.
M
D.2
:
D
irectl
y
compare two ob
j
ects
with a measurable
attri
b
ute in
common, using
words such as
longer
/
shorter;
h
eavier
/
lighter; or
taller
/
shorter.
4
Year
s
A.
D
escri
b
e and
C
ompare
M
easurea
b
le
A
ttri
b
ute
s
K
.
M
D.1
:
D
escri
b
e
measura
b
le
attri
b
utes of
o
b
j
ects, such as
lengt
h
or weig
h
t.
D
escri
b
e several
measura
b
le
attri
b
utes of a
single ob
j
ect.
K
.
M
D.2
:
D
irectl
y
compare
t
wo
o
b
j
ects with a
measura
b
le
attri
b
ute in
common,
t
o
s
ee
which ob
j
ect has
“more of”
/
“
less
o
f” the attribute,
and descri
b
e the
d
ifference. For
example, directl
y
compare t
h
e
h
eights of two
chil
d
ren an
d
d
escri
b
e one child
as taller
/
shorter.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A.
M
easure
L
engths Indirectl
y
and by Iterating
L
engt
h
Unit
s
1
.
M
D.1
:
O
r
d
er
three ob
j
ects b
y
lengt
h
; compare t
h
e
lengt
h
s
o
f
two
o
b
j
ects indirectl
y
b
y using a third
o
b
j
ect.
1
.
M
D.2
:
Express
the length of an
o
b
j
ect as a whole
n
umber of length
u
nits, by laying
multiple copies of a
shorter ob
j
ect (the
length unit) end to
end; understand
t
h
at t
h
e lengt
h
measurement of an
o
b
j
ect is t
h
e
n
um
b
er of sam
e
-
size lengt
h
units
t
h
at span it wit
h
no
gaps or overlaps.
L
imit to contexts
A.
M
easure an
d
Estimate Lengt
h
s in
S
tan
d
ar
d
Unit
s
2.
M
D.1
:
M
easure
the length of an
o
b
j
ect by selecting
and using
appropriate tools
suc
h
as rulers,
yardsticks, meter
sticks, an
d
measuring tapes.
2.
M
D.2
:
M
easure
Gra
d
e
2
the length of an
o
b
j
ect twice, using
length units of
d
ifferent lengths for
t
h
e two
measuremen
t
s;
d
escribe how the
t
wo measuremen
t
s
relate to the size of
t
h
e unit c
h
osen.
D
o
main
:
M
at
h
ematic
s
S
tran
d:
M
easurement &
D
ata
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
D
escribe and com
p
are measureable attributes.
continued on next page
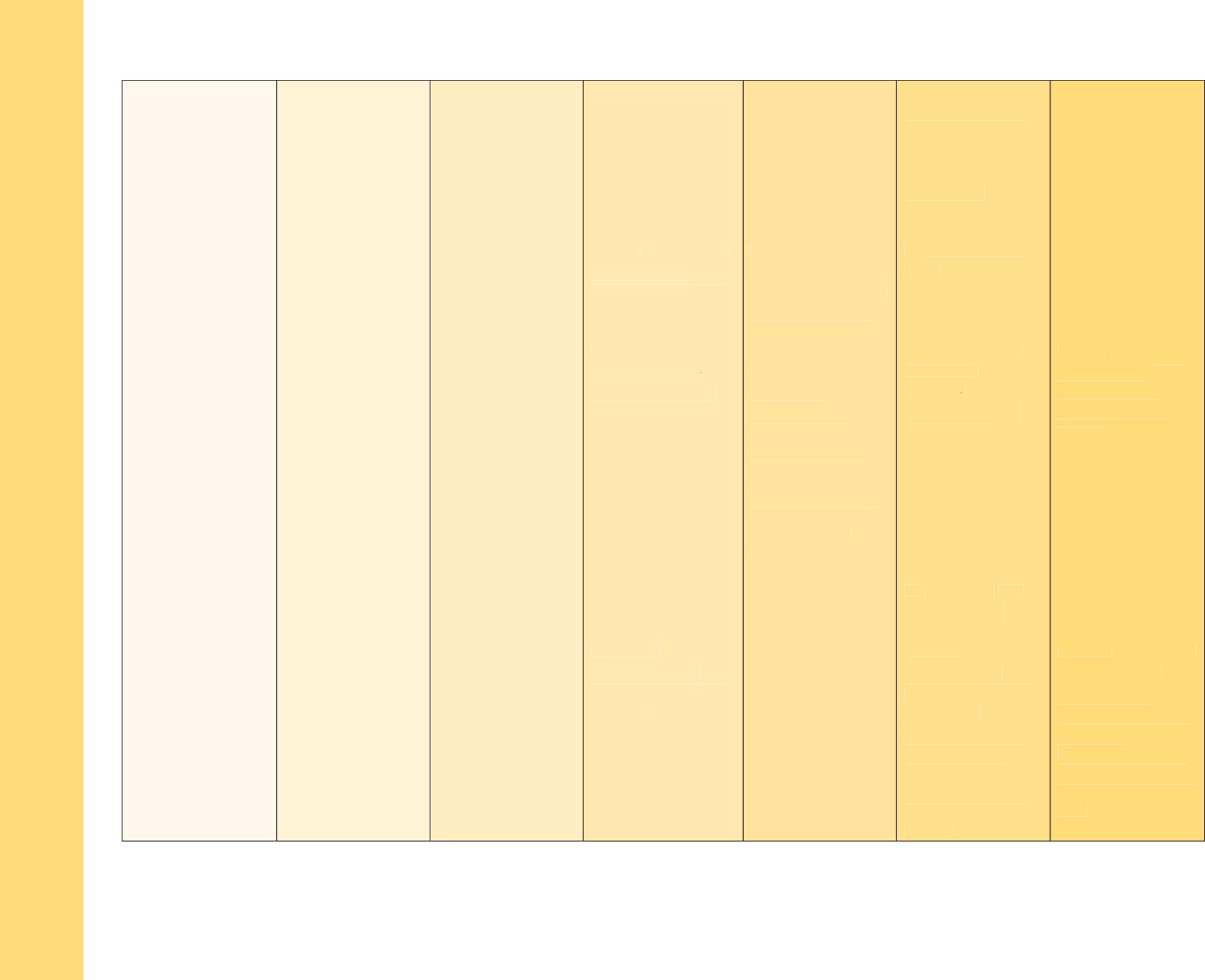
Appendix | 71
M
A. Sort Objects into
Categories and
Compare Quantities
PK.MD.3: Sort
objects into self-
selected and given
categories.
PK.MD.4: Compare
categories using
words such as more
or same.
A. Classify Objects
and Count the
Number of Objects
in Each Category
K.MD.3: Classify
objects into given
categories; count
the number of
objects in each
category and sort
the categories by
count (Limit
category counts to
be less than or
equal to 10.).
where the object
being measured is
spanned by a whole
number of length
units with no gaps
or overlaps.
A. Tell and Write
Time
1.MD.3: Tell and
write time in hours
and half-hours
using analog and
digital clocks.
A. Represent and
Interpret Data
1.MD.4: Organize,
represent, and
interpret data with
up to three
categories; ask and
answer questions
about the total
number of data
points, how many
in each category,
2.MD.3: Estimate
lengths using units
of inches, feet,
centimeters, and
meters.
2.MD.4: Measure to
determine how
much longer one
object is than
another, expressing
the length
difference in terms
of a standard length
unit.
A.
S
ort
O
b
j
ects into
Categories and
Compare Quantitie
s
P
K
.
MD
.
3
:
S
ort
objects into self
-
f
f
selected and given
categories.
P
K
.
MD
.
4
:
C
ompare
categories using
words such as more
or
same.
A.
Classify Ob
j
ects
an
d
Count the
Number of Ob
j
ects
in Eac
h
Categor
y
K
.
MD
.
3
:
Classif
y
o
b
j
ects into given
categories;
c
oun
t
the num
b
er of
o
b
j
ects in each
category and sort
the categories b
y
count
(
Limit
ca
t
egory coun
t
s
t
o
b
e less than or
equal to 10.).
where the ob
j
ect
b
eing measured is
spanned by a whole
n
umber of length
u
nits wit
h
no gaps
o
r overlaps.
A.
Tell and Write
T
im
e
1
.
MD
.
3
:
Tell an
d
write tim
e
in
h
ours
and half
-
f
f
h
ours
u
sing analog and
d
igital clocks.
A.
R
epresent an
d
Interpret
D
ata
1
.
MD
.
4
:
O
rganize,
represent, and
interpret data with
u
p to t
h
ree
categories; ask and
answer questions
a
b
out the total
n
um
b
er of data
points,
h
ow man
y
in ea
ch
ca
t
egory,
2.
MD
.
3
:
Estimate
lengt
h
s using
u
nits
o
f inches, feet,
centimeters, and
me
t
ers.
2.
MD
.
4
:
M
easure to
d
etermine ho
w
muc
h
longer one
o
b
j
ect is than
anot
h
er, expressing
t
h
e lengt
h
d
ifference in terms
o
f a standard length
u
nit
.
continued from previous page

72 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
and how many
more or less are in
one category than
in another.
A. Relate Addition
and Subtraction to
Length
2.MD.5: Use
addition and
subtraction within
100 to solve word
problems involving
lengths that are
given in the same
units (e.g., by using
drawings - such as
drawings of rulers
and equations with
a symbol for the
unknown number
to represent the
problem.
2.MD.6: Represent
whole numbers as
lengths from zero
on a number line
diagram with
equally spaced
points
corresponding to
the number 0, 1, 2,
…, and represent
whole-number
sums and
and how man
y
more or less are in
o
ne category t
h
an
in anot
h
er
.
A.
R
elate A
dd
ition
and Su
b
traction to
L
engt
h
2
.MD.5
:
Use
a
dd
ition an
d
subtraction within
100 to solve word
problems involving
lengt
h
s t
h
at are
given in t
h
e sa
m
e
u
nits (e.g., by using
d
rawings
-
suc
h
as
d
rawings of ruler
s
and equations with
a symbol for the
u
nknown number
to represent t
h
e
problem.
2.
M
D
.6
:
R
epresent
whole numbers as
lengths from
z
er
o
o
n a num
b
er line
d
iagram with
equally spaced
points
corresponding to
the number 0, 1, 2,
…, and represent
w
h
ol
e
-
n
um
b
er
sums an
d
continued on next page

Appendix | 73
M
differences within
100 on a number
line diagram.
A. Work with Time
and Money.
2.MD.7: Tell and
write time from
analog and digital
clocks to the
nearest five
minutes, using a.m.
and p.m.
2.MD.8: Solve
word problems
involving dollar
bills, quarters,
dimes, nickels, and
pennies, using “$”
and “¢” symbols
appropriately.
Example: If you
have two dimes and
three pennies, how
many cents do you
have?
2.MD.9: Generate
measurement data
by measuring
lengths of several
objects to the
nearest whole unit,
or by making
repeated
d
ifferences within
100 on a num
b
er
line diagram.
A.
Wor
k
with Time
an
d
M
o
ne
y
.
2.
M
D.7
:
Tell an
d
write time from
analog and digital
cloc
k
s to the
n
earest five
minutes, using a.m.
and p.m.
2.
M
D.
8
:
S
olve
word problems
involving dollar
b
ills, quarters,
d
imes, nickels, and
pennies, using “
$
”
an
d
“
¢
”
symbols
appropriately.
Example: If you
h
ave
t
w
o
d
imes an
d
t
h
re
e
pennies,
h
o
w
many cents do you
h
ave?
2
.MD.
9
:
Generate
measurement
d
ata
b
y measuring
lengths of several
o
b
j
ects to the
n
earest w
h
ole unit,
o
r by making
re
p
eated
continued from previous page

74 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
measurements of
the same object.
Show the
measurements by
making a line plot,
where the
horizontal scale is
marked off in
whole-number
units.
A. Represent and
Interpret Data
2.MD.10: Draw a
picture graph and a
bar graph (with
single-unit scale) to
represent a data set
with up to four
categories. Solve
simple put-
together, take-apart,
and compare
problems using
information
presented in a bar
graph.
measurements of
the same ob
j
ect.
Sh
ow t
h
e
measuremen
ts
by
ma
k
ing a line plot,
w
h
ere t
h
e
h
orizontal scale is
marke
d
off in
w
h
ol
e
-
n
um
b
er
u
nits.
A.
R
epresent and
Interpret
D
ata
2
.MD.1
0
:
D
raw a
picture graph and a
b
ar graph (with
singl
e
-
u
nit scale
)
to
represent a data set
with up to four
categories. Solve
simple put
-
together, ta
ke
-
apar
t
,
and compare
problems using
inf
o
rmati
o
n
presented in a bar
grap
h
.

Appendix | 75
M
Domain: Mathematics
Strand: Geometry
Standard: Identify and describe shapes/reason with shapes and their attributes.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Use objects and
toys more
purposefully,
exploring cause and
effect relationships
(e.g., put round
shapes into the
round holes more
accurately).
Show interest in
concepts, such as
matching and
sorting according
to color, shape and
size (e.g., can
match the colors
and shapes in a
matching puzzle).
Show beginning
interest in geometry
(e.g., make
symmetrical
designs with shape
blocks, find
examples of shapes
in the
environment).
A. Identify and
Describe Two-
Dimensional Shapes
(Circles, Triangles,
Rectangles;
Including a Square
Which is a Special
Rectangle)
PK.G.1: Match like
(congruent and
similar) shapes.
PK.G.2: Group the
shapes by attributes.
A. Identify and
Describe Shapes
(Squares, Circles,
Triangles,
Rectangles,
Hexagons, Cubes,
Cones, Cylinders,
and Spheres)
K.G.1: Describe
objects in the
environment using
names of shapes,
and describe the
relative positions of
these objects using
terms such as
above, below,
beside, in front of,
behind, and next
to.
K.G.2: Correctly
name shapes
regardless of their
orientations or
overall size.
A. Reason with
Shapes and Their
Attributes
1.G.1: Distinguish
between defining
attributes (e.g.,
triangles are closed
and three-sided)
versus non-defining
attributes (e.g.,
color, orientation,
overall size); build
and draw shapes to
possess defining
attributes.
1.G.2: Compose
two-dimensional
shapes (rectangles,
squares, trapezoids,
triangles, half-
circles, and quarter-
circles) or three-
dimensional shapes
(cubes, right
rectangular prisms,
A. Reason with
Shapes and Their
Attributes
2.G.1: Recognize
and draw shapes
having specific
attributes, such as a
given number of
angles or a given
number of equal
faces. Identify
triangles,
quadrilaterals,
pentagons,
hexagons, and
cubes.
2.G.2: Partition a
rectangle into rows
and columns of
same-size squares
and count to find
the total number of
them.
Use ob
j
ects and
t
oys more
purposefully,
exploring cause and
effect relationships
(
e.g., put round
s
h
apes into t
h
e
roun
d
holes more
accurately).
1 Year
Sh
ow interest in
concepts, suc
h
as
matching and
sorting according
to color, s
h
ap
e
an
d
size (e.g., can
matc
h
t
h
e colors
and shapes in a
matc
h
ing puzzle).
yp
2
Year
s
S
how beginning
interest in geometr
y
(
e.g., ma
k
e
symmetrical
d
esigns with shape
b
locks,
f
in
d
examples of shapes
in t
h
e
environment
)
.
p
3
Year
s
A.
Identify and
D
escribe Tw
o
-
D
imensional S
h
apes
(
Circles,
T
riangles,
R
ectangles;
Including a Squa
r
e
W
h
ic
h
is a Special
R
ectangle)
P
K
.
G
.
1:
M
at
c
h li
k
e
(
congruent and
similar) s
h
apes.
P
K
.
G
.
2: Group t
h
e
shapes by attributes.
p
4
Year
s
A.
Identify and
D
escri
b
e
S
h
a
p
e
s
(
Squares, Circles,
T
riangles,
R
ectangles,
H
exagons, Cubes,
Cones, Cylinders,
and Spheres)
K
.
G
.1
:
D
escri
b
e
o
b
j
ects in the
environment using
n
ames of sha
p
e
s
,
and descri
b
e the
relative positions of
these ob
j
ects using
terms suc
h
as
above, below,
b
eside, in front of,
b
ehind, and next
t
o
.
K
.
G
.2
:
Correctl
y
n
ame s
h
apes
regardless of their
o
rientations or
o
verall size.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A.
R
eason wit
h
S
hapes and Their
A
ttri
b
ute
s
1
.
G
.1
:
D
istinguis
h
b
etween defining
attributes (e.g.,
triangles are closed
an
d
thre
e
-
sided
)
ve
r
sus no
n
-
d
efining
attributes (e.g.,
color, orientation,
o
verall size
)
; build
and draw shapes to
possess defining
attri
b
utes.
1
.
G
.2
:
C
ompose
t
w
o
-
d
imensional
s
h
apes (rectangles,
sq
u
ares, trapezoids,
triangles, half
-
f
f
circles, and quarter
-
circles
)
or t
h
re
e
-
d
imensional shapes
(
cubes, right
rectangular prisms,
A.
R
eason wit
h
S
hapes and Their
A
ttri
b
ute
s
2.
G
.1
:
R
ecognize
and draw shapes
h
aving specific
attributes, such as a
Gra
d
e
2
given number of
angles or a given
n
um
b
er
o
f equal
f
aces. Identif
y
triangles,
quadrilaterals,
pen
t
agons,
h
exagons, and
cu
b
es.
2.
G
.2
:
P
artiti
o
n a
rectangle into rows
an
d
columns of
sam
e
-
size squares
an
d
count to fin
d
the total num
b
er of
t
h
em
.
D
o
main
:
M
at
h
ematic
s
S
tran
d:
Geometr
y
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Identify and describe shapes/r
eason with shapes and their attributes
.

76 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
A. Work with
Three-Dimensional
Shapes to Gain
Foundation for
Geometric Thinking
PK.G.3: Match and
sort three-
dimensional shapes.
K.G.3: Identify
shapes as two-
dimensional (lying
in a plane, “flat”) or
three-dimensional
(“solid”).
right circular cones,
and right circular
cylinders) to create
a composite shape,
and compose new
shapes from the
composite shape.
1.G.3: Partition
circles and
rectangles into two
and four equal
shares, describe the
shares using the
words halves,
fourths, and
quarters, and use
the phrases half of,
fourth of, and
quarter of.
Describe the whole
as two of, or four
of the shares.
Understand for
these examples that
decomposing into
more equal shares
creates smaller
shares.
2.G.3: Partition
circles and
rectangles into two,
three, or four equal
shares, describe the
shares using the
words halves,
thirds, half of, a
third of, etc., and
describe the whole
as two halves, three
thirds, four fourths.
Recognize that
equal shares of
identical wholes
need not have the
same shape.
A.
Wor
k
with
T
h
re
e
-
D
imensional
Sh
apes to Gain
F
oun
d
ation for
Geometric Thin
k
in
g
P
K
.
G
.
3:
M
atch an
d
sort t
h
re
e
-
d
imensional shapes.
K
.
G
.
3
:
I
dentif
y
s
h
apes as
t
w
o
-
d
imensional (lying
in a plane, “flat”) or
t
h
re
e
-
d
imensional
(
“solid”).
rig
h
t circular cones,
and right circular
cylinders) to create
a composite s
h
ape,
and compose ne
w
shapes from the
composite s
h
ape.
1
.
G
.
3
:
P
artiti
o
n
circles an
d
rectangles into two
and four equal
shares, describe the
s
h
ares using t
h
e
words halves,
f
ourths, and
quarters, and use
the phrases half
o
f,
f
ourth of, and
quarter of.
D
escribe the whole
as two of, or four
o
f the shares.
U
nd
erstan
d
for
t
h
ese examples t
h
at
d
ecomposing into
m
o
re equal s
h
ares
creates smaller
s
h
ares.
2.
G
.
3
:
P
artiti
o
n
circles an
d
rectangles into two,
three, or four equal
shares, describe the
s
h
ares using t
h
e
words halves,
thirds, half of, a
third of, etc., and
d
escribe the whole
as two
h
alves, t
h
ree
thirds, four fourths.
R
ecognize t
h
at
equal shares of
identical wholes
n
eed not hav
e
t
h
e
same s
h
ape.
continued on next page

Appendix | 77
M
PK.G.4: Describe
three-dimensional
objects using
attributes.
PK.G.5: Compose
and describe
structures using
three-dimensional
shapes. Descriptions
may include shape
attributes, relative
position, etc.
A. Analyze,
Compare, Create,
and Compose
Shape
K.G.4: Analyze and
compare two- and
three-dimensional
shapes, in different
sizes and
orientations, using
informal language
to describe their
similarities,
differences, parts
(e.g., number of
sides and vertices
/”corners”) and
other attributes
(e.g., having sides
of equal length).
K.G.5: Model
shapes in the world
by building shapes
from components
(e.g., sticks and clay
balls) and drawing
shapes.
K.G.6: Compose
simple shapes to
form larger shapes.
For example, “Can
you join these two
triangles with full
sides touching to
make a rectangle?”
P
K
.
G
.
4:
D
escri
b
e
t
h
re
e
-
d
imensional
o
b
j
ects using
attri
b
utes.
P
K.G.5:
C
ompose
and descri
b
e
structures using
t
h
re
e
-
d
imensional
s
h
apes.
D
escriptions
may include shape
attributes, relative
position, etc.
A.
A
nalyze,
C
ompare,
C
rea
te
,
and Compose
S
h
ap
e
K
.
G
.
4
:
A
nalyze and
compare
t
w
o
-
an
d
t
h
re
e
-
d
imensional
shapes, in different
sizes an
d
o
rientations, using
informal language
to descri
b
e their
similarities,
d
ifferences, parts
(
e.g., number of
sides and vertice
s
/
”corners”
)
and
o
ther attri
b
utes
(
e.g., having sides
o
f equal length).
K.G.5
:
M
o
d
el
shapes in the world
b
y building shapes
f
rom components
(
e.g., sticks and cla
y
b
alls) and drawing
s
h
apes.
K
.
G
.6
:
C
ompose
simple s
h
apes to
f
orm larger shapes.
F
or example, “Can
you
j
oin t
h
ese two
triangles with full
sides touching to
ma
k
e a rectangle?”
continued from previous page

78 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Social Studies
Strand: Political Science
Standard: Students will understand the historical development and current status of the democratic principles and the development
of skills and attitudes necessary to become responsible citizens.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Gain in self-control
and regulation (e.g.,
stop hitting another
child when you say
the child’s name,
allow another child
to use a favored
toy).
Have beginning
understanding of
consequences when
following routines
and recreating
familiar events (e.g.,
participate in
creating class rules,
accept the
consequences of
his actions, and say,
“I’m sorry” when
prompted).
Show increasing
self-regulation (e.g.,
gain control of
emotions with help
of trusted adult or
comfort item, begin
to wait turn for
juice or snack).
Have beginning
understanding of
consequences when
following routines
and recreating
familiar events (e.g.,
try to follow the
rules of a simple
board game and
become frustrated
when not
understanding why
something has
changed, help to
clean up, saying,
“We are a team”).
Have increased
self-regulation,
following
classroom rules and
routines and
guidance (e.g.,
manage transitions
between activities
with a few
reminders, use
classroom materials
respectfully).
A. The Foundations
and Function of
Government
1. Identify the
importance of rules.
A. The
Foundations and
Function of
Government
1. Identify the
importance of
rules.
A. The
Foundations and
Function of
Government
1. Explain the
importance of
rules.
A. The
Foundations and
Function of
Government
1. Explain how
rules and laws are
made and necessary
to maintain order
and protect citizens.
continued on next page
Gain in self
-
f
f
c
ontrol
and regulatio
n
(
e.g.,
stop
h
itting anot
h
er
child when you sa
y
the chil
d
’s nam
e
,
allow another child
to use a favored
toy
)
y
y
.
1 Year
H
ave beginning
u
nderstanding of
consequences w
h
en
f
ollowing routines
and recreating
f
amiliar event
s
(
e.g.,
participate in
creating class rules,
accept t
h
e
consequences of
h
is actions, and say,
“I’m sorry” w
h
en
prompted)
.
Sh
ow increa
s
ing
self
-
f
f
regulatio
n
(
e.g.,
gain control of
emotions wit
h
h
elp
o
f truste
d
a
d
ult or
comfort item, begin
to wait turn for
j
uice or snac
k
)
.
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
H
ave beginning
u
nderstanding of
consequences w
h
en
f
ollowing routines
and recreating
f
amiliar event
s
(
e.g.,
try to fol
l
o
w t
h
e
rules of a simple
b
oard game and
b
ecome frustrated
w
h
en not
u
nderstanding wh
y
somet
h
ing
h
as
change
d
,
h
elp to
clean up, saying,
“We are a team
”
)
.
H
ave increased
self
-
f
f
regulation,
f
ollowing
classroom rules an
d
routines an
d
guidanc
e
(
e.g.,
manage
t
ransitions
b
etween activities
with a fe
w
reminders, use
classroom materials
respectfully)
.
4
Year
s
A
. The Foun
d
ations
an
d
Function of
Government
1
.
Identify the
importance of rule
s
.
Kindergarte
n
A.
The
F
oun
d
ations an
d
F
un
c
tion of
Government
1
.
Identify the
importance of
rule
s
.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
The
F
oun
d
ations an
d
F
un
c
tion of
Government
1
.
Explain t
h
e
importance of
rule
s
.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
The
F
oun
d
ations an
d
F
un
c
tion of
Government
1. Explain
h
o
w
rules and laws are
made and necessar
y
to
maintain or
d
er
and protect citizen
s
.
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
S
tran
d:
P
olitical Scienc
e
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will understand the historical development and current status of the democratic principles and the development
o
f skills and attitudes necessary to become responsible citizens.

Appendix | 79
M
Rely on trusted
adults to feel safe
trying new activities
(e.g., look to you
for reassurance, for
example, a word, a
smile or a gesture).
Continue to need
the adult approval
but show more
independence (get
up from the lunch
table after a few
bites, following
mom as she leaves
the room, then
returning after
knowing what she
is doing).
Imitate and try to
please familiar
adults (e.g., pick up
own trash after
seeing the task
modeled by a
caregiver, pretend
to wash the dishes
and put them away
in places where the
teacher has shown
where they belong).
2. Identify symbols
and practices
associated
with the
United States
of America.
B. Individual and
Group Participation
in the Political
System
1. Recognize people
important to the
American political
system.
C. Protecting Rights
and Maintaining
Order
1. Identify the roles,
rights, and
responsibilities of
being a member of
the family and
school.
2. Identify symbols
and practices
associated with the
United States of
America.
B. Individual and
Group
Participation in the
Political System
1. Identify people
important to the
American political
system.
C. Protecting
Rights and
Maintaining Order
1. Describe the
roles, rights, and
responsibilities of
being a member of
the family and
school.
2. Identify and
discuss the
meaning of
symbols and
practices associated
with the United
States of America.
B. Individual and
Group
Participation in the
Political System
1. Identify and
describe people
important to the
American political
system.
C. Protecting
Rights and
Maintaining Order
1. Describe the
rights and
responsibilities of
being a
participating
member of the
family, school and
neighborhood.
2. Explain how
democratic skills
and attitudes are
associated with
being a responsible
citizen.
B. Individual and
Group Participation
in the Political
System
1. Explain how
contributions and
events are
important to the
American political
system.
C. Protecting
Rights and
Maintaining Order
1. Describe the
rights and
responsibilities of
being a
participating
member of the
school and the
community.
continued from previous page
R
ely on trusted
a
d
ults to feel safe
trying new activities
(
e.g., loo
k
to you
f
or reassurance, for
example, a word, a
smile or a gesture).
Continue to nee
d
the adult approval
b
ut show more
independenc
e
(
get
u
p from the lunch
table after a fe
w
b
ites, following
mom as s
h
e leaves
t
h
e room, t
h
en
returning after
k
nowing what she
is doing)
.
Imitate and try to
please familiar
a
d
ult
s
(
e.g., pic
k
up
o
wn trash after
seeing the tas
k
modeled by a
caregiver, pretend
to wash the dishes
and put them awa
y
in places w
h
ere t
h
e
teac
h
er
h
as s
h
own
where they belong)
.
2
.
Identify symbols
and practice
s
associate
d
wit
h
t
h
e
Unite
d
States
o
f Ameri
c
a
.
B. Individual and
Group Participation
in t
h
e Politi
c
al
S
yste
m
1. Recognize people
important to t
he
A
merican political
sys
t
e
m
.
C. Protecting Rig
h
ts
and Maintaining
O
r
d
er
1. Identify the roles,
rights, an
d
responsibilities of
b
eing a member of
the family and
sc
h
oo
l
.
2
.
Identify
s
ymbols
and practices
associate
d
wit
h
t
h
e
Unite
d
States of
A
meri
c
a
.
B. Individual and
Group
P
articipation in t
h
e
P
olitical Syste
m
1. Identify people
important to t
he
A
merican political
sys
t
e
m
.
C
. Protecting
R
ig
h
ts an
d
M
aintaining Order
1. Descri
b
e the
roles, rights, an
d
responsibilities of
b
eing a member
o
f
t
h
e
f
amily and
sc
h
oo
l
.
2
.
Identify and
d
i
s
cuss t
h
e
meaning of
symbols and
practices associated
with the United
S
tates of America
.
B. Individual and
Group
P
articipation in t
he
P
olitical Syste
m
1. Identify a
nd
d
escribe people
important to t
h
e
A
merican political
sys
t
e
m
.
C
. Protecting
R
ights and
M
aintaining Order
1. Descri
b
e the
rights and
responsibilities of
b
eing a
participating
mem
b
er of t
h
e
f
amily, school an
d
n
eighborhoo
d
.
2
. Explain
h
o
w
d
emocratic skills
an
d
attitu
d
es ar
e
associated with
b
eing a responsible
c
itizen
.
B. Individual and
Group Participation
in t
he
P
oliti
c
al
S
yste
m
1. Explain
h
ow
contri
b
utions and
even
t
s are
important to t
h
e
A
merican political
sys
t
e
m
.
C
. Protecting
R
ights and
M
aintaining Order
1. Descri
b
e the
rig
h
ts an
d
responsibilities of
b
eing a
participating
mem
b
er of the
school an
d
th
e
communit
y
.

80 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Social Studies
Strand: Peoples of the Nation and the World
Standard: Students will understand how people in Maryland, the United States and around the world are alike and different.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Begin to be aware
of the feelings of
other children (e.g.,
think that other
children would like
the same games or
food as he does,
look sad or worried
when another child
is in distress and
seek comfort from
either a caregiver or
cuddly toy).
Interact with other
children (e.g.,
choose to play in
the same area as
another child, offer
a toy to another
Show more
awareness of the
feelings of another
child (e.g., feel and
express remorse by
saying “I sorry”
after accidentally
knocking another
child down,
comfort another
child who may be
upset by patting or
hugging the child).
Play alongside
other children (e.g.,
need adult help to
resolve conflicts,
have short periods
of play with other
Be able to better
understand the
feelings of other
children (e.g., share
a toy car with a
child who cries
because of not
having one, watch
other children to
see how they react).
Participate, with
help, in the group
life of the class
(e.g., help to clean
up after hearing the
signal and being
A. Elements of
Culture
1. Identify
themselves as
individuals and
members of families
that have the same
human needs as
others.
B. Cultural
Diffusion
C. Conflict and
Compromise
1. Identify how
groups of people
interact.
A. Elements of
Culture
1. Identify
similarities and
differences in
people’s
characteristics,
habits, and living
patterns to describe
how they meet the
same human needs.
B. Cultural
Diffusion
C. Conflict and
Compromise
1. Demonstrate
how groups of
people interact.
A. Elements of
Culture
1. Observe and
describe ways that
people of different
Cultural
backgrounds meet
human needs and
contribute to the
community.
B. Cultural
Diffusion
1. Recognize that
individuals and
groups share and
borrow from other
cultures.
C. Conflict and
Compromise
1. Explain how
groups of people
interact.
A. Elements of
Culture
1. Analyze elements
of two different
cultures and how
each meets their
human needs and
contributes to
the community.
B. Cultural
Diffusion
1. Explain that
individuals and
groups share and
borrow from other
cultures to form a
community.
C. Conflict,
Cooperation and
Compromise
1. Analyze ways in
which people
interact.
1 Year
Begin t
o
b
e aware
o
f the feelings of
o
ther children (e.g.,
thin
k
that
o
ther
children would like
t
h
e same games or
f
oo
d
as he does,
look sad or worried
when another child
is in
d
istress an
d
see
k
comfort from
eit
h
er a caregiver or
cuddly toy).
Intera
c
t wit
h
ot
h
er
children (e.g.,
c
h
oose to play in
t
h
e same area as
another child, offer
a toy to anot
h
er
2
Year
s
Sh
ow more
awareness of the
f
eelings of another
child (e.g., feel and
express remorse b
y
saying “I sorry
”
after accidentall
y
k
noc
k
ing another
child down,
c
omfort another
child who may be
u
pset by patting or
h
ugging the child)
.
P
lay alongside
o
ther children (e.g.,
n
eed adult help to
resolve conflicts,
h
ave short periods
o
f play with other
pp y
3
Year
s
Be a
b
le to
b
etter
u
n
d
erstan
d
the
f
eelings of other
children (e.g., share
a toy car wit
h
a
child who cries
b
ecause of not
h
aving one, watc
h
o
ther chil
d
ren to
see
h
ow t
h
ey react).
P
articipate, wit
h
h
elp, in t
h
e gr
o
u
p
life of the class
(
e.g.,
h
elp to clean
u
p after hea
r
ing the
signal and being
y,
4
Year
s
A.
Elements of
C
ultur
e
1. Identif
y
t
h
emselves as
individuals an
d
mem
b
ers of families
t
h
at
h
ave t
h
e sam
e
h
uman nee
d
s as
o
t
h
er
s
.
B
.
C
ultural
D
iffusio
n
C.
Conflict an
d
C
ompromis
e
1. Identify ho
w
groups of people
intera
c
t
.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Elements of
C
ultur
e
1. Identif
y
similarities an
d
d
ifferences in
people’
s
c
h
aracteristics,
h
abits, and living
patterns to describ
e
h
ow t
h
ey meet t
h
e
same human nee
ds
.
B
.
C
ultural
D
iffusio
n
C. Conflict an
d
C
ompromis
e
1.
D
emonstrate
h
ow groups of
people interact
.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Elements of
C
ultur
e
1. O
b
serve and
d
escribe ways that
people of different
C
ultural
b
ackgrounds mee
t
h
uman nee
d
s an
d
contri
b
ute t
o
t
h
e
communit
y
.
B
.
C
ultural
D
iffusio
n
1. Recognize t
h
at
individ
u
als an
d
groups share and
b
orro
w
f
r
o
m
o
ther
culture
s
.
C. Conflict an
d
C
ompromis
e
1. Explain
h
o
w
groups of people
intera
c
t
.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
Elements of
C
ultur
e
1. Analyze elements
o
f two different
culture
s
an
d
h
o
w
eac
h
meets t
h
eir
h
uman nee
d
s an
d
contri
b
utes t
o
t
h
e communit
y
.
B
.
C
ultural
D
iffusio
n
1. Explain t
h
at
individuals and
groups share an
d
b
orrow from other
culture
s
t
o
f
o
rm a
communit
y
.
C.
Conflict,
Cooperation and
C
ompromis
e
1. Analyze ways in
w
h
ic
h
people
intera
c
t
.
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
S
tran
d:
P
eoples of the Nation and the Worl
d
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Students will understand how people in Maryland, the United States and around the world are alike and different.
continued on next page

Appendix | 81
M
child, but show
distress when he
takes it).
children, but
mostly play beside
them).
encouraged by you,
join in group games
such as playing
“Farmer in the
Dell”).
child, but sho
w
d
istress when he
takes it
).
t
children, but
mostly play beside
t
h
em
)
.
encouraged by you,
j
oin in group games
suc
h
as playing
“Farmer in t
h
e
D
ell”
)
.
continued from previous page

82 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Social Studies
Strand: Geography
Standard: Students will use geographic concepts and processes to understand location and its relationship to human activities.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Using
Geographic Tools
1. Recognize that a
globe and maps are
used to help people
locate places.
B. Geographic
Characteristics of
Places and Regions
1. Recognize that
places in the
immediate
environment have
specific physical and
human-made
features.
C. Movement of
People, Goods and
Ideas
1. Identify the role
of transportation in
the community.
A. Using
Geographic Tools
1. Identify and
describe how a
globe and maps
can be used to help
people locate
places.
B. Geographic
Characteristics of
Places and Regions
1. Describe places
in the immediate
environment
Using natural/
physical and
human-made
features.
C. Movement of
People, Goods and
Ideas
1. Describe how
transportation and
communication
link people and
places.
1. Using
Geographic Tools
1. Use geographic
tools to locate and
describe places on
Earth.
B. Geographic
Characteristics of
Places and Regions
1. Describe places
in the environment
using geographic
characteristics.
C. Movement of
People, Goods and
Ideas
1. Explain how
transportation and
communication
link people and
places by the
movement of
goods, messages,
A. Using
Geographic Tools
1. Use geographic
tools to locate and
describe places on
Earth.
B. Geographic
Characteristics of
Places and Regions
1. Classify places
and regions in an
environment using
geographic
characteristics.
C. Movement of
People, Goods and
Ideas
1. Explain how
transportation and
communication
link places by the
movement of
people, goods, and
ideas.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
A
. Using
Geograp
h
ic Tool
s
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
at a
globe and maps ar
e
u
sed to help people
lo
c
ate place
s
.
B. Geograp
h
ic
Characteristics of
P
laces and Region
s
1. Recognize t
h
at
places in t
he
imme
d
iate
environment
h
ave
specific p
h
ysical an
d
h
uman
-
ma
d
e
f
eature
s
.
C. Movement of
P
eople, Goo
d
s an
d
I
d
ea
s
1. Identify the role
o
f transportation i
n
t
h
e communit
y
.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Using
Geograp
h
ic Tool
s
1. Identify and
d
escribe how a
globe an
d
map
s
can be used to help
people locate
place
s
.
B. Geograp
h
ic
Characteristics of
P
lace
s
and Region
s
1. Describe places
in the imme
d
iate
environment
Using
n
atural
/
p
h
ysical an
d
h
uman
-
ma
de
f
eature
s
.
C. Movement of
P
eople, Goods and
Id
ea
s
1. Describe ho
w
transportation an
d
c
ommuni
c
ation
link people and
place
s
.
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
Using
Geograp
h
ic Tool
s
1
.
Use geograp
h
ic
tools to locate an
d
d
escri
b
e place
s
o
n
Eart
h
.
B. Geograp
h
ic
Characteristics of
P
laces and Region
s
1
.
D
escribe places
in t
h
e environment
u
sing geograp
h
ic
c
h
aracteristic
s
.
C. Movement of
P
eople, Goods and
I
d
ea
s
1. Explain
h
o
w
transportation and
c
ommuni
c
ation
lin
k
people and
places
b
y the
movemen
t
o
f
good
s
,
m
e
ss
age
s
,
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Using
Geograp
h
ic Tool
s
1. Use geograp
h
ic
tools to locate an
d
d
escri
b
e place
s
o
n
Eart
h
.
B
.
Geograp
h
ic
Characteristics of
P
laces and Region
s
1. Classif
y
places
and regions in an
e
n
vironment
u
sing
geograp
h
ic
c
h
aracteristic
s
.
C. Movement of
P
eople, Goods and
I
d
ea
s
1. Explain
h
o
w
transportation and
c
ommuni
c
ation
lin
k
places
b
y the
movemen
t
o
f
people, good
s
, an
d
i
d
ea
s
.
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
S
tran
d:
Geograp
hy
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will use
g
eo
g
ra
p
hic conce
p
ts and
p
rocesses to understand location and its relationshi
p
to human activities.
continued on next page

Appendix | 83
M
Explore more
complex situations
and concepts,
beginning to
understand some
people’s jobs and
care for the
environment.
D. Modifying and
Adapting to the
Environment
1. Describe how
people adapt to their
immediate
environment.
D. Modifying and
Adapting to the
Environment
1. Describe how
people adapt to and
modify their
immediate
environment.
and people.
D. Modifying and
Adapting to the
Environment
1. Explain how
people modify,
protect, and adapt
to their
environment.
D. Modifying and
Adapting to the
Environment
1. Explain how
people modify,
protect, and adapt
to their
environment.
Explore more
complex situations
and concepts,
b
eginning to
u
n
d
erstan
d
some
people’s
j
obs and
c
are for the
environment.
D
. Modifying and
A
dapting to th
e
Environment
1. Describe ho
w
people adapt to their
imme
d
iate
environment
.
D
. Modifying and
A
dapting to th
e
Environment
1. Descri
be
h
o
w
people adapt to and
modif
y
t
h
eir
imme
d
iate
environment
.
and peopl
e
.
D
. Modifying and
A
dapting to the
Environment
1. Explain
h
o
w
people modify,
protect, and adapt
t
o
t
h
eir
environment
.
D
. Modifying and
A
dapting to the
Environment
1. Explain
h
o
w
people modify,
protect, and adapt
to
t
h
eir
environment
.
continued from previous page

84 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Social Studies
Strand: Economics
Standard: Students will identify the economic principles and processes that are helpful to producers and consumers when making
good decisions.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Scarcity and
Economic Decision-
Making
1. Recognize that
people have to make
choices because of
unlimited economic
wants.
2. Identify that
materials/resources
are used to make
products.
3. Explain how
technology affects
the way people live,
work, and play.
B. Economic
Systems and the
Role of
Government in the
Economy
1. Identify types of
local markets.
A. Scarcity and
Economic
Decision-Making
1. Describe choices
people make
because of
unlimited economic
wants.
2. Identify that
resources are used
to make products.
3. Explain how
technology affects
the way people live,
work, and play.
B. Economic
Systems and the
Role of
Government in the
Economy
1. Identify types of
local markets.
A. Scarcity and
Economic
Decision-making
1. Describe
economic choices
people make about
goods and services.
2. Describe the
production process.
3. Explain how
technology affects
the way people live,
work, and play.
B. Economic
Systems and the
Role of
Government in
the Economy
1. Describe types
of markets in the
community.
A. Scarcity and
Economic
Decision-Making
1. Explain why
people have to
make economic
choices about
goods and services.
2. Explain the
production process.
3. Examine how
technology affects
the way people live,
work and play.
B. Economic
Systems and the
Role of
Government in
the Economy
1. Describe
different types of
markets.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
A
. Scarcity and
Economic Decision
-
M
a
k
ing
1. Recognize t
h
at
people have to ma
ke
choices
b
ecause of
u
nlimite
d
e
c
onomi
c
wan
ts
.
2
. Identify that
materials
/
resources
a
re
u
se
d
to make
product
s
.
3
. Explain
h
o
w
tec
h
nolog
y
affects
t
he
way people live,
work, and pla
y
.
B. E
c
onomi
c
S
ystems and the
Ro
l
e
o
f
Government in t
h
e
Econom
y
1. Identify types of
lo
c
al mar
k
ets.
Kindergarte
n
A.
S
carcity and
E
c
onomi
c
D
ecision
-
M
a
k
ing
1. Descri
be
c
h
oices
people ma
k
e
b
ecause of
u
nlimite
d
e
c
onomi
c
wan
ts
.
2.
I
d
entify that
r
esou
r
ces a
r
e
u
se
d
t
o
ma
ke
p
ro
d
uct
s
.
3.
Explain
h
o
w
tec
h
nolog
y
affects
t
h
e wa
y
people live,
work, and pla
y
.
B. E
c
onomi
c
S
ystems and the
Ro
le
o
f
Government in t
h
e
Econom
y
1. Identify types of
lo
c
al mar
k
et
s
.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Scarcity and
E
c
onomi
c
D
ecision
-
ma
k
ing
1. Descri
b
e
economic c
h
oices
people make about
goods an
d
service
s
.
2.
D
escri
b
e the
production proces
s
.
3
. Explain
h
o
w
tec
h
nolog
y
affects
t
h
e
w
ay people live,
work, and pla
y
.
B. E
c
onomi
c
S
ystems and the
Ro
le
o
f
Government in
t
h
e Econom
y
1. Describe types
o
f mar
k
ets in t
h
e
community.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Scarcity and
E
c
onomi
c
De
cisio
n
-
M
a
k
ing
1. Explain w
hy
people
h
ave to
ma
k
e e
c
onomi
c
c
h
oice
s
a
b
out
goods an
d
service
s
.
2
. Explain t
h
e
production proces
s
.
3.
Examine
h
o
w
tec
h
nolog
y
affects
t
h
e way people live,
work and pla
y
.
B. E
c
onomi
c
S
ystems and the
Ro
le
o
f
Government i
n
t
h
e Econom
y
1. Descri
b
e
d
ifferent types of
mar
k
ets.
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
S
tran
d:
Economic
s
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will identify the economic principles and processes that are helpful to producers and consumers when making
good decisions.
continued on next page

Appendix | 85
M
2. (Indicator begins
in Grade 3)
2. Identify how
goods are acquired.
2. (Indicator begins
in Grade 3)
2. Describe how
goods are acquired.
2. (Indicator begins
in Grade 3)
2. Describe how
goods and services
are acquired.
2. (Indicator begins
in Grade 3)
2. Describe how
consumers acquire
goods and
Services.
2
. (Indicator begins
in Grade 3
)
2
. Identify ho
w
goods are acquired.
2
. (Indicator begins
in Grade 3
)
2
. Describe ho
w
goods are acquired.
2
. (Indicator begins
in Grade 3
)
2
. Describe ho
w
goods an
d
servic
e
s
are acquired.
2
. (Indicator begins
in Grade 3
)
2
. Describe ho
w
consumers acquire
goods an
d
S
ervices.
continued from previous page

86 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Social Studies
Strand: History
Standard: Students will use historical thinking skills to understand how individuals and events have changed society over time.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Change Over
Time
1. Distinguish
among past, present,
and future time.
A. Change Over
Time
1. Distinguish
among past,
present, and future
time.
2. Compare daily
life and objects of
today and long ago.
A. Individuals and
Societies Change
Over Time
1. Examine
differences
between past and
present time.
2. Compare people
and objects of
today and long ago.
A. Individuals and
Societies Change
Over Time
1. Examine
differences between
past and present
time.
2. Describe people,
places and artifacts
of today and long
ago.
1 Year
2
Year
s
g
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
A
. Change Ove
r
T
im
e
1. Distinguis
h
among pas
t
, presen
t
,
an
d
futur
e
t
ime
tt
.
A
. Change Ove
r
T
im
e
1. Distinguis
h
among pas
t
,
present, and
f
uture
tim
e
.
2
.
Compare dail
y
life and ob
j
ects of
today and long ag
o
.
Kindergarte
n
g
Gra
d
e
1
A.
I
n
d
ividuals and
S
ocieties C
h
ange
O
ver
T
im
e
1
.
Examine
d
ifferences
b
etween past and
presen
t
tim
e
.
2
. Compare people
and ob
j
ects of
today and long ag
o
.
A
. Individuals and
S
ocieties C
h
ange
O
ver
T
im
e
1
.
Examin
e
d
ifferences between
past and present
tim
e
.
2
.
Describe people,
place
s
an
d
artifacts
o
f today and long
a
go
.
y
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
S
tran
d:
H
istor
y
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Students will use historical thinking skills to understand how individuals and events have changed
society over time.

Appendix | 87
M
Domain: Social Studies
Strand: Social Studies Skills and Processes
Standard: Students shall use reading, writing, and thinking processes and skills to gain knowledge and understanding of political,
historical, and current events using chronological and spatial thinking, economic reasoning, and historical interpretation, by framing
and evaluating questions from primary and secondary sources.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Learn to Read
and Construct
Meaning about
Social Studies
1. Develop and
apply social studies
vocabulary through
exposure to a
variety of text and
portions of text.
2. Use strategies to
prepare for reading
(before reading.)
3. Use strategies to
monitor
understanding and
derive meaning
from text and
portions of text
(during reading).
4. Use strategies to
demonstrate
understanding of the
text (after reading).
A. Learn to Read
and Construct
Meaning about
Social Studies
1. Develop and
apply social studies
vocabulary through
exposure to a
variety of text and
portions of text.
2. Use strategies to
prepare for reading
(before reading).
3. Use strategies to
monitor
understanding and
derive meaning
from text and
portions of text
(during reading).
4. Use strategies to
demonstrate
understanding of
the text (after
reading).
A. Learn to Read
and Construct
Meaning about
Social Studies
1. Develop and
apply social studies
vocabulary through
exposure to a
variety of text and
portions of text.
2. Use strategies to
prepare for reading
(before reading).
3. Use strategies to
monitor
understanding and
derive meaning
from text and
portions of text
(during reading).
4. Use strategies to
demonstrate
understanding of
the text (after
reading).
A. Learn to Read
and Construct
Meaning about
Social Studies
1. Develop and
apply social studies
vocabulary through
exposure to a
variety of text and
portions of text.
2. Use strategies to
prepare for reading
(before reading).
3. Use strategies to
monitor
understanding and
derive meaning
from text and
portions of text
(during reading).
4. Use strategies to
demonstrate
understanding of
the text (after
reading).
gq
1 Year
py
2
Year
s
yy
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
A
. Learn to Rea
d
an
d
Construct
M
eaning about
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
1. Develop and
apply social studies
vocabulary through
exposure
t
o a
variety of text and
portions of text
.
2
. Use strategies to
prepare for reading
(
before reading
.
)
3
. Use strategies to
m
o
nit
o
r
u
nderstanding and
d
erive meaning
f
rom text an
d
portions of text
(
during reading)
.
4.
Use strategies to
d
emonstrate
u
nderstanding of the
text (after reading)
.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Learn to Rea
d
an
d
Construct
M
eaning about
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
1. Develop and
apply social studies
vocabulary through
exposure
t
o a
variety of text and
portions of text
.
2
. Us
e
strategies to
prepare for reading
(
before reading)
.
3
. Use strategies to
m
o
nit
o
r
u
nderstanding and
d
erive meaning
f
rom text an
d
portions of text
(
during reading)
.
4.
Use strategies to
d
emonstrate
f
u
nderstanding o
f
the text
(
after
reading)
.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Learn to Rea
d
an
d
Construct
M
eaning about
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
1. Develop and
apply social studies
vocabulary through
exposure
t
o a
variety of text and
porti
o
ns of text
.
2
. Use strategies to
prepare for reading
(
before reading)
.
3
. Use strategies to
m
o
nit
o
r
u
nderstanding and
d
erive meaning
f
rom text an
d
portions of text
(
during reading)
.
4.
Use strategies to
d
emonstrate
f
u
nderstanding o
f
the text
(
after
reading)
.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Learn to Rea
d
an
d
Construct
M
eaning about
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
1. Develop and
apply social studies
vocabulary through
exposure
t
o a
variety of text an
d
portions of text
.
2
. Use strategies to
prepare for reading
(
before reading)
.
3
. Use strategies to
m
o
nit
o
r
u
nderstanding and
d
erive meaning
f
rom text an
d
portions of text
(
during reading)
.
4.
Use strategies to
d
emonstrate
f
u
nderstanding o
f
t
h
e text
(
after
reading)
.
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
S
tran
d:
S
ocial Stu
d
ies Skills an
d
Processe
s
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents shall use reading, writing, and thinking processes and skills to gain knowledge and understanding of political,
h
istorical, and current events using chronological and spatial thinking, economic reasoning, and historical interpretation, by framing
and evaluating questions from primary and secondary sources.

88 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
B. Learn to Write
and Communicate
Social Studies
Understandings
1. Compose oral,
written, and visual
presentations that
express personal
ideas, inform, and
persuade.
2. Locate, retrieve,
and use information
from various
sources to
accomplish a
purpose.
C. Ask Social
Studies Questions
1. Identify a topic
that requires further
study.
2. Identify a
situation or problem
that requires study.
D. Acquire Social
Studies Information
1. Identify primary
and secondary
sources of
B. Learn to Write
and Communicate
Social Studies
Understandings
1. Compose oral,
written, and visual
presentations that
express personal
ideas, inform, and
persuade.
2. Locate, retrieve,
and use
information from
various sources to
accomplish a
purpose.
C. Ask Social
Studies Questions
1. Identify a topic
that requires
further study.
2. Identify a
situation or
problem that
requires study.
D. Acquire Social
Studies
Information
1. Identify primary
and secondary
sources of
B. Learn to Write
and Communicate
Social Studies
Understandings
1. Compose oral,
written, and visual
presentations that
express personal
ideas, inform, and
persuade.
2. Locate, retrieve,
and use
information from
various sources to
accomplish a
purpose.
C. Ask Social
Studies Questions
1. Identify a topic
that requires
further study.
2. Identify a
situation or
problem that
requires study.
D. Acquire Social
Studies
Information
1. Identify primary
and secondary
sources of
B. Learn to Write
and Communicate
Social Studies
Understandings
1. Compose oral,
written, and visual
presentations that
express personal
ideas, inform, and
persuade.
2. Locate, retrieve,
and use
information from
various sources to
accomplish a
purpose.
C. Ask Social
Studies Questions
1. Identify a topic
that requires further
study.
2. Identify a
situation or
problem that
requires study.
D. Acquire Social
Studies Information
1. Identify primary
and secondary
sources of
B
.
Learn to Write
an
d
C
ommuni
c
ate
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
Understanding
s
1. Compose oral,
written, and visual
presentations t
h
at
express personal
ideas, inform, and
persuad
e
.
2
. Locate, retrieve,
an
d
use information
f
rom various
sources
to
accomplis
h
a
purpos
e
.
C. Ask Social
S
tu
d
ies Question
s
1. Identify a topic
that requires further
stud
y
.
2
. Identify a
situation or problem
that requires stud
y
.
D
. Acquire Social
S
tu
d
ies Informatio
n
1. Identify primar
y
and secondar
y
sources of
B
.
Learn to Write
an
d
Communicate
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
Understanding
s
1. Compose oral,
written, and visual
presentations t
h
at
express personal
ideas, inform, and
persuad
e
.
2
. Locate, retrieve,
an
d
use
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
various sources t
o
accomplis
h
a
purpos
e
.
C. Ask Social
S
tudies Question
s
1. Identify a topic
t
h
at requires
f
urther stud
y
.
2
. Identify a
situation or
problem that
requires stud
y
.
D
. Acquire Social
S
tu
d
ies
I
n
f
o
rmati
o
n
1. Identify primar
y
and secondar
y
sources of
B
.
Learn to Write
an
d
Communicate
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
Understanding
s
1. Compose oral,
written, and visual
presentations t
h
at
express personal
ideas, inform, and
persuad
e
.
2
. Locate, retrieve,
an
d
use
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
various sources t
o
accomplis
h
a
purpos
e
.
C. Ask Social
S
tudies Question
s
1. Identify a topic
t
h
at requires
f
urther stud
y
.
2
. Identify a
situation or
problem that
requires stud
y
.
D
. Acquire Social
S
tu
d
ies
Inf
o
rmati
on
1. Identify primar
y
and secondar
y
sources of
B
.
Learn to Write
an
d
Communicate
S
ocial Stu
d
ie
s
Understanding
s
1. Compose oral,
written, and visual
presentations t
h
at
express personal
ideas, inform, and
persuad
e
.
2
. Locate, retrieve,
an
d
use
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
various sources t
o
a
cco
mplis
h
a
purpos
e
.
C. Ask Social
S
tudies Question
s
1. Identify a topic
that requires further
stud
y
.
2
. Identify a
situation or
problem that
requires stud
y
.
D
. Acquire Social
S
tu
d
ies Information
1. Identify primar
y
and secondar
y
sources of
continued on next page

Appendix | 89
M
information that
relate to the
topic/situation/
problem being
studied.
2. Engage in field
work that relates to
the topic/
situation/ problem
being studied.
E. Organize Social
Studies Information
1. Organize
information from
non-print sources.
2. Organize
information from
print sources.
F. Analyze Social
Studies Information
1. Interpret
information from
secondary sources
including pictures,
graphics, maps,
atlases, and
timelines.
G. Answer Social
Studies Questions
information that
relate to the
topic/situation/
problem being
studied.
2. Engage in field
work that relates to
the topic/
situation/ problem
being studied.
E. Organize Social
Studies
Information
1. Organize
information from
non-print sources.
2. Organize
information from
print sources.
F. Analyze Social
Studies
Information
1. Interpret
information from
secondary sources
including pictures,
graphics, maps,
atlases, and
timelines.
G. Answer Social
Studies Questions
information that
relate to the
topic/situation/
problem being
studied.
2. Engage in field
work that relates to
the topic/
situation/ problem
being studied.
E. Organize Social
Studies
Information
1. Organize
information from
non-print sources.
2. Organize
information from
print sources.
F. Analyze Social
Studies
Information
1. Interpret
information from
secondary sources
including pictures,
graphics, maps,
atlases, and
timelines.
G. Answer Social
Studies Questions
information that
relate to the
topic/situation/
problem
being studied.
2. Engage in field
work that relates to
the topic/
situation/ problem
being studied.
E. Organize Social
Studies Information
1. Organize
information from
non-print sources.
2. Organize
information from
print sources.
F. Analyze Social
Studies Information
1. Interpret
information from
secondary sources
including pictures,
graphics, maps,
atlases, and
timelines.
G. Answer Social
Studies Questions
inf
o
rmati
o
n that
relate t
o
t
h
e
topic
/
situation
/
proble
m
b
eing
stu
d
ie
d
.
2
. Engage in field
wor
k
that relates to
the topic
/
situation
/
problem
b
eing studie
d
.
E. Organize Social
S
tu
d
ies Information
1. Organize
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
no
n
-
print source
s
.
2
. Organize
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
print source
s
.
F
.
Analyze
S
ocial
S
tu
d
ies Information
1. Interpret
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
secondary sources
including pictures,
grap
h
ics, maps,
atlases, and
timeline
s
.
G. Answer Social
S
tudies Question
s
inf
o
rmati
o
n that
relate t
o
t
h
e
topic
/
situation
/
proble
m
b
eing
stu
d
ie
d
.
2
. Engage in field
wor
k
that relates to
the topic
/
situation
/
problem
b
eing studie
d
.
E. Organize Social
S
tu
d
ies
Inf
o
rmati
on
1. Organize
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
no
n
-
print source
s
.
2
. Organize
i
nf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
print sou
r
ce
s
.
F
.
Analyze Social
S
tu
d
ies
I
nf
o
rmati
o
n
1. Interpret
i
nf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
secondary sources
i
ncluding pictures,
grap
h
ics, maps,
atlases, and
timeline
s
.
G. Answer Social
S
tudies Question
s
inf
o
rmati
o
n that
relate t
o
t
h
e
topic
/
situation
/
proble
m
b
eing
stu
d
ie
d
.
2
. Engage in field
wor
k
that relates to
the topic
/
situation
/
problem
b
eing studie
d
.
E. Organize Social
S
tu
d
ies
Inf
o
rmati
on
1. Organize
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
no
n
-
print source
s
.
2
. Organize
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
print source
s
.
F
.
Analyze Social
S
tu
d
ies
Inf
o
rmati
on
1. Interpret
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
secondary sources
including pictures,
grap
h
ics, maps,
atlases, and
timeline
s
.
G. Answer Social
S
tudies Question
s
inf
o
rmati
o
n t
h
at
relate t
o
t
h
e
topic
/
situation
/
proble
m
b
eing studie
d
.
2
. Engage in field
wor
k
that relates to
the topic
/
situation
/
problem
b
eing studie
d
.
E. Organize Social
S
tu
d
ies Informatio
n
1. Organize
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
no
n
-
print source
s
.
2
. Organize
informat
ion from
t
t
print source
s
.
F
.
Analyze Social
S
tu
d
ies Information
1. Interpret
inf
o
rmati
o
n fr
o
m
secondary sources
including pictures,
grap
h
ics, maps,
atlases, and
timeline
s
.
G. Answer Social
S
tudies Question
s
continued from previous page

90 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
1. Describe how the
community has
changed over time
and how people
have contributed to
its change, drawing
from maps,
photographs,
newspapers, and
other sources.
1. Describe how
the community has
changed over time
and how people
have contributed to
its change, drawing
from maps,
photographs,
newspapers, and
other sources.
1. Describe how
the community has
changed over time
and how people
have contributed to
its change, drawing
from maps,
photographs,
newspapers, and
other sources.
1. Describe how
the community has
changed over time
and how people
have contributed to
its change, drawing
from maps,
photographs,
newspapers, and
other sources.
1. Describe how the
community
h
as
changed over time
and ho
w
people
h
ave contri
b
ut
e
d
to
its change, drawing
f
rom maps,
p
h
otograp
h
s,
n
ewspapers, and
o
t
h
er source
s
.
1. Describe ho
w
t
h
e community
h
as
changed over time
and ho
w
p
e
o
ple
h
ave contri
b
uted to
its change, drawing
f
rom maps,
p
h
otograp
h
s,
n
ewspapers, and
o
t
h
er source
s
.
1. Describe ho
w
t
h
e community
h
as
changed over time
a
n
d ho
w
people
h
ave contri
b
uted to
its change, drawing
f
rom maps,
p
h
otograp
h
s,
n
ewspapers, and
o
t
h
er source
s
.
1. Describe ho
w
t
h
e community
h
as
changed over time
and ho
w
people
h
ave contri
b
uted to
its change, drawing
f
rom maps,
p
h
otograp
h
s,
n
ewspapers, and
o
t
h
er source
s
.

Appendix | 91
M
Domain: Science
Strand: Skills & Processes
Standard: Students will demonstrate the thinking and acting inherent in the practice of science.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Use his senses to
investigate the
world around him,
including solving
problems (e.g.,
dump and fill
objects, stack and
knock down big
blocks, push and
pull a wagon,
watching the wheels
turn when trying
different tactics to
move it).
Use objects and
toys more
purposefully,
exploring cause and
effect relationships
(e.g., roll a ball back
and forth with an
adult).
Look at the correct
picture or object
when it is named
(e.g., identify
objects, body parts,
and people).
Explore new ways
to do things (e.g.,
use a spoon to dig
in the garden, try to
move the large toy
car on the
playground by
pushing it, but then
decide to try pulling
it instead).
Seek information
through
observation,
exploration and
descriptive
investigations (e.g.,
use senses to
observe and gather
information, want
to pick up
interesting things
found on a walk,
use tools for
investigation).
Use scientific
thinking as well as
his senses to
discover the world
around him, and
make comparisons
between objects
(e.g., ask questions
about everything he
sees, put the
modeling clay in
water to see what
happens).
Seek information
through
observation,
exploration and
descriptive
investigations with
simple science tools
(e.g., ask lots of
“why” questions,
use tools such as
magnifying glass,
balance scale and
measuring cups for
investigation, guess
that a nut is inside
an acorn, and
A. Constructing
Knowledge
1. Raise questions
about the world
around them and be
willing to seek
answers to some of
them by making
careful observations
and trying things
out.
B. Applying
Evidence and
Reasoning
1. People are more
likely to believe your
ideas if you can give
good reasons for
them.
C. Communicating
Scientific
Information
1. Ask, "How do
you know?" in
appropriate
situations and
attempt reasonable
answers when others
A. Constructing
Knowledge
1. Raise questions
about the world
around them and
be willing to seek
answers to some of
them by making
careful
observations and
trying things out.
B. Applying
Evidence and
Reasoning
1. People are more
likely to believe
your ideas if you
can give good
reasons for them.
C. Communicating
Scientific
Information
1. Ask, "How do
you know?" in
appropriate
situations and
attempt reasonable
answers when
A. Constructing
Knowledge
1. Raise questions
about the world
around them and
be willing to seek
answers to some of
them by making
careful
observations and
trying things out.
B. Applying
Evidence and
Reasoning
1. People are more
likely to believe
your ideas if you
can give good
reasons for them.
C. Communicating
Scientific
Information
1. Ask, "How do
you know?" in
appropriate
situations and
attempt reasonable
answers when
A. Constructing
Knowledge
1. Raise questions
about the world
around them and
be willing to seek
answers to some of
them by making
careful observations
and trying things
out.
B. Applying
Evidence and
Reasoning
1. People are more
likely to believe
your ideas if you
can give good
reasons for them.
C. Communicating
Scientific
Information
1. Ask, "How do
you know?" in
appropriate
situations and
attempt reasonable
answers when
D
o
main
:
S
cienc
e
S
tran
d:
Sk
ills & Processe
s
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the thinkin
g
and actin
g
inherent in the
p
ractice of science.
Use
h
is senses to
investigate t
h
e
world around him,
including solving
problems (e.g.,
d
ump and fill
o
b
j
ects, stack and
knock down big
b
locks, push and
pull a wagon,
watc
h
ing t
h
e w
h
eels
turn w
h
en trying
d
ifferent tactics to
move it
)
.
Use ob
j
ects and
t
oys more
purposefully,
exploring cause and
effect relationship
s
(
e.g., roll a ball bac
k
and forth with an
adult
)
.
L
oo
k
at the
c
orre
c
t
picture or ob
j
ect
when it is name
d
(
e.g., identif
y
o
bj
ects, body parts,
and people)
.
1 Year
Explore new ways
to do thing
s
(
e.g.,
u
se a spoon to dig
in the garden, try to
move t
h
e large to
y
c
ar on t
h
e
playground b
y
pus
h
ing it,
b
ut then
d
ecide to try pulling
it instead
)
.
S
ee
k
information
t
h
roug
h
o
bservation,
exploration and
d
escriptive
investigation
s
(
e.g.,
u
se senses
t
o
o
bserve and gather
information, want
to pic
k
up
interesting t
h
ings
f
ound on a wal
k
,
u
se tools for
inve
s
tigation
)
n
n
.
2
Year
s
Use scientific
thin
k
ing as well as
h
is senses to
d
iscover the world
around him, and
ma
k
e comparisons
b
etween ob
j
ect
s
(
e.g., as
k
questions
about everything he
sees, put t
h
e
modeling clay in
water to see w
h
at
h
appens)
.
S
ee
k
information
t
h
roug
h
o
bservation,
exploration and
d
escriptive
investigations wit
h
simple science tools
(
e.g., as
k
lots of
“w
h
y” questions,
u
se tools suc
h
as
magnifying glass,
b
alance scale an
d
measuring cups for
investigation, guess
that a nut is insi
d
e
an acorn, and
g
3
Year
s
A
. Constructing
Knowledg
e
1
.
R
aise questions
about the world
aroun
d
them an
d
b
e
willing to see
k
answers to some of
them by making
c
areful
o
b
servations
and trying things
o
u
t.
B. Applying
Evidence and
R
easoning
1
.
P
eople are more
likely to believe your
ideas if you can give
good reasons for
t
h
em
.
C
.
C
ommunicating
S
cientific
Inf
o
rmati
on
1
.
A
sk,
"
How do
you know?
"
in
appropriate
situations an
d
attempt reasonabl
e
answers w
h
en ot
h
ers
g
4
Year
s
A
. Constructing
Knowledg
e
1
.
R
aise questions
about the world
aroun
d
them an
d
b
e willing to see
k
answers to some of
them by making
c
areful
ob
servations and
trying t
h
ings out.
B. Applying
Evidence and
R
easoning
1
.
P
eople are more
likely to believe
your ideas if you
can give good
reasons for them.
C
.
C
ommunicating
S
cientific
Inf
o
rmati
on
1
.
A
sk,
"
How do
you know?
"
in
appropriate
situations an
d
attempt reasonabl
e
answers w
h
en
p
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Constructing
Knowledg
e
1
.
R
aise questions
about the wor
l
d
aroun
d
them an
d
b
e willing to see
k
answers to some of
them by making
c
areful
ob
servations and
trying t
h
ings out.
B. Applying
Evidence and
R
easoning
1
.
P
eople are more
likely to believe
your ideas if you
can give good
r
easons for them.
C.
C
ommunicating
S
cientific
Inf
o
rmati
on
1
.
A
sk,
"
How do
you know?
"
in
appropriate
situations an
d
attempt reasonabl
e
answers w
h
en
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Constructing
Knowledg
e
1
.
R
aise questions
about the world
aroun
d
them an
d
b
e willing to see
k
answers to some of
them by making
careful o
b
servations
and trying things
o
u
t.
B. Applying
Evidence and
R
easoning
1
.
P
eople are more
likely to believe
your ideas if you
can give good
reasons for them.
C.
C
ommunicating
S
cientific
Inf
o
rmati
on
1
.
A
sk,
"
How do
you know?
"
in
appropriate
situations an
d
attempt reasonabl
e
answers w
h
en

92 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Use object and toys
more purposefully.
Show interest in
quantity and
number
relationships (fill
large and small
containers with
sand or water).
confirm that
prediction by
breaking, with
assistance, the
acorn to find out).
Use more advanced
problem solving
skills, testing his
understanding and
ideas in real
situations (e.g., get
a toy broom and
use the handle to
get a ball out from
under a shelf where
it has rolled).
Show interest in
quantity, measuring
and number
relationships (e.g.,
fill a balance scale
with beads, making
one side go down,
then the other).
ask them the same
question.
D. Technology
1. Design and make
things with simple
tools and a variety
of materials.
2. Practice
identifying the parts
of things and how
one part connects to
and affects another.
3. Examine a variety
of physical models
and describe what
they teach about the
real things they are
meant to resemble.
others ask them the
same question.
D. Technology
1. Design and make
things with simple
tools and a variety
of materials.
2. Practice
identifying the
parts of things and
how one part
connects to and
affects another.
3. Examine a
variety of physical
models and
describe what they
teach about the real
things they are
meant to resemble.
others ask them the
same question.
D. Technology
1. Design and make
things with simple
tools and a variety
of materials.
2. Practice
identifying the
parts of things and
how one part
connects to and
affects another.
3. Examine a
variety of physical
models and
describe what they
teach about the real
things they are
meant to resemble.
others ask them the
same question.
D. Technology
1. Design and make
things with simple
tools and a variety
of materials.
2. Practice
identifying the parts
of things and how
one part connects
to and affects
another.
3. Examine a
variety of physical
models and
describe what they
teach about the real
things they are
meant to resemble.
Use ob
j
ect and toys
more purposefully.
Sh
ow interest in
quantity and
n
umber
relations
h
ip
s
(
fill
large and small
containers wit
h
sand or water
)
.
c
onfirm that
prediction b
y
b
reaking, with
assistance, t
h
e
a
c
o
r
n
to find out
).
t
Use more advanced
problem solving
s
k
ills, testing his
u
nderstanding and
i
d
eas in real
situation
s
(
e.g., get
a toy broom and
u
se the han
d
le to
get a ball out from
u
nder a shelf where
it has rolled
)
.
Sh
ow interest in
quantity, measuring
and num
b
er
relations
h
ip
s
(
e.g.,
f
ill a
b
alance scale
with beads, making
o
ne side go down,
t
h
en t
h
e ot
h
er
)
.
as
k
them the same
question.
D
. Tec
h
nolog
y
1
.
D
esign and make
t
h
ings wit
h
simple
tools and a variet
y
o
f materials.
2.
P
ra
c
ti
c
e
identifying the par
t
s
o
f things and ho
w
o
ne par
t
connec
t
s
t
o
an
d
affect
s
anot
h
er
.
3.
Examine a variet
y
o
f physical models
and describe what
they teach about the
rea
l
t
h
ings t
h
ey are
meant to resem
b
le.
o
thers as
k
them the
same question.
D
. Tec
h
nolog
y
1
.
D
esign and make
t
h
ings wit
h
simple
tools and a variet
y
o
f materials.
2.
P
ra
c
ti
c
e
identif
ying the
f
f
parts of things and
h
ow one part
connects to an
d
affects another.
3.
Examine a
variety of physical
mo
d
els an
d
d
escribe what the
y
teach a
b
out the real
t
h
ings t
h
ey are
meant to resem
b
le.
o
thers as
k
them the
same question.
D
. Tec
h
nolog
y
1
.
D
esign and make
t
h
ings wit
h
simple
tools and a variet
y
o
f materials.
2.
P
ra
c
ti
c
e
identifying the
parts of things and
h
ow one part
connects to an
d
affects another.
3.
Examine a
variety of physical
mo
d
els an
d
d
escribe what the
y
teach a
b
out the real
t
h
ings t
h
ey are
meant to resem
b
le.
o
thers as
k
them the
same question.
D
. Tec
h
nolog
y
1
.
D
esign and make
t
h
ings wit
h
simple
tools and a variet
y
o
f materials.
2.
P
ra
c
ti
c
e
identifying the parts
o
f things and ho
w
o
ne par
t
connec
t
s
to an
d
affects
anot
h
er
.
3.
Examine a
variety of physical
mo
d
els an
d
d
escribe what the
y
teach a
b
out the real
t
h
ings t
h
ey are
meant to resem
b
le.
continued on next page

Appendix | 93
M
Show interest in
concepts, such as
matching and
sorting according
to color, shape and
size (e.g., group
items of similar
colors, compare the
color of his toy car
to that of another
child).
Use imagination,
memory and
reasoning to plan
and make things
happen (e.g., put a
cushion sideways
on the couch and
pretend to be
daddy driving to
work, tell his
caregiver that he is
going to be a
firefighter before
going to the
dramatic play area).
Show interest in
concepts such as
matching and
sorting according
to a single criteria
(e.g., help to put
away the utensils,
matching the large
spoons with the
other large spoons).
Use prior
knowledge and
imagination to
think through what
he wants to play
(e.g., use the blocks
as garages and
houses that the cars
and trucks drive to,
use the Unifix
Cubes with several
friends to try to
make a rod that
reaches across the
room).
Sh
ow interest in
concepts, suc
h
as
matching and
sorting according
to color, shape and
siz
e
(
e.g., group
items of similar
colors, compare t
h
e
color of his toy car
t
o
that
o
f an
o
ther
child
)
.
Use imagination,
memory and
reasoning to plan
and make things
h
appen
(
e.g., put a
cushion sideways
o
n the couch an
d
pretend to be
d
addy driving to
wor
k
, tell
h
is
caregiver t
h
at
h
e is
going to be a
f
irefighter before
going to t
h
e
d
ramatic play area)
.
Sh
ow interest in
concepts suc
h
as
matching and
sorting according
to a single criteria
(
e.g.,
h
elp to put
away t
h
e utensils,
matc
h
ing t
h
e large
spoons wit
h
t
h
e
o
t
h
er large spoons).
Use prior
knowledge and
imagination to
thin
k
through what
h
e wants to pla
y
(
e.g., us
e
the
b
locks
as garages and
h
ouses t
h
at t
h
e cars
and trucks drive to,
u
se the Unifix
Cubes with several
f
riends to try to
make a ro
d
that
reac
h
es across t
h
e
room
)
.
continued from previous page

94 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Science
Strand: Earth/Space
Standard: Students will use scientific skills and processes to explain the chemical and physical interactions (i.e., natural forces and
cycles, transfer of energy) of the environment, Earth, and the universe that occur over time.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Materials and
Processes That
Shape A Planet
B. Earth History
C. Plate Tectonics
D. Astronomy
E. Interactions of
Hydrosphere and
Atmosphere
A. Materials and
Processes That
Shape A Planet
1. Investigate
objects and
materials in the
environment.
B. Earth History
C. Plate Tectonics
D. Astronomy
1. Observe celestial
objects that are
visible in the day
and night sky.
E. Interactions of
Hydrosphere and
Atmosphere
A. Materials and
Processes That
Shape A Planet
B. Earth History
C. Plate Tectonics
D. Astronomy
2. Recognize that
there is a
relationship
between the sun
and the earth.
E. Interactions of
Hydrosphere and
Atmosphere
1. Describe
observable changes
in water on the
surface of the
Earth.
A. Materials and
Processes That
Shape A Planet
1. Describe and
compare properties
of a variety of
Earth materials.
B. Earth History
C. Plate Tectonics
D. Astronomy
1. Observe and
describe changes
over time in the
properties, location,
and motion of
celestial objects.
E. Interactions of
Hydrosphere and
Atmosphere
1. Recognize and
describe that the
surface of Earth
is more than half
covered with water.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
A.
M
aterials an
d
P
rocesses T
h
at
S
hape A Planet
B. Eart
h
Histor
y
C. Plate
T
ectonic
s
D
. Astronom
y
E. Interactions of
H
ydrosphere and
A
tmospher
e
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A
. Materials an
d
P
rocesses T
h
at
S
hape A Planet
1
.
Investigate
o
b
j
ects and
materials in t
he
environment.
B. Eart
h
Histor
y
C. Plate
T
ectonic
s
D
. Astronom
y
1
.
Ob
serve celestial
o
b
j
ects that are
visible in the da
y
and night sky.
E
.
Interactions of
H
ydrosphere and
A
tmospher
e
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Materials an
d
P
rocesses T
h
at
S
hape A Planet
B. Eart
h
Histor
y
C. Plate
T
ectonic
s
D
. Astronom
y
2
. Recognize t
h
at
t
h
ere is a
relations
h
ip
b
etween t
h
e sun
an
d
the earth.
E. Interactions of
H
ydrosphere and
A
tmospher
e
1
.
D
escri
b
e
o
bservable changes
in water on t
he
surface of the
Eart
h.
A
. Materials an
d
P
rocesses T
h
at
S
hape A Planet
1
.
D
escri
b
e and
compare properties
o
f a variety of
Eart
h
materials.
B. Eart
h
Histor
y
C. Plate
T
ectonic
s
D
. Astronom
y
1. O
b
serve and
d
escribe changes
o
ver time in t
he
properties, location,
an
d
motion of
c
elestia
l
o
b
j
ects.
E. Interactions of
H
ydrosphere and
A
tmospher
e
1
.
Recognize and
d
escri
b
e that the
surface of Eart
h
is more t
h
an
h
alf
covered with water
.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
S
cienc
e
S
tran
d:
Earth
/
Spac
e
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will use scientific skills and processes to explain the chemical and physical interactions (i.e., natural
f
orce
s
an
d
cycles, transfer of
energy
) of the
y
y
environment, Earth, and the universe that occur over time.
continued on next page

Appendix | 95
M
2. Describe the
weather using
observations.
A. Diversity of Life
1. Observe a variety
of familiar plants
and animals to
describe how they
are alike and how
they are different.
B. Cells
2. Investigate and
gather information
about changes in
weather.
A. Diversity of Life
1. Observe a variety
of familiar animals
and plants (perhaps
on the school
grounds, in the
neighborhood, and
at home) to
discover similarities
and differences
among them.
2. Gather
information and
direct evidence that
humans have
external features
that can differ in
size, shape, etc., but
that they are more
like other humans
than like other
animals.
B. Cells
2. Describe that
some events in
nature have
repeating patterns.
A. Diversity of Life
1. Compare and
explain how
external features of
plants and animals
help them survive
in different
environments.
B. Cells
1. Describe
evidence from
investigations that
living things are
made of parts too
.
A. Diversity of Life
B. Cells
2.
D
escri
b
e the
weat
h
er using
o
bservations.
A
. Diversity of Lif
e
1
.
O
bserve a variet
y
o
f familiar plants
an
d
animals
to
d
escribe how the
y
are alike and ho
w
t
h
ey ar
e
d
ifferent.
B
.
Cell
s
2.
Investigate and
gather information
about c
h
anges in
weat
h
er.
A
. Diversity of Lif
e
1
.
O
bserve a variet
y
o
f familiar animals
and plants
(
per
h
a
p
s
o
n t
h
e sc
h
ool
grounds, in t
h
e
n
eighborhood, and
at
h
ome
)
to
d
iscover similaritie
s
an
d
d
ifferences
among t
h
e
m
.
2.
Gat
h
er
information an
d
d
irect evidence that
h
umans
h
ave
external features
that can
d
iffer in
size, shape, etc., b
u
t
t
h
at t
h
ey are more
li
k
e
o
ther
h
umans
than li
k
e
o
ther
animals.
B
.
Cell
s
2.
D
escri
b
e that
some events in
n
ature
h
av
e
repeating patterns.
A
. Diversity of Lif
e
1
.
Compare and
explain
h
o
w
external features of
plants and animals
h
el
p
t
h
em survive
in
d
ifferent
environments.
B. Cell
s
1
.
D
escri
b
e
evidence from
investigations t
h
at
livin
g
t
h
ings are
made of parts too
.
A.
D
iversity of Lif
e
B. Cell
s
continued from previous page

96 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Begin to recognize
his own physical
and family
characteristics and
those of others
(e.g., count how
many boys are in
the group he is
playing with, go to
the table when the
teacher says that
everyone who has
brown hair may
go).
C. Genetics
1. Observe, describe
and compare
different kinds of
animals and their
offspring.
D. Evolution
C. Genetics
1. Observe,
describe and
compare the life
cycles of different
kinds of animals
and plants.
D. Evolution
1. Recognize that
living things are
found almost
everywhere in the
world and that
there are somewhat
different kinds of
living things in
different places.
small to be seen
with the unaided
eye.
2. Provide evidence
that all organisms
are made of parts
that help them
carry out the basic
functions of life.
C. Genetics
1. Explain that
there are
differences among
individuals in any
population.
2. Recognize that
all living things
have offspring,
usually with two
parents involved.
D. Evolution
C. Genetics
1. Explain that
there are
identifiable stages
in the life cycles
(growth,
reproduction, and
death) of plants and
animals.
D. Evolution
1. Observe and
describe examples
of variation
(differences) among
individuals of one
kind within a
population.
Begin to recognize
h
is own p
h
ysical
and famil
y
c
h
aracteristics an
d
those of other
s
(
e.g., count
h
o
w
many boys are in
t
h
e group
h
e is
playing wit
h
, go to
the table when the
teac
h
er says t
h
at
everyone w
h
o
h
as
b
rown hair ma
y
go
)
.
C. Genetic
s
1
.
O
bserve, describe
and compare
d
ifferent kin
d
s of
animals an
d
their
o
ffspring
.
D.
Evolutio
n
C. Genetic
s
1
.
O
bserve,
d
escri
b
e and
compar
e
the life
cycles of
d
ifferent
kin
d
s of animals
and plants.
D
. Evolution
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
at
living t
h
ings are
f
oun
d
almost
everyw
h
ere in t
h
e
world and that
t
h
ere are somew
h
at
d
ifferent kin
d
s of
living t
h
ings in
d
ifferent places.
small to
b
e seen
wit
h
the unai
d
e
d
e
y
e
.
2.
P
rovide evidence
t
h
at all organisms
are ma
d
e of par
t
s
t
h
at
h
elp t
h
em
carry out the basic
f
unctions of life
.
C. Genetic
s
1
.
Explain t
h
at
t
h
ere are
d
ifferences amon
g
individuals in an
y
population.
2.
R
ecognize t
h
at
all living t
h
ings
h
ave offspring,
u
sually wit
h
two
parents involved.
D.
Evolutio
n
C. Genetic
s
1
.
Explain t
h
at
t
h
ere are
identifiable stages
in t
he
life cycles
(
growt
h
,
r
eproduction, and
d
eath
)
of plants and
animals.
D
. Evolutio
n
1
.
Ob
serve and
d
escribe examples
o
f variatio
n
(
differences) among
individuals of one
kind within a
population.
continued on next page

Appendix | 97
M
E. Flow of Matter
and Energy
F. Ecology
E. Flow of Matter
and Energy
1. Develop an
awareness of the
relationship of
features of living
things and their
ability to satisfy
basic needs that
support their
growth and
survival.
F. Ecology
1. Investigate a
variety of familiar
places where plants
and animal live to
describe the place
and the living
things found there.
E. Flow of Matter
and Energy
1. Describe some
of the ways in
which animals
depend on plants
and on each other.
F. Ecology
E. Flow of Matter
and Energy
F. Ecology
1. Explain that
organisms can grow
and survive in many
very different
habitats.
E. Flow of Matter
and Energ
y
F
. Ecolog
y
E. Flow of Matter
and Energ
y
1
.
D
evelop an
awareness of the
relationship of
f
eatures of living
things and their
ability to satisf
y
b
asic needs that
support t
h
eir
growth and
survival.
F
. Ecolog
y
1
.
Investigate a
v
ariety of familiar
places w
h
ere plants
and animal li
v
e
to
d
escribe the place
an
d
the livin
g
things found there.
E. Flo
w
o
f Matter
and Energ
y
1
.
Describe some
o
f the ways in
w
h
ic
h
animal
s
d
epend on plants
an
d
on each other.
F
. Ecolog
y
E. Flow of Matter
and Energ
y
F
. Ecolog
y
1
.
Explain t
h
at
o
rganisms can gro
w
and survive i
n
man
y
very different
h
a
b
itats.
continued from previous page

98 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Science
Strand: Chemistry
Standard: Students will use scientific skills and processes to explain the composition, structure, and interactions of matter in order
to support the predictability of structure and energy transformations.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Use scientific
thinking as well as
his senses to
discover the world
around him, and
make comparisons
between objects
(e.g., watch the fish
and tell that he likes
the biggest one
best).
A. Structure of
Matter
1. Use evidence
from investigations
to describe the
observable
properties of a
variety of objects.
B. Conservation of
Matter
C. States of Matter
D. Physical and
Chemical Changes
A. Structure of
Matter
1. Compare the
observable
properties of a
variety of objects
and the materials
they are made of
using evidence
from investigations.
B. Conservation of
Matter
C. States of Matter
D. Physical and
Chemical Changes
A. Structure of
Matter
B. Conservation of
Matter
C. States of Matter
D. Physical and
Chemical Changes
A. Structure of
Matter
1. Cite evidence
from investigations
that most things are
made of parts.
B. Conservation of
Matter
1. Provide evidence
from investigations
that things can be
done to materials to
change some of
their properties.
C. States of Matter
D. Physical and
Chemical Changes
1. Provide evidence
from investigations
to identify
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
Use scientific
thin
k
ing as well as
h
is sens
e
s
to
d
iscover the world
around him, and
ma
k
e comparisons
b
etween ob
j
ect
s
(
e.g., watch the fish
an
d
tell that he likes
the biggest one
b
est
)
.
4
Year
s
A
. Structure of
M
atter
1
.
Use evidence
f
r
om
investigations
to descri
b
e th
e
ob
serva
b
le
properties of a
variety of ob
j
ects.
B
.
Conservation of
M
atter
C.
S
tates of Matter
D.
P
hysical and
C
h
emical C
h
ange
s
Kindergarte
n
A
. Structure of
M
atter
1
.
Compare t
h
e
ob
serva
b
le
properties of a
variet
y
o
f ob
j
ects
an
d
the materials
they are made of
u
sing evidence
f
rom investigations.
B. Conservation of
M
atter
C. States of Matter
D
. Physical and
C
h
emical C
h
ange
s
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Structure of
M
atter
B.
C
onservation
o
f
M
atter
C. States of Matter
D
. Physical and
C
h
emical C
h
ange
s
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Structure of
M
atter
1
.
Cite evidence
f
rom investigations
t
h
at most t
h
ings are
made of parts.
B. Conservation of
M
atter
1
.
P
rovide evidence
f
rom investigations
t
h
at t
h
ings can
b
e
d
one to materials to
change some of
t
h
eir properties.
C. States of Matter
D
. Physical and
C
h
emical C
h
ange
s
1
.
P
rovide evidence
f
rom investigations
to identif
y
D
o
main
:
S
cienc
e
S
tran
d:
C
h
emistr
y
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will use scientific skills and processes to explain the composition, structure, and interactions of matter in order
to support the predictability of structure and energy transformations.
continued on next page

Appendix | 99
M
processes that can
be used to change
physical properties
of materials.
processes t
h
at can
b
e used to change
p
h
ysica
l
properties
o
f materials.
continued from previous page

100 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Science
Strand: Physics
Standard: Students will use scientific skills and processes to explain the interactions of matter and energy and the energy
transformations that occur.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Mechanics
B.
Thermodynamics
C. Electricity and
Magnetism
A. Mechanics
1. Compare the
different ways
objects move.
2. Explain that
there must be a
cause for changes
in the motion of an
object.
B. Thermodynamics
1. Describe that
sunlight warms the
land, air, and water
using observations
and age appropriate
tools.
C. Electricity and
Magnetism
3. Observe and
gather information
from the
explorations to
describe how
magnets affect
some objects.
A. Mechanics
B. Thermodynamics
C. Electricity and
Magnetism
3. Describe the
effect magnets have
on a variety of
objects.
A. Mechanics
B. Thermodynamics
1. Identify and
describe ways in
which heat can be
produced.
C. Electricity and
Magnetism
1. Identify and
describe the
sources and uses of
electricity in daily
life.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
A.
M
ec
h
anic
s
B
.
Thermodynamic
s
C.
Electricity and
M
agnetis
m
Kindergarte
n
A
. Mechanic
s
1
.
Compare t
h
e
d
ifferent ways
o
b
j
ects move.
2
. Explain t
h
at
there must
b
e a
cause for changes
in t
h
e m
o
ti
o
n
o
f an
o
b
j
ect.
B
.
Thermodynamic
s
1
.
D
escri
b
e that
sunlig
h
t warms t
h
e
land, air, an
d
wa
t
er
u
sing observations
and age appropriate
tools.
C.
Electricity and
M
agnetis
m
3.
Ob
serve and
gather information
f
r
o
m th
e
explorations to
d
escribe ho
w
magne
t
s affe
c
t
som
e
o
b
j
ects.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
M
ec
h
anic
s
B
.
Thermodynamic
s
C.
Electricity and
M
agnetis
m
3.
D
escri
b
e the
effect magnets have
o
n a variety of
o
b
j
ects.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
M
ec
h
anic
s
B
.
T
h
ermodynamic
s
1
.
I
dentify and
d
escribe ways in
which heat can b
e
produced.
C. Electricity and
M
agnetis
m
1
.
I
dentify and
d
escri
b
e th
e
s
o
urces an
d
uses of
electricity in dail
y
life
.
continued on next page

Appendix | 101
M
D. Wave
Interactions
D. Wave
Interactions
2. Observe and
describe that sound
is produced by
vibrating objects.
D. Wave
Interactions.
D. Wave
Interactions
D
. Wave
Interaction
s
D.
W
ave
Interaction
s
2.
O
bserve and
d
escri
b
e that sound
is produced b
y
vibrating ob
j
ects.
D
. Wave
Interactions.
D
. Wave
Interaction
s
continued from previous page

102 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Science
Strand: Environmental Science
Standard: Students will use scientific skills and processes to explain the interactions of environmental factors (living and non-living)
and analyze their impact from a local to a global perspective.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Natural
Resources and
Human Needs
B. Environmental
Issues
A. Natural
Resources and
Human Needs
B. Environmental
Issues
1. Identify aspects
of the environment
that are made by
humans and those
that are not made
by humans.
A. Natural
Resources and
Human Needs
B. Environmental
Issues
1. Recognize that
caring about the
environment is an
important human
activity.
A. Natural
Resources and
Human Needs
1. Recognize and
explain how Earth’s
natural resources
from the natural
environment are
used to meet
human needs.
B. Environmental
Issues
1. Recognize and
describe that the
activities of
individuals or
groups of
individuals can
affect the
environment.
y
1
Year
p
2
Year
s
gpp
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
A
. Natural
R
esources an
d
H
uman Need
s
B. Environmental
Issue
s
Kindergarte
n
A
. Natural
R
esources an
d
H
uman Need
s
B. Environmental
Issue
s
1
.
Identify aspects
o
f the environment
t
h
at ar
e
made b
y
h
umans an
d
those
that are not ma
d
e
by
h
umans.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Natural
R
esources an
d
H
uman Need
s
B. Environmental
Issue
s
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
at
caring about the
environment i
s
an
important
h
uman
activity.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Natural
R
esources an
d
H
uman Need
s
1
.
R
ecognize and
explain
h
ow Eart
h
’s
n
atura
l
r
esou
r
ces
f
r
o
m the natural
environment are
u
se
d
t
o
mee
t
h
uman nee
d
s.
B. Environmental
Issue
s
1
.
R
ecognize and
d
escri
b
e that the
activities of
individuals or
groups of
i
n
dividuals can
affe
c
t th
e
environment.

Appendix | 103
M
Domain: Health
Strand: Safety & Injury Prevention
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to apply prevention and intervention knowledge, skills, and processes to promote
safe living in the home, school, and community.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Rely on trusted
adults to feel safe
trying new activities
(e.g., show with
words and gestures
that he wants a
trusted adult to be
near him).
Have beginning
understanding of
consequences when
following routines
and recreating
familiar events (e.g.,
participate in
creating class rules).
Have beginning
understanding of
consequences when
following routines
and recreating
familiar events (e.g.,
participate in
creating rules for
the class).
A. Emergencies
1. Recognize how to
respond
appropriately to
emergency
situations.
B. Safety Rules &
Procedures
A. Emergencies
1. Recognize how
to respond
appropriately to
emergency
situations.
B. Safety Rules &
Procedures
1. Identify ways to
be safe when
outdoors.
2. Identify actions
to stay safe from
fires.
3. Identify ways to
be safe in a car.
4. Tell what to
know when lost
(separated).
A. Emergencies
1. Describe how to
respond
appropriately to
emergency
situations.
B. Safety Rules &
Procedures
1. Identify ways to
be safe when
outdoors.
5. Identify ways to
stay safe around
animals.
C. Harassment
A. Emergencies
1. Demonstrate the
ability to respond
appropriately to
emergency
situations.
B. Safety Rules &
Procedures
1. Identify ways to
stay safe outdoors.
R
ely on trusted
a
d
ults to feel safe
trying new activities
(
e.g., s
h
ow wit
h
words and gestures
t
h
at
h
e wants a
trusted adult to
b
e
n
ear
h
im
)
.
1 Year
H
ave beginning
u
nderstanding of
consequences w
h
en
f
ollowing routines
an
d
recreating
f
amiliar events (e.g.,
participate in
creating class rules).
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
H
ave beginning
u
nderstanding of
consequences w
h
en
f
ollowing routines
and recreating
f
amiliar events (e.g.,
participate in
creating rules for
t
h
e class
)
.
4
Year
s
A.
Emergencie
s
1
.
R
ecognize
h
ow to
respon
d
appropriately to
eme
r
genc
y
situations.
B. Safety Rules &
P
roce
d
ure
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
Emergencie
s
1
.
R
ecognize
h
o
w
to respond
appropriately to
eme
r
genc
y
situations.
B
.
S
afety Rules &
P
roce
d
ure
s
1
.
Identify ways to
b
e safe when
o
ut
d
oors.
2.
Identif
y
actions
to stay safe from
f
ires.
3
.
Identify ways to
b
e safe in a car.
4
.
Tell w
h
at to
k
now when lost
(
separated).
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Emergencie
s
1
.
D
escribe how to
respond
appropriately to
eme
r
genc
y
situations.
B
.
S
afety Rules &
P
roce
d
ure
s
1
.
Identify ways to
b
e safe when
o
ut
d
oors.
5
.
Identify ways to
stay safe around
animals.
C.
H
arassment
Gra
d
e
2
A.
Emergencie
s
1
.
D
emonstrate t
h
e
ability to respond
appropriately to
eme
r
genc
y
situations.
B
.
S
afety Rules &
P
roce
d
ure
s
1
.
Identify ways to
stay safe outdoors.
D
o
main
:
H
ealt
h
S
tran
d:
S
afety & In
j
ury Preventio
n
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to apply prevention and intervention knowledge, skills, and processes to promote
safe living in the home, school, and community.

104 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
1 Identify the
characteristics of a
bully.
2. Define and
identify telling and
tattling.
D. Abuse &
Assault
1. Identify ways to
stay safe from
strangers.
D. Abuse & Assault
1. Identify actions
to stay safe from
strangers.
2. Describe actions
to stay safe around
familiar people.
1
Identify the
characteristics of a
b
ully.
2
.
D
efine an
d
identify telling and
tattling.
D.
Ab
use &
A
ssault
1
.
Identify ways to
stay safe from
s
t
rangers.
D.
Ab
use & Assault
1
.
Identify actions
to stay safe from
s
t
rangers.
2
.
D
escri
b
e actions
to stay safe around
f
amiliar people.

Appendix | 105
M
Domain: Health
Strand: Nutrition & Fitness
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to use nutrition and fitness knowledge, skills, and strategies to promote a healthy
lifestyle.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Responses to
Food
1. Identify the
relationship between
food and the senses.
E. Food & Health
1. Recognize the
relationship between
food and health.
A. Responses to
Food
1. Identify the
relationship
between food and
the senses.
B. Food
Production
1. Tell the source
of different foods.
C. Manners
1. Define proper
eating manners.
D. Nutrients
E. Food & Health
1. Recognize the
relationship
between food and
health.
A. Responses to
Food
1. Demonstrate the
relationship
between food and
the senses.
B. Food
Production
C. Manners
D. Nutrients
E. Food & Health
1. Recognize the
relationship
between food and
health.
A. Responses to
Food
B. Food Production
C. Manners
D. Nutrients
1. Define nutrients.
E. Food & Health
2. Explain the
relationship
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
A.
R
esponses to
F
oo
d
1
.
Identify the
relationship between
f
oo
d
an
d
the sense
s
.
E
.
F
oo
d
& Healt
h
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
relationship between
f
oo
d
an
d
health.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
R
esponses to
F
oo
d
1
.
Identify the
relations
h
ip
b
etween food and
t
h
e senses.
B
.
F
oo
d
P
ro
d
uction
1
.
Tell t
h
e source
o
f
d
ifferent foo
d
s.
C.
M
anner
s
1
.
D
efine proper
eating manner
s
.
D
. Nutrient
s
E
.
F
oo
d
& Healt
h
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
relations
h
i
p
b
etween
f
oo
d
an
d
h
ealt
h.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
R
esponses to
F
oo
d
1
.
D
emonstrate t
h
e
relations
h
ip
b
etween food and
t
h
e senses.
B
.
F
oo
d
P
ro
d
uction
C.
M
anner
s
D
. Nutrient
s
E
.
F
oo
d
& Healt
h
1
.
R
ecogniz
e
t
h
e
relations
h
ip
b
etween food and
h
ealt
h.
A.
R
esponses to
F
oo
d
Gra
d
e
2
B
.
F
oo
d
Pro
d
uction
C.
M
anner
s
D
. Nutrient
s
1
.
D
efine
n
utrient
s
.
E
.
F
oo
d
& Healt
h
2
.
Explain t
h
e
relations
h
ip
D
o
main
:
H
ealt
h
S
tran
d:
Nutrition & Fitnes
s
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to use nutrition and fitness knowledge, skills, and strategies to promote a health
y
lifestyle.

106 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
F. Nutrition &
Physical Activity
1. Identify food
categories.
F. Nutrition &
Physical Activity
1. Recognize that
foods are
categorized into
groups.
between personal
fitness and a
healthy lifestyle.
F. Nutrition &
Physical Activity
1. Demonstrate that
foods are
categorized into
groups.
2. Identify the
Nutrition Facts
Label.
F.
Nutrition &
P
hysical Activit
y
1
.
Identify food
categories.
F.
Nutrition &
P
hysical Activit
y
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
at
f
oo
d
s are
categorized into
group
s
.
b
etween personal
f
itness an
d
a
h
ealthy lifestyle.
F.
Nutrition &
P
hysical Activit
y
1
.
D
emonstrate t
h
at
f
oo
d
s are
categorized into
groups.
2.
Identify the
Nutrition Facts
L
a
b
el.

Appendix | 107
M
Domain: Health
Strand: Personal and Consumer Health
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to use consumer knowledge, skills, and strategies to develop sound personal health
practices involving the use of health care products, services, and community services.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Personal Health
Maintenance
1. Identify ways to
care for your body.
A. Personal Health
Maintenance
1. Explain how to
improve or
maintain personal
health.
B. Information,
Products, and
Services
1. Identify health
services available in
the school.
C. Pollution and
Personal Health
Issues
1. Identify health
issues created by
pollution.
A. Personal Health
Maintenance
1. Explain how to
improve or
maintain personal
health.
B. Information,
Products and
Services
1. Identify health
services available in
the school.
C. Pollution and
Personal Health
Issues
1. Identify health
issues created by
pollution.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
P
ersonal Healt
h
M
aintenan
ce
1
.
Identify ways to
care for your body.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
P
ersonal
H
ealt
h
M
aintenan
ce
1
.
Explain
h
ow to
improve or
maintain personal
h
ealt
h.
B
.
Information,
P
roducts, and
S
ervice
s
1
.
Identify health
services availa
b
le in
t
h
e sc
h
ool.
C
.
P
ollution an
d
P
ersonal Healt
h
Issue
s
1
.
Identify health
issues created b
y
pollution.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
P
ersonal Healt
h
M
aintenan
ce
1
.
Explain
h
ow to
improve or
maintain personal
h
ealt
h.
B
.
Inf
ormation,
ff
P
ro
d
ucts an
d
S
ervice
s
1
.
Identify health
services availa
b
le in
t
h
e sc
h
ool.
C
.
P
ollution an
d
P
ersonal H
e
alt
h
Issue
s
1
.
Identify health
issues created b
y
pollution.
D
o
main
:
H
ealt
h
S
tran
d:
P
ersonal an
d
Consumer Healt
h
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to use consumer knowledge, skills, and strategies to develop sound personal
h
ealt
h
practices involving the use of health care products, services, and community services.

108 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Health
Strand: Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drugs
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to use drug knowledge, decision-making skills, and health enhancing strategies to
address, the use, non-use, and abuse of medications, alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Medicine
1. Identify
appropriate uses of
medicine.
A. Medicine
1. Identify
appropriate uses of
medicine.
B. Tobacco
1. Identify how
tobacco use harms
health.
C. Alcohol
1. Identify the
physical effects of
using alcohol.
A. Medicine
1. Identify practices
for using medicine
safely.
B. Tobacco
1. Identify how
tobacco use affects
health.
C. Alcohol
1. Identify the
physical
consequences of
the use of alcohol.
E. Drugs and the
Law
1. Identify ways to
say no to unsafe
medicine/drug use.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
M
e
d
icin
e
1
.
Identif
y
appropriate uses of
me
d
icine.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
M
e
d
icin
e
1. Identif
y
appropriate uses of
me
d
icine.
B
.
To
b
acc
o
1
.
I
dentify ho
w
to
b
acco use harms
h
ealt
h.
C.
A
l
c
ohol
1
.
I
dentify the
physical effects of
u
sing alco
h
ol.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
M
e
d
icin
e
1. Identify practices
f
or using medicine
safely.
B
.
To
b
acc
o
1
.
Identify ho
w
to
b
acco use affects
h
ealt
h.
C.
A
l
c
oho
l
1
.
Identify the
p
h
ysical
consequences of
the use of alcohol.
E
.
D
rugs and the
L
a
w
1
.
Identify ways to
say no to unsafe
medicine
/
drug use.
D
o
main
:
H
ealt
h
S
tran
d:
A
lcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drug
s
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to use drug knowledge, decisio
n
-
making skills, and health enhancing strategies to
address, the use, non
-
u
se, and abuse of medications, alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs.

Appendix | 109
M
Domain: Health
Strand: Family Life and Human Sexuality
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to use human development knowledge, social skills, and health enhancing strategies
to promote positive relationships and health growth and development through the life cycle.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Family Unit
1. Define a family
unit.
A. Family Unit
1. Identify what is
special about your
family.
B. Physical, Mental,
and Social Growth
1. Describe the
growth process.
A. Family Unit
1. Identify how
your family helps
you and you help
your family.
B. Physical, Mental,
and Social Growth
1 .Describe the
physical, social,
mental growth
processes.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
F
amily Unit
1
.
D
efine a famil
y
u
nit
.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Family Unit
1
.
Identify what is
special about your
f
amily.
B
.
Ph
ysical, Mental,
and Social Growt
h
1
.
D
escri
b
e the
growt
h
process.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Family Unit
1
.
Identify ho
w
your family helps
you and you help
you
r
f
amily.
B
.
Ph
ysical, Mental,
and Social Growt
h
1
.
D
escri
b
e the
p
h
ysical, social,
mental growt
h
processes.
D
o
main
:
H
ealt
h
S
tran
d
:
F
amily Life and Human Sexualit
y
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to use human development knowledge, social skills, and health enhancing strategies
to promote positive relationships and health growth and development through the life cycle.

110 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Health
Strand: Disease & Prevention
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to apply prevention and treatment knowledge, skills, and strategies to reduce
susceptibility and manage disease.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Enjoy doing for
himself whatever
he thinks he can do
(e.g., perform at
least some skills
involved in using
the toilet, such as
pulling up his own
pants afterwards
and wash his hands
and use a towel to
dry them).
Feel more grown
up as he
accomplishes self-
help and
housekeeping tasks
with reminders
(e.g., take of his
own toileting needs
and wash and dry
his own hands).
A. Disease
Classification
1. Define disease.
B. Prevention
Practices
1. Identify ways to
reduce risk for
becoming sick.
A. Disease
Classification
B. Prevention
Practices
1. Identify basic
ways to prevent the
spread of germs.
A. Disease
Classification
1. Describe disease.
1 Year
2
Year
s
En
j
oy doing for
h
imself whatever
h
e thinks he can
d
o
(
e.g., perform at
least some s
k
ills
involved in using
t
h
e toilet, suc
h
as
pulling up
h
is own
pants afterwards
and wash his hands
and use a towel to
d
ry them).
3
Year
s
F
eel more grown
u
p as
h
e
accomplishes self
-
f
f
h
elp and
h
ouse
k
eeping tas
k
s
with reminders
(
e.g., ta
k
e
o
f
h
is
o
wn toileting needs
and wash and dr
y
h
is own hands
)
.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
D
isease
Classification
1
.
D
efine
d
isease.
B
.
P
revention
P
ractice
s
1
.
Identify ways to
re
d
uce risk for
b
ecoming sick.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Disease
Classification
B
.
P
revention
P
ractice
s
1. Identify basic
ways to prevent t
h
e
spread of germs.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Disease
Classificatio
n
1
.
D
escri
b
e disease.
D
o
main
:
H
ealt
h
S
tran
d:
D
isease & Preventio
n
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to apply prevention and treatment knowledge, skills, and strategies to reduce
susceptibility and manage disease.

Appendix | 111
M
Domain: Physical Education
Strand: Skillfulness
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to enhance their performance of a variety of physical skills by developing
fundamental movement skills, creating original skill combinations, combining skills effectively in skill themes, and applying skills.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Move constantly,
showing increasing
large muscle
control (e.g., walk
more than he
crawls and pull a
toy behind him as
he walks, or push a
toy in front of him).
Use his whole body
to develop spatial
awareness (e.g.,
walk around a circle
holding hands with
other children and
push himself on
riding toys).
Move with
confidence and
stability,
coordinating
movements to
accomplish simple
tasks. (e.g., go over,
under, around
through on an
obstacle course and
easily use riding
toys, such as
tricycles and Big
Wheels).
A. Fundamental
Movement
1. Show
fundamental
movement skills.
B. Creative
Movement
1. Show creative
movement.
C. Skill Themes
1. Show skill
themes.
A. Fundamental
Movement
1. Show
fundamental
movement skills.
B. Creative
Movement
1. Show creative
movement.
C. Skill Themes
1. Show skill
themes.
A. Fundamental
Movement
1. Show
fundamental
movement skills.
B. Creative
Movement
1. Show creative
movement.
C. Skill Themes
1. Show skill
themes.
A. Fundamental
Movement
1. Show
fundamental
movement skills.
B. Creative
Movement
1. Show creative
movement.
C. Skill Themes
1. Show skill
themes.
M
ove constantly,
s
h
owing increasing
large muscle
control (e.g., wal
k
m
o
re t
h
an
h
e
crawls and pull a
toy behind him as
h
e wal
k
s, or push a
toy in front of him).
1 Year
Use his whole b
o
dy
to develop spatial
awareness
(
e.g.,
walk around a circle
h
olding hands with
o
ther chil
d
ren an
d
push himself on
ri
d
i
n
g toys
)
.
2
Year
s
M
ove wit
h
confi
d
ence an
d
stability,
coordinating
movemen
t
s
t
o
accomplis
h
simple
tas
k
s.
(
e.g., go ove
r
,
u
nder, around
t
h
roug
h
on an
ob
stacle course and
easily use riding
toys, suc
h
as
tricycles and Big
W
h
eels
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
F
un
d
amental
M
ovement
1
.
Sh
o
w
f
un
d
amental
movement s
k
ills.
B
.
C
reative
M
ovement
1
.
Sh
ow creative
movemen
t
.
C.
Sk
ill Theme
s
1
.
S
how s
k
ill
t
h
emes.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
F
un
d
amental
M
ovement
1
.
Sh
o
w
f
undamental
f
f
movement s
k
ills.
B
.
C
reative
M
ovement
1
.
Sh
ow creative
movemen
t
.
C.
Sk
ill Theme
s
1
.
S
how s
k
ill
t
h
emes.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Fun
d
amental
M
ovement
1
.
Sh
o
w
f
un
d
amental
movement s
k
ills.
B
.
C
reative
M
ovement
1
.
Sh
ow creative
movemen
t
.
C.
Sk
ill Theme
s
1
.
S
how s
k
ill
t
h
emes.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Fun
d
amental
M
ovement
1
.
Sh
o
w
f
un
d
amental
movement s
k
ills.
B
.
C
reative
M
ovement
1
.
Sh
ow creative
movemen
t
.
C.
Sk
ill Theme
s
1
.
S
how s
k
ill
t
h
emes.
D
o
main
:
P
hysical Educatio
n
S
tran
d:
Sk
illfulnes
s
S
tandard: Students will demonstrate the ability to enhance their performance of a variety of physical skills b
y
d
eveloping
f
undamental movement skills, creating original skill combinations, combining skills effectively in skill themes, and applying s
k
ills.

112 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Physical Education
Strand: Biomechanical Principles
Standard: Students will demonstrate an ability to use the principles of biomechanics to generate and control force to improve their
movement effectiveness and safety.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Perform more
complex
movements with
his arms and legs
(e.g., walk more
than he crawls and
pull a toy behind
him as he walks or
push a toy in front
of him).
Use his whole body
to develop spatial
awareness (e.g.,
walk around in a
circle holding
hands with other
children and push
himself on riding
toys).
Move with
confidence and
stability,
coordinating
movements to
accomplish simple
tasks (e.g., go over,
under, around
through on an
obstacle course and
easily use riding
toys, such as
tricycles and Big
Wheels).
A. Effects on
Objects
1. Identify ways that
people and objects
move.
B. Balance
1. Identify balance
through movement.
A. Effects on
Objects
1. Identify ways
that people and
objects move.
B. Balance
1. Identify balance
through movement.
A. Effects on
Objects
1. Identify ways
that people and
objects move.
B. Balance
1. Identify balance
through movement.
A. Effects on
Objects
1. Identify ways
that people and
objects move.
B. Balance
1. Identify balance
through movement.
P
erf
o
rm m
o
re
complex
movements wit
h
h
is arms and leg
s
(
e.g., wal
k
more
than he crawls and
pull a toy behind
h
im as he wal
k
s or
push a toy in front
o
f him
)
.
1 Year
Use his whole bod
y
to develop spatial
awareness
(
e.g.,
walk around in a
circle holding
h
ands with other
children and push
h
imself on riding
toys
)
.
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
M
ov
e
wit
h
confi
d
ence an
d
stability,
coordinating
movemen
t
s
t
o
accomplis
h
simple
tas
ks
(
e.g., go ove
r
,
u
nder, around
t
h
roug
h
on an
ob
stacle course and
easily use riding
toys, suc
h
as
tricycles and Big
W
h
eels
)
.
4
Year
s
A.
Effects on
O
b
j
ect
s
1
.
Identify ways that
peopl
e
and ob
j
ects
move.
B
.
Balan
ce
1
.
Identify balance
t
h
roug
h
movement.
Kindergarte
n
A
. Effects on
O
b
j
ect
s
1
.
Identify ways
that people and
o
b
j
ects move.
B
.
Balan
ce
1
.
Identify balance
t
h
roug
h
movement.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Effects on
O
b
j
ect
s
1
.
Identify ways
that people and
o
b
j
ects move.
B
.
Balan
ce
1
.
Identify balance
t
h
roug
h
movement.
Gra
d
e
2
A
. Effects on
O
b
j
ect
s
1
.
Identify ways
that people and
o
b
j
ects move.
B
.
Balan
ce
1
.
Identify balance
t
h
roug
h
movement.
D
o
main
:
P
hysical Educatio
n
S
tran
d:
Biomec
h
anical Principle
s
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate an ability to use the principles of biomechanics to generate and control force to improve their
movement effectiveness and safety.

Appendix | 113
M
Domain: Physical Education
Strand: Motor Learning Principles:
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to use motor skill principles to learn and develop proficiency through frequent
practice opportunities in which skills are repeatedly performed correctly in a variety of situations.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Appropriate
Practices
1. Recognize that
skills will develop
over time with
appropriate practice
and use of the
correct cues.
B. Corrective
Feedback
1. Identify the
importance of
corrective feedback
on performance.
A. Appropriate
Practices
1. Recognize that
skills will develop
over time with
appropriate
practice and use of
the correct cues.
B. Corrective
Feedback
1. Identify the
importance of
corrective feedback
on performance.
A. Appropriate
Practices
1. Recognize that
skills will develop
over time with
appropriate
practice and use of
the correct cues.
B. Corrective
Feedback
1. Identify the
importance of
corrective feedback
on performance.
A. Appropriate
Practices
1. Recognize that
skills will develop
over time with
appropriate practice
and use of the
correct cues.
B. Corrective
Feedback
1. Identify the
importance of
corrective feedback
on performance.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
A.
A
ppropriate
P
ractice
s
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
at
skills will develop
o
ver time wit
h
appropriate practice
an
d
use of the
correc
t
cues.
B
.
C
orrective
F
eed
b
ac
k
1
.
Identify the
importance of
corrective feed
b
ac
k
o
n performance.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A
. Appropriate
P
ractice
s
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
at
skills will develop
o
ver time wit
h
appropriate
practice and use of
t
h
e correct cues.
B
.
C
orrective
F
eed
b
ac
k
1
.
Identify the
importance of
c
orre
c
tive feed
b
ac
k
o
n performance.
Gra
d
e
1
A
. Appropriate
P
ractice
s
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
at
skills will develop
o
ver time wit
h
appropriate
practice and use of
t
h
e correct cues.
B
.
C
orrective
F
eed
b
ac
k
1
.
Identify the
importance of
corrective feed
b
ac
k
o
n performance.
A
. Appr
o
priate
P
ractice
s
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
at
skills will develop
o
ver time wit
h
appropriate practice
an
d
use of the
correc
t
cues.
B
.
C
orrective
F
eed
b
ac
k
1
.
Identify the
importance of
corrective feed
b
ac
k
o
n performance.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
P
hysical Educatio
n
S
tran
d:
M
otor Learning Principles:
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to use motor skill principles to learn and develop proficiency through frequent
practice opportunities in which skills are repeatedly performed correctly in a variety of si
tuations.
ppp
pp

114 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Physical Education
Strand: Exercise Physiology
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to use scientific principles to design and participate in a regular, moderate to
vigorous physical activity program that contributes to personal health and enhances cognitive and physical performance in a variety
of academic, recreational, and life tasks.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Effects of
Physical Activity on
the Body
1. Identify the
effects of physical
activity on the body
systems.
B.FITT Guidelines
C. Components of
Fitness
1. Identify the
components of
fitness.
D. Benefits of
Physical Activity
1. Recognize the
benefits of physical
activity.
E. Nutrition and
Physical Activity
A. Effects of
Physical Activity on
the Body
1. Identify the
effects of physical
activity on the body
systems.
B.FITT Guidelines
C. Components of
Fitness
1. Identify the
components of
fitness.
.D. Benefits of
Physical Activity
1. Recognize the
benefits of physical
activity.
E. Nutrition and
Physical Activity
A. Effects of
Physical Activity on
the Body
1. Identify the
effects of physical
activity on the body
systems.
B.FITT Guidelines
C. Components of
Fitness
1. Identify the
components of
fitness.
D. Benefits of
Physical Activity
1. Recognize the
benefits of physical
activity.
E. Nutrition and
Physical Activity
A. Effects of
Physical Activity on
the Body
1. Identify the
effects of physical
activity on the body
systems.
B.FITT Guidelines
1. Identify
components of the
FITT guidelines.
C. Components of
Fitness
1. Identify the
components of
fitness.
D. Benefits of
Physical Activity
1. Recognize the
benefits of physical
activity.
E. Nutrition and
Physical Activity
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
A.
Effects of
P
hysical Activity on
the Bod
y
1
.
Identify the
effects of physical
activity on the bod
y
sys
t
ems.
B
.
F
I
TT
Gui
d
eline
s
C
.
C
o
mponents of
F
itnes
s
1
.
Identify the
components of
f
itness.
D.
Benefits of
P
hysical Activit
y
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
b
enefits of physical
activity.
E
.
Nutrition and
P
hysical Activit
y
4
Year
s
A.
Effects of
P
hysical Activity on
the Bod
y
1
.
Identify the
effects of physical
activity on the bod
y
sys
t
ems.
B
.
F
ITT Gui
d
eline
s
C.
C
omponents
o
f
F
itnes
s
1
.
Identify the
components of
f
itness.
.
D.
Benefits of
P
hysical Activit
y
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
b
enefits of physical
activity.
E
.
Nutrition and
P
hysical Activit
y
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A.
Effects of
P
hysical Activity on
the Bod
y
1
.
Identify the
effects of physical
activity on the bod
y
sys
t
ems.
B
.
F
ITT Gui
d
eline
s
C.
Components of
F
itnes
s
1
.
Identify the
components of
f
itness.
D.
Benefits of
P
hysical Activit
y
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
b
enefits of physical
activity.
E
.
Nutrition and
P
hysical Activit
y
A.
Effects of
P
hysical Activity on
the Bod
y
1
.
Identify the
effects of physical
activity on the bod
y
sys
t
ems.
B
.
F
ITT Gui
d
eline
s
1
.
Identif
y
components of the
F
ITT guidelines.
C.
Components of
F
itnes
s
1
.
Identify the
components of
f
itness.
D.
Benefits of
P
hysical Activit
y
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
b
enefits of physical
activity.
E
.
Nutrition and
P
hysical Activit
y
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
P
hysical Educatio
n
S
tran
d:
Exercise P
h
ysiolog
y
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to use scientific principles to design and participate in a regular, moderate to
vigorous physical activity program that contributes to personal health and enhances cognitive and physica
l
performance in a variet
y
o
f academic, recreational, and life tasks.
continued on next page
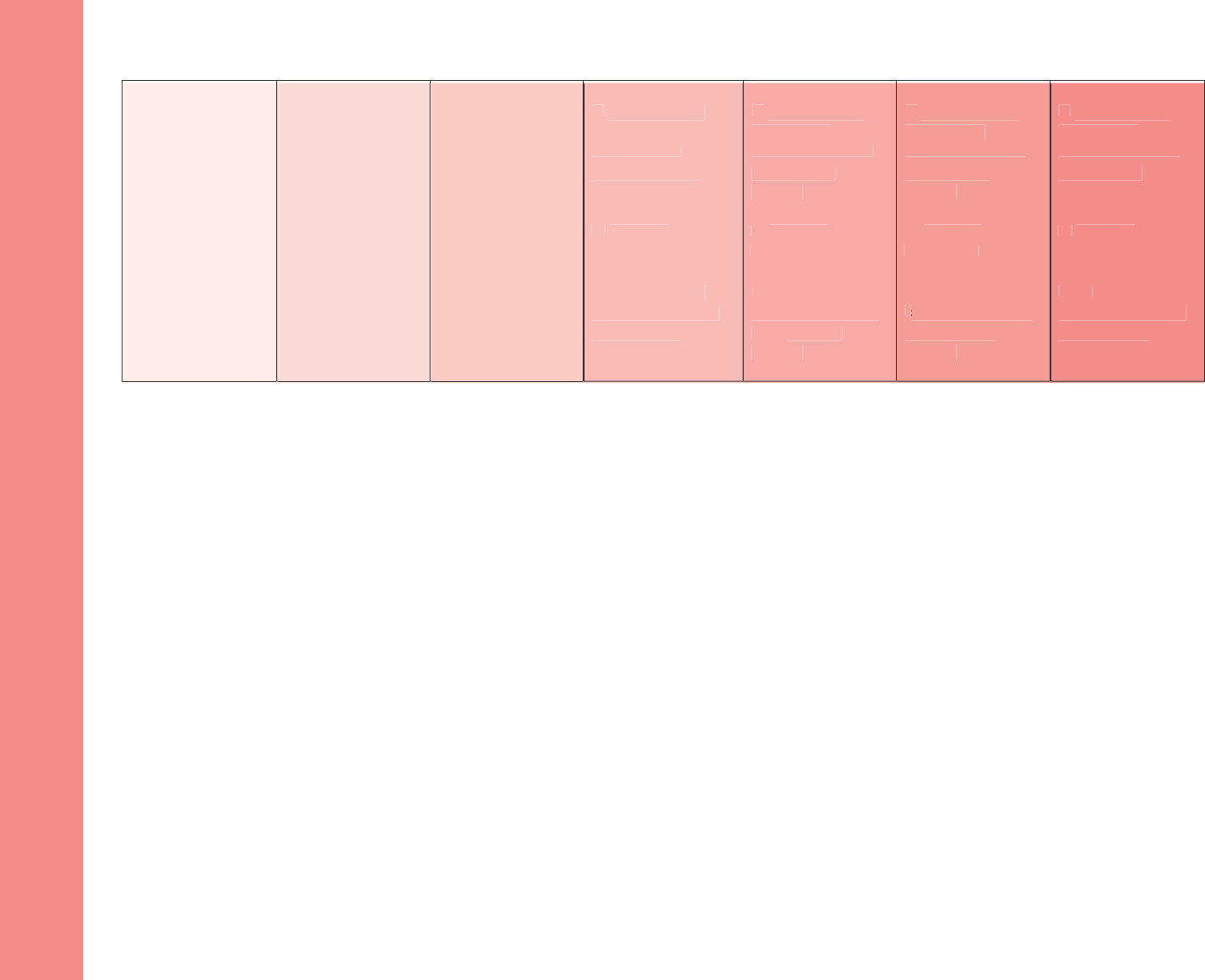
Appendix | 115
M
1. Recognize the
relationship between
nutrition and
physical activity.
F. Exercise
Adherence
1. Recognize the
factors influencing
daily physical
activity.
1. Recognize the
relationship
between nutrition
and physical
activity.
F. Exercise
Adherence
1. Recognize the
factors influencing
daily physical
activity.
1. Recognize the
relationship
between nutrition
and physical
activity.
F. Exercise
Adherence
1. Recognize the
factors influencing
daily physical
activity.
1. Recognize the
relationship
between nutrition
and physical
activity.
F. Exercise
Adherence
1. Recognize the
factors influencing
daily physical
activity.
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
relationship between
n
utrition an
d
p
h
ysical activity.
F.
Exercise
Ad
herenc
e
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
f
actors influencing
d
aily physical
activity.
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
relations
h
ip
b
etween nutrition
and physical
activity.
F.
Exercise
Ad
herenc
e
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
f
actors influencing
d
ail
y
p
h
ysical
activity.
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
relations
h
ip
b
etween nutrition
and physical
activity.
F.
Exercise
Ad
herenc
e
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
f
actors influencing
ff
d
aily physical
activity.
1
.
R
ecognize t
h
e
relations
h
ip
b
etween nutrition
and physical
activity.
F.
Exercise
Ad
herenc
e
1
.
Re
cognize t
h
e
f
actors influencing
d
aily physical
activity.
continued from previous page

116 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Physical Education
Strand: Physical Activity
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to use the principles of exercise physiology, social psychology, and biomechanics to
design and adhere to a regular, personalized, purposeful program of physical activity consistent with their health, performance, and
fitness goals in order to gain health and cognitive/academic benefits.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Aerobic Fitness
1. Identify and show
individual aerobic
capacity/cardio
respiratory fitness.
B. Muscular
Strength and
Endurance
1. Identify and show
activities for
muscular strength
and muscular
endurance.
C. Flexibility
1. Identify and show
activities for
flexibility.
A. Aerobic Fitness
1. Identify and
show individual
aerobic capacity/
cardio respiratory
fitness.
B. Muscular
Strength and
Endurance
1. Identify and
show activities for
muscular strength
and muscular
endurance.
C. Flexibility
1. Identify and
show activities for
flexibility.
A. Aerobic Fitness
1. Identify and
show individual
aerobic capacity/
cardio respiratory
fitness.
B. Muscular
Strength and
Endurance
1. Identify and
show activities for
muscular strength
and muscular
endurance.
C. Flexibility
1. Identify and
show activities for
flexibility.
A. Aerobic Fitness
1. Identify and
show individual
aerobic capacity/
cardio respiratory
fitness.
B. Muscular
Strength and
Endurance
1. Identify and
show activities for
muscular strength
and muscular
endurance.
C. Flexibility
1. Identify and
show activities for
flexibility.
D
o
main
:
P
hysical Educatio
n
S
tran
d:
P
hysical Activit
y
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to use the principles of exercise physiology, social psychology, and biomechanics to
d
esign and adhere to a regular, personalized, purposeful program of physical activity consistent with their health, performance, an
d
f
itness goals in order to gain health and cognitive
/
academic benefits.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
A.
A
ero
b
ic Fitnes
s
1
.
Identify and sho
w
individual aero
b
ic
capacity
/
cardio
respiratory fitness.
B. Muscular
S
trength and
En
d
uranc
e
1
.
I
d
entify and sho
w
activities for
muscular strengt
h
an
d
muscular
en
d
urance.
C.
F
lexibilit
y
1
.
Identify and sho
w
activities for
f
lexibility.
Kindergarte
n
A.
A
ero
b
ic Fitnes
s
1
.
Ident
ify and
t
t
show individual
aero
b
ic capacity
/
cardio respirator
y
f
itness.
B
.
M
uscular
S
trength and
En
d
uranc
e
1
.
Identify and
show activities for
muscular strengt
h
an
d
muscular
en
d
uranc
e
.
C.
F
lexibilit
y
1
.
Identify and
show activities for
f
lexibility.
Gra
d
e
1
A.
A
ero
b
ic Fitnes
s
1
.
Identify and
show individual
aerobic capacity
/
cardio respirator
y
f
itness.
B
.
M
uscular
S
trength and
En
d
uranc
e
1
.
Identify and
show activities for
muscular strengt
h
an
d
muscular
en
d
urance.
C.
F
lexibilit
y
1
.
Identify and
show activities for
f
lexibility.
Gra
d
e
2
A.
A
ero
b
ic Fitnes
s
1
.
I
d
entify and
show individual
aerobic capacity
/
cardio respirator
y
f
itness.
B
.
M
uscular
S
trength and
En
d
uranc
e
1
.
Identify and
show activities for
muscular strengt
h
an
d
muscular
en
d
urance.
C.
F
lexibilit
y
1
.
Identify and
show activities for
f
lexibility.

Appendix | 117
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Dance: Perceiving, Performing, and Responding
Standard: Aesthetic Education: Students will demonstrate the ability to perceive, perform, and respond to dance.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Recognize and react
to the sounds of
language (e.g.,
move rhythmically
to familiar songs).
Use his whole body
to develop spatial
awareness (e.g.,
dance to music,
including songs
that direct
movement).
Explore more
complex situations
and concepts,
beginning to
understand some
people’s jobs, and
care for the
environment (e.g.,
show a finger play
that he learned to a
friend, then make
up hand motions to
go with a new
song).
1. Demonstrate
knowledge of how
elements of dance
are used to
communicate
meaning.
2. Demonstrate
kinesthetic
awareness and
technical proficiency
in dance movement.
3. Respond to dance
through
observation,
experience, and
analysis.
1. Demonstrate
knowledge of how
elements of dance
are used to
communicate
meaning.
2. Demonstrate
kinesthetic
awareness and
technical
proficiency in
dance movement.
3. Respond to
dance through
observation,
experience, and
analysis.
1. Demonstrate
knowledge of how
elements of dance
are used to
communicate
meaning.
2. Demonstrate
kinesthetic
awareness and
technical
proficiency in
dance movement.
3. Respond to
dance through
observation,
experience, and
analysis.
1. Demonstrate
knowledge of how
elements of dance
are used to
communicate
meaning.
2. Demonstrate
kinesthetic
awareness and
technical
proficiency in dance
movement.
3. Respond to
dance through
observation,
experience, and
analysis.
R
ecognize and react
to the soun
d
s of
language (e.g.,
move r
h
yt
h
micall
y
to familiar songs).
1 Year
Use his whole bod
y
to develop spatial
awareness
(
e.g.,
d
ance to music,
including songs
that
d
irect
movement
)
.
2
Year
s
Explore more
complex situations
and concepts,
b
eginning to
u
n
d
erstan
d
some
people’s
j
obs, and
c
are for the
environment (e.g.,
show a finger pla
y
that he learne
d
to a
f
riend, then make
u
p hand motions
to
go wit
h
a ne
w
song
)
.
3
Year
s
1
.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of ho
w
elements of
d
ance
are use
d
to
c
ommuni
c
ate
meaning
.
2.
D
emonstrate
k
inesthetic
awareness and
technical proficienc
y
in dance movement
.
3.
R
espond to dance
t
h
roug
h
o
bservation,
experience, and
analysi
s
.
4
Year
s
1
.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of ho
w
elements of
d
ance
are use
d
to
c
ommuni
c
ate
meaning
.
2.
D
emonstrate
k
inesthetic
awareness and
te
ch
ni
c
al
proficiency in
d
ance movement
.
3.
R
espond to
d
ance through
o
bservation,
experience, and
analysi
s
.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of ho
w
elements of
d
ance
are use
d
to
c
ommuni
c
ate
meaning
.
2.
D
emonstrate
k
inesthetic
awareness and
te
ch
ni
c
al
proficiency in
d
ance movement
.
3.
R
espond to
d
ance through
o
bservation,
experience, and
analysi
s
.
Gra
d
e
2
1
.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of ho
w
elem
e
n
ts of
d
ance
are use
d
to
c
ommuni
c
ate
meaning
.
2.
D
emonstrate
k
inesthetic
awareness and
te
ch
ni
c
al
proficiency in dance
movemen
t
.
3.
R
espond to
d
ance through
o
bservation,
experience, and
analysi
s
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
D
an
c
e:
P
ercei
v
ing, Performing, and Responding
v
v
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
esthetic E
d
ucatio
n
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the abilit
y
to perceive, perform, and respond to dance.

118 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Dance: Historical, Cultural, and Social Context
Standard: Students will demonstrate an understanding of dance as an essential aspect of history and human experience.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Demonstrate
knowledge of
dances from a
variety of cultures.
2. Relate dance to
history, society, and
personal experience.
3. Demonstrate
understanding of the
relationships
between and among
dance and other
content areas.
1. Demonstrate
knowledge of
dances from a
variety of cultures.
2. Relate dance to
history, society, and
personal
experience.
3. Demonstrate
understanding of
the relationships
between and
among dance and
other content areas.
1. Demonstrate
knowledge of
dances from a
variety of cultures.
2. Relate dance to
history, society, and
personal
experience.
3. Demonstrate
understanding of
the relationships
between and
among dance and
other content areas.
1. Demonstrate
knowledge of
dances from a
variety of cultures.
2. Relate dance to
history, society, and
personal
experience.
3. Demonstrate
understanding of
the relationships
between and among
dance and other
content areas.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
1
.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
d
ances from a
variety of culture
s
.
2.
R
elate
d
ance to
h
istory, society, and
personal experienc
e
.
3.
D
emonstrate
u
nderstanding of the
relations
h
ips
b
etween and among
d
ance an
d
other
con
t
en
t
area
s
.
4
Year
s
1
.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
d
ances from a
variety of culture
s
.
2.
R
elate
d
ance to
h
istory, society, and
personal
experienc
e
.
3.
D
emonstrate
u
nderstanding of
t
h
e relations
h
ips
b
etween and
among dance and
o
t
h
er content area
s
.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
d
ances from a
variety of culture
s
.
2.
R
elate
d
ance to
h
istory, society, and
personal
experienc
e
.
3.
D
emonstrate
u
nderstanding of
t
h
e relations
h
ips
b
etween and
among dance and
o
t
h
er content area
s
.
1
.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
d
ances from a
variety of culture
s
.
2.
R
elate
d
ance to
h
istory, society, and
personal
experienc
e
.
3.
D
emonstrate
Gra
d
e
2
u
nderstanding of
t
h
e relations
h
ips
b
etween and among
d
ance an
d
other
con
t
en
t
area
s
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
D
an
c
e:
H
istorical, Cultural, and Social Context
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate an understanding of dance as an essential aspect of history and human experience.

Appendix | 119
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Dance: Creative Expression and Production
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to create and perform dance.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Develop the
ability to improvise
dance.
2. Develop the
ability to combine
the elements,
aesthetic principles,
and choreographic
forms of dance to
communicate
meaning.
3. Develop
knowledge and
execution of
performance
competencies in
dance.
1. Develop the
ability to improvise
dance.
2. Develop the
ability to combine
the elements,
aesthetic principles,
and choreographic
forms of dance to
communicate
meaning.
3. Develop
knowledge and
execution of
performance
competencies in
dance.
1. Develop the
ability to improvise
dance.
2. Develop the
ability to combine
the elements,
aesthetic principles,
and choreographic
forms of dance to
communicate
meaning.
3. Develop
knowledge and
execution of
performance
competencies in
dance.
1. Develop the
ability to improvise
dance.
2. Develop the
ability to combine
the elements,
aesthetic principles,
and choreographic
forms of dance to
communicate
meaning.
3. Develop
knowledge and
execution of
performance
competencies in
dance.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
1
.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to improvise
d
anc
e
.
2.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to combine
t
h
e elements,
aest
h
etic principles,
and choreographic
f
orms of
d
ance to
c
ommuni
c
ate
meaning
.
3.
D
evelop
knowledge and
exe
c
ution of
performance
competencies in
d
anc
e
.
4
Year
s
1
.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to improvise
d
anc
e
.
2.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to combine
t
h
e elements,
aest
h
etic principles,
and choreographic
f
orms of
d
ance to
c
ommuni
c
ate
meaning
.
3.
D
evelop
knowledge an
d
exe
c
ution of
performance
competencies in
d
anc
e
.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to improvise
d
anc
e
.
2.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to combine
t
h
e elements,
aest
h
etic principles,
and choreographic
f
orms of
d
ance to
c
ommuni
c
ate
meaning
.
3.
D
evelop
knowledge and
exe
c
uti
o
n
o
f
performance
competencies in
d
anc
e
.
1
.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to improvise
d
anc
e
.
2.
Gra
d
e
2
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to combine
t
h
e elements,
aest
h
etic principles,
and choreographic
f
orms of
d
ance to
c
ommuni
c
ate
meaning
.
3.
D
evelop
knowledge and
exe
c
ution of
performance
competencies in
d
anc
e
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
D
an
c
e: Creative Expression and Productio
n
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to create and perfor
m
d
anc
e
.

120 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Dance: Aesthetics and Criticism
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to make aesthetic judgments in dance.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Identify and apply
criteria to evaluate
choreography and
performance.
1. Identify and
apply criteria to
evaluate
choreography and
performance.
1. Identify and
apply criteria to
evaluate
choreography and
performance.
1. Identify and
apply criteria to
evaluate
choreography and
performance.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
1
.
Identify and appl
y
criteria to evaluate
choreography and
performanc
e
.
Kindergarte
n
1
.
Identify and
apply criteria to
evaluate
choreography and
performanc
e
.
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
Identify and
apply criteria to
evaluate
choreography and
performanc
e
.
Gra
d
e
2
1
.
Identify and
apply criteria to
evaluate
choreography and
performanc
e
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
D
an
ce
:
A
esthetics an
d
Criticis
m
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to make aesthetic
j
udgments in dance.

Appendix | 121
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Music: Perceiving, Performing, and Responding
Standard: Aesthetic Education: Students will demonstrate the ability to perceive, perform, and respond to music.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Recognize and react
to the sounds of
language (e.g.,
move rhythmically
to familiar songs).
Use his whole body
to develop spatial
awareness (e.g.,
dance to music,
including songs
that direct
movement).
Explore more
complex situations
and concepts,
beginning to
understand some
people’s jobs, and
care for the
environment (e.g.,
wait until you point
to his group to play
the jingle bells
during the song,
after the woods and
triangles have had
their solos).
1. Develop
awareness of the
characteristics of
musical sounds and
silence, and the
diversity of sounds
in the environment.
2. Experience
performance
through singing,
playing instruments,
and listening to
performances of
others.
3. Respond to music
through movement.
4. Experiment with
standard and
individually created
symbols to represent
sounds.
1. Develop
awareness of the
characteristics of
musical sounds and
silence, and the
diversity of sounds
in the environment.
2. Experience
performance
through singing,
playing
instruments, and
listening to
performances of
others.
3. Respond to
music through
movement.
4. Experiment with
standard and
individually created
symbols to
represent sounds.
1. Develop
awareness of the
characteristics of
musical sounds and
silence, and the
diversity of sounds
in the environment.
2. Experience
performance
through singing,
playing
instruments, and
listening to
performances of
others.
3. Respond to
music through
movement.
4. Experiment with
standard and
individually created
symbols to
represent sounds.
1. Develop
awareness of the
characteristics of
musical sounds and
silence, and the
diversity of sounds
in the environment.
2. Experience
performance
through singing,
playing instruments,
and listening to
performances of
others.
3. Respond to
music through
movement.
4. Experiment with
standard and
individually created
symbols to
represent sounds.
1 Year
R
ecognize and react
to the soun
d
s of
language (e.g.,
move r
h
yt
h
micall
y
to familiar songs).
2
Year
s
Use his whole bod
y
to develop spatial
awareness
(
e.g.,
d
ance to music,
including songs
that
d
irect
movement
)
.
3
Year
s
Explore more
complex situations
and concepts,
b
eginning to
u
n
d
erstan
d
some
people’s
j
obs, and
c
are for the
environment (e.g.,
wait until you point
to
h
is group to pla
y
the
j
ingle bells
d
uring the song,
after the woods and
triangles have had
t
h
eir solos
)
.
4
Year
s
1. Develop
awareness of the
characteristics of
musical soun
d
s an
d
silence, and the
d
iversity of sounds
in t
h
e environment.
2.
Experience
performance
t
h
roug
h
singing,
playing instruments,
and listening to
performances of
o
t
h
er
s
.
3.
R
espond to music
t
h
roug
h
movement
.
4.
Experiment wit
h
stan
d
ar
d
an
d
individually created
t
symbols to represen
t
soun
ds
.
Kindergarte
n
1
.
D
evelop
awareness of the
characteristics of
musical soun
d
s an
d
silence, and the
d
iversity of sounds
in t
h
e environment
.
2.
Experience
performance
t
h
roug
h
singing,
playing
instruments, and
listening to
performances of
o
t
h
er
s
.
3.
R
espond to
music t
h
roug
h
movemen
t
.
4.
Experiment wit
h
stan
d
ar
d
an
d
individually created
symbols to
represent sound
s
.
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
D
evelop
awareness of the
characteristics of
musical soun
d
s an
d
silence, and the
d
iversity of sounds
in t
h
e environment
.
2.
Experience
performance
t
h
roug
h
singing,
playing
instruments, and
listening to
performances of
o
t
h
er
s
.
3.
R
espond to
music t
h
roug
h
movemen
t
.
4.
Experiment wit
h
stan
d
ar
d
an
d
individually created
individually created
symbols to
represent sound
s
.
Gra
d
e
2
1
.
D
evelop
awareness of the
characteristics of
musical soun
d
s an
d
silence, and the
d
iversity of sounds
in t
h
e environment
.
2.
Experience
performance
t
h
roug
h
singing,
playing instruments,
and listening to
performances of
o
t
h
er
s
.
3.
R
espond to
music t
h
roug
h
movemen
t
.
4.
Experiment wit
h
stan
d
ar
d
an
d
individually created
individually created
symbols to
represent sound
s
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
M
usic:
P
erceiving, Performing, and Responding
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
esthetic Education: Students will demonstrate the ability to perceive, perform, and respond to music.

122 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Music: Historical, Cultural, and Social Context
Standard: Students will demonstrate an understanding of music as an essential aspect of history and human experience.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Develop the
ability to recognize
music as a form of
individual and
cultural expression
through
experiencing music
as both personal and
societal expression.
2. Become
acquainted with the
roles of music in the
lives of people.
3. Explore the
relationship of
music to dance,
theatre, the visual
arts and other
disciplines.
4. Develop
knowledge of a wide
variety of styles and
genres through the
study of music
history.
1. Develop the
ability to recognize
music as a form of
individual and
cultural expression
through
experiencing music
as both personal
and societal
expression.
2. Become
acquainted with the
roles of music in
the lives of people.
3. Explore the
relationship of
music to dance,
theatre, the visual
arts and other
disciplines.
4. Develop
knowledge of a
wide variety of
styles and genres
through the study
of music history.
1. Develop the
ability to recognize
music as a form of
individual and
cultural expression
through
experiencing music
as both personal
and societal
expression.
2. Become
acquainted with the
roles of music in
the lives of people.
3. Explore the
relationship of
music to dance,
theatre, the visual
arts and other
disciplines.
4. Develop
knowledge of a
wide variety of
styles and genres
through the study
of music history.
1. .Develop the
ability to recognize
music as a form of
individual and
cultural expression
through
experiencing music
as both personal
and societal
expression.
2. Become
acquainted with the
roles of music in
the lives of people.
3. Explore the
relationship of
music to dance,
theatre, the visual
arts and other
disciplines.
4. Develop
knowledge of a
wide variety of
styles and genres
through the study
of music history.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
1
.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to recognize
music as a form of
individual and
cultural expression
t
h
roug
h
experiencing music
as both personal and
societal expression
.
2.
Be
c
ome
acquainted with the
roles of music in the
lives of peopl
e
.
3.
Explore t
h
e
relationship of
music to dance,
t
h
eatre, t
h
e visual
arts an
d
other
d
iscipline
s
.
4.
D
evelop
knowledge of a wide
variet
y
o
f styles and
genres t
h
roug
h
t
h
e
study of music
h
istor
y
.
4
Year
s
1
.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to recognize
music as a form of
individual and
cultural expression
t
h
roug
h
experiencing music
as both personal
an
d
societal
expressio
n
.
2.
Be
c
ome
acquainted with the
roles of music in
the lives of peopl
e
.
3.
Explore t
h
e
relationship of
music to dance,
t
h
eatre, t
h
e visual
arts an
d
other
d
iscipline
s
.
4.
D
evelop
knowledge of a
wide variety of
styles and genres
through the stud
y
o
f music histor
y
.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to recogni
z
e
music as a form of
individual and
cultural expression
t
h
roug
h
experiencing music
as both personal
an
d
societal
expressio
n
.
2.
Be
c
ome
acquainted with the
roles of music in
the lives of peopl
e
.
3.
Explore t
h
e
relationship of
music to dance,
t
h
eatre, t
he
visual
arts an
d
other
d
iscipline
s
.
4.
D
evelop
knowledge of a
wide variety of
styles and genres
through the stud
y
o
f music histor
y
.
1
.
.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to recognize
music as a form of
individual and
cultural expression
t
h
roug
h
experiencing music
a
s
b
oth personal
an
d
societal
expressio
n
.
2.
Be
c
ome
acquainted with the
roles of music in
the lives of peopl
e
.
3
.
Explore t
h
e
relationship of
music to dance,
t
h
eatre, t
h
e visual
arts an
d
other
d
iscipline
s
.
4.
D
evelop
knowledge of a
wide variety of
styles a
n
d genres
Gra
d
e
2
through the stud
y
o
f music histor
y
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
M
usic:
H
istorical, Cultural, and Social Context
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate an
u
nderstanding of music as an essential aspect of history and human experience.

Appendix | 123
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Music: Creative Expression and Production
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to organize musical ideas and sounds creatively.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Develop
confidence in the
ability to improvise
music through
experimentation
with sound.
2. Investigate
composing music
through
experimentation
with sound and the
tools of
composition.
1. Develop
confidence in the
ability to improvise
music through
experimentation
with sound.
2. Investigate
composing music
through
experimentation
with sound and the
tools of
composition.
1. Develop
confidence in the
ability to improvise
music through
experimentation
with sound.
2. Investigate
composing music
through
experimentation
with sound and the
tools of
composition.
1. Develop
confidence in the
ability to improvise
music through
experimentation
with sound.
2. Develop the
ability to compose
and arrange music
by experimenting
with sound and the
tools of
composition.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
1
.
D
evelop
confi
d
ence in the
ability to improvise
music t
h
roug
h
experimentation
with soun
d
.
2.
Investigate
composing music
t
h
roug
h
experimentation
with sound and the
tools of
compositio
n
.
1
.
D
evelop
confi
d
ence in the
ability to improvise
music t
h
roug
h
experimentation
with soun
d
.
2.
Investigate
composing music
t
h
roug
h
experimentation
with sound and the
tools of
compositio
n
.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
D
evelop
confi
d
ence in the
ability to improvise
music t
h
roug
h
experimentation
with soun
d
.
2.
Investigate
composing music
t
h
roug
h
experimentation
with sound and the
tools of
compositio
n
.
1
.
D
evelop
confi
d
ence in the
ability to improvise
music t
h
roug
h
experimentation
with soun
d
.
2.
D
evelop t
h
e
ability to compose
and arrange music
b
y experimenting
w
ith sound and the
w
w
tools of
compositio
n
.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
M
usic
:
Creative Expression and Productio
n
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to organize musical ideas and sounds creatively.

124 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Music: Aesthetics and Criticism
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to make aesthetic judgments.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Express
preferences about
selected musical
compositions.
1. Express
preferences about
selected musical
compositions.
2. Develop and
apply personal
aesthetic criteria for
evaluating musical
performances.
1. Express
preferences about
selected musical
compositions.
2. Develop and
apply personal
aesthetic criteria for
evaluating musical
performances.
1. Express
preferences about
selected musical
compositions.
2. Develop and
apply personal
aesthetic criteria for
evaluating musical
performances.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
1
.
Express
preferences about
selecte
d
musical
composition
s
.
Kindergarte
n
1
.
Express
preferences about
selecte
d
musical
composition
s
.
2.
D
evelop and
apply personal
aesthetic criteria for
evaluating musical
performance
s
.
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
Express
preferences about
selecte
d
musical
composition
s
.
2.
D
evelop and
apply personal
aesthetic criteria for
evaluating musical
performance
s
.
Gra
d
e
2
1
.
Express
preferences about
selecte
d
musical
composition
s
.
2.
D
evelop and
apply personal
aesthetic criteria for
evaluating musical
performance
s
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
M
usic:
A
esthetics an
d
Criticis
m
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to make aesthetic
j
udgments.

Appendix | 125
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Theatre: Perceiving and Responding
Standard: Aesthetic Education: Students will demonstrate the ability to perceive, interpret, perform, and respond to the
development of a variety of dramatic forms over time and the aesthetic qualities they reflect.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Show an increasing
ability to remember
and participate in
imitative play (e.g.,
imitate the actions
of an adult such as
turning a steering
wheel in a play car).
Use improved eye-
hand coordination
to explore and
manipulate objects
(e.g., do finger
plays that require
hand-eye
coordination, such
as “The Itsy Bitsy
Spider”).
Explore more
complex situations
and concepts
beginning to
understand some
people’s jobs, and
care for the
environment (e.g.,
pretend to be a
firefighter and
spray the dramatic
play center with a
play hose, telling
everyone to get
out).
1. Describe ways
that theatre depicts
themes and stories.
2. Identify and
describe the visual,
aural, oral, and
kinesthetic elements
of dramatic
performances.
1. Describe ways
that theatre depicts
themes and stories.
2. Identify and
describe the visual,
aural, oral, and
kinesthetic
elements of
dramatic
performances.
1. Describe ways
that theatre depicts
themes and stories.
2. Identify and
describe the visual,
aural, oral, and
kinesthetic
elements of
dramatic
performances.
1. Describe ways
that theatre depicts
themes and stories.
2. Identify and
describe the visual,
aural, oral, and
kinesthetic
elements of
dramatic
performances.
Sh
ow an increasing
ability to remember
and participate in
imitative play (e.g.,
imitate t
h
e actions
o
f an a
d
ult such as
turning a steering
w
h
eel in a play car).
1 Year
Use improved ey
e
-
h
an
d
coor
d
ination
to explore and
manipulate ob
j
ects
(
e.g.,
d
o fi
n
ge
r
plays t
h
at require
h
an
d
-
e
y
e
coordination, such
as “T
h
e Itsy Bits
y
S
pider”).
2
Year
s
Explore more
complex situations
and concepts
b
eginning to
u
n
d
erstan
d
some
people’s
j
obs, and
c
a
re
fo
r the
environment (e.g.,
pretend to be a
f
irefighter and
spray the dramatic
play center wit
h
a
play
h
ose, telling
everyone
t
o ge
t
o
ut
)
.
3
Year
s
1
.
D
escribe ways
that theatre depicts
themes an
d
storie
s
.
2.
Identify and
d
escribe the visual,
aural, oral, and
k
inesthetic elements
o
f
d
ramatic
performance
s
.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
1
.
D
escribe ways
that theatre depicts
themes an
d
storie
s
.
2.
Identify and
d
escribe the visual,
aural, oral, and
k
inesthetic
elements of
d
ramatic
performance
s
.
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
D
escribe ways
that theatre depicts
themes an
d
storie
s
.
2.
Identify and
d
escribe the visual,
aural, oral, and
k
inesthetic
elements of
d
ramatic
performance
s
.
Gra
d
e
2
1
.
D
escribe ways
that theatre depicts
themes an
d
storie
s
.
2.
Identify and
d
escribe the visual,
aural, oral, and
k
inesthetic
elements of
d
ramatic
performance
s
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
T
h
eatre
:
P
erceiving and Responding
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
esthetic Education: Students will demonstrate the ability to perceive, interpret, perform, and respond to the
d
evelopment of a variety of dramatic forms over time and the aesthetic qualities they reflect.

126 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Theatre: Historical, Cultural, and Social Context
Standard: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the history, traditions, and conventions of theatre, dramatic works, and
other literature of the theatre.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Express a range
of responses to a
variety of stimuli.
2. Demonstrate
knowledge of
theatrical
conventions as
performers and as
an audience.
1. Express a range
of responses to a
variety of stimuli.
2. Demonstrate
knowledge of
theatrical
conventions as
performers and as
an audience.
1. Express a range
of responses to a
variety of stimuli.
2. Demonstrate
knowledge of
theatrical
conventions as
performers and as
an audience.
1. Express a range
of responses to a
variety of stimuli.
2. Demonstrate
knowledge of
theatrical
conventions as
performers and as
an audience.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
1
.
Express a range
o
f responses to a
variety of stimuli
.
2.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
t
h
eatri
c
al
conventions as
performers and as
an au
d
ienc
e
.
Kindergarte
n
1
.
Express a range
o
f responses to a
variety of stimuli
.
2.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
t
h
eatri
c
al
conventions as
performers and as
an au
d
ienc
e
.
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
Express a range
o
f responses to a
variety of stimuli
.
2.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
t
h
eatri
c
al
conventions as
performers and as
an au
d
ienc
e
.
Gra
d
e
2
1
.
Express a range
o
f responses to a
variety of stimuli
.
2.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
t
h
eatri
c
al
conventions as
performers and as
an au
d
ienc
e
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
T
h
eatre
:
H
istorical, Cultural, and Social Context
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate an understanding of the history, traditions, and conventions of theatre, dramatic works, and
o
ther literature
o
f the t
h
eatre
.

Appendix | 127
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Theatre: Creative Expression and Production
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to apply theatrical knowledge, principles, and practices to collaborative theatre
presentations.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Show an increasing
ability to remember
and participate in
imitative play (e.g.,
imitate the actions
of an adult such as
turning a steering
wheel in a play car).
Use imagination
memory and
reasoning to plan
and make things
happen (e.g.,
pretend to feed a
baby doll).
Use prior
knowledge and
imagination to
think through what
he wants to play
(e.g., decide in
advance who will
be the dad and who
will be the son in
the dramatic play
areas and take turns
playing teacher,
acting out circle
time routines with a
friend, talking first
about what they
each will do).
1. Use a variety of
theatrical elements
to communicate
ideas and feelings.
2. Demonstrate
knowledge of
theatre performance
and production
skills in formal and
informal
presentations.
1. Use a variety of
theatrical elements
to communicate
ideas and feelings.
2. Demonstrate
knowledge of
theatre
performance and
production skills in
formal and
informal
presentations.
1. Use a variety of
theatrical elements
to communicate
ideas and feelings.
2. Demonstrate
knowledge of
theatre
performance and
production skills in
formal and
informal
presentations.
1. Use a variety of
theatrical elements
to communicate
ideas and feelings.
2. Demonstrate
knowledge of
theatre
performance and
production skills in
formal and
informal
presentations.
Sh
ow an increasing
ability to remember
and participate in
imitative play (e.g.,
imitate t
h
e actions
o
f an a
d
ult such as
turning a steering
w
h
eel in a play car).
1 Year
Use imagination
memory and
reasoning to plan
and make things
h
appen (e.g.,
pretend to feed a
b
aby doll).
2
Year
s
Use prior
knowledge and
imagination to
thin
k
through what
h
e wants t
o
pla
y
(
e.g.,
d
eci
d
e in
advance who will
b
e the dad and who
will be the son in
the dramatic pla
y
areas an
d
take turns
playing teac
h
er,
acting out circle
time routines wit
h
a
f
riend, talking first
about what the
y
each will do
)
.
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
1
.
Use a variety of
t
h
eatri
c
al elements
to
c
ommuni
c
ate
ideas and feeling
s
.
2.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
theatre performance
and production
skills in formal an
d
inf
o
rmal
presentation
s
.
Kindergarte
n
1
.
Use a variety of
t
h
eatrical elements
to
c
ommuni
c
ate
ideas and feeling
s
.
2.
D
emonstrate
knowledg
e
o
f
t
h
eatre
performance and
production skills in
f
ormal an
d
inf
o
rmal
presentation
s
.
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
Use a variety of
t
h
eatrical elements
to
c
ommuni
c
ate
ideas and feeling
s
.
2.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
t
h
eatre
performance and
production skills in
f
ormal an
d
inf
o
rmal
presentation
s
.
Gra
d
e
2
1
.
Use a variety of
t
h
eatrical elements
to
c
ommuni
c
ate
ideas and feeling
s
.
2.
D
emonstrate
knowledge of
t
h
eatre
performance and
production skills in
f
ormal an
d
inf
o
rmal
presentation
s
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
T
h
eatre
:
Creative Expression and Production
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to apply theatrical knowledge, principles, and practices to collaborative theatre
presentations.

128 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Theatre: Aesthetics and Criticism
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to make aesthetic judgments.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Identify, describe,
and apply criteria to
assess individual and
group theatre
processes.
2. Identify, describe,
and apply criteria to
assess dramatic
works and other
literature of the
theatre.
1. Identify,
describe, and apply
criteria to assess
individual and
group theatre
processes.
2. Identify,
describe, and apply
criteria to assess
dramatic works and
other literature of
the theatre.
1. Identify,
describe, and apply
criteria to assess
individual and
group theatre
processes.
2. Identify,
describe, and apply
criteria to assess
dramatic works and
other literature of
the theatre.
1. Identify,
describe, and apply
criteria to assess
individual and
group theatre
processes.
2. Identify,
describe, and apply
criteria to assess
dramatic works and
other literature of
the theatre.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
4
Year
s
1
.
Identify, describe,
and apply criteria to
assess individual and
group t
h
eatre
processe
s
.
2.
Identify, describe,
and apply criteria to
assess
d
ramatic
works and other
literature
o
f the
t
h
eatr
e
.
1
.
Identify,
d
escribe, and appl
y
criteria to assess
individual and
group t
h
eatre
processe
s
.
2.
Identify,
d
escribe, and appl
y
criteria to assess
d
ramatic
w
o
rks an
d
o
ther literature
o
f
t
h
e t
h
eatr
e
.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
Identify,
d
escribe, and appl
y
criteria to assess
individual and
group t
h
eatre
processe
s
.
2.
Identify,
d
escribe, and appl
y
criteria to assess
d
ramatic works and
o
ther literature
o
f
t
h
e t
h
eatr
e
.
1
.
Identify,
d
escribe, and appl
y
criteria to assess
individual and
group t
h
eatre
processe
s
.
2.
Identify,
d
escribe, and appl
y
criteria to assess
d
ramatic works and
o
ther literature
o
f
t
h
e t
h
eatr
e
.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
T
h
eatre
:
A
esthetics an
d
C
riticis
m
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to make aesthetic
j
udgments.

Appendix | 129
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Visual Arts: Perceiving and Responding
Standard: Aesthetic Education: Students will demonstrate the ability to perceive, interpret, and respond to ideas, experiences, and
the environment through visual art.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Use his senses to
investigate the
world around him,
including solving
problems (e.g.,
push, poke,
squeeze, pat and
sniff the play dough
as he explores how
it feels and smells).
Recognize that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(e.g., paint some
lines across the
paper with broad
strokes and
movements, using a
few different
colors, and tell you
that it is a rainbow).
Develop finger
skills through many
forms of play (e.g.,
make a snowman
out of play dough
after watching an
older child make
balls and put them
together and
practice using
scissors to cut out
shapes, but be
unable to stay on
the lines).
1. Identify, describe,
and interpret
observed form.
2. Identify and
compare ways in
which selected
artworks represent
what people see,
know, feel, and
imagine.
3. Experiment with
the elements of art
and principles of
design to develop
personally
meaningful
compositions.
1. Identify,
describe, and
interpret observed
form.
2. Identify and
compare ways in
which selected
artworks represent
what people see,
know, feel, and
imagine.
3. Experiment with
the elements of art
and principles of
design to develop
personally
meaningful
compositions.
1. Identify,
describe, and
interpret observed
form.
2. Identify and
compare ways in
which selected
artworks represent
what people see,
know, feel, and
imagine.
3. Experiment with
the elements of art
and principles of
design to develop
personally
meaningful
compositions.
1. Identify,
describe, and
interpret observed
form.
2. Identify and
compare ways in
which selected
artworks represent
what people see,
know, feel, and
imagine.
3. Experiment with
the elements of art
and principles of
design to develop
personally
meaningful
compositions.
Use
h
is senses to
investigate t
h
e
world around him,
including solving
problems (e.g.,
push, po
k
e,
squeeze, pat and
sniff the play dough
as
h
e explores
h
o
w
it feels and smells
)
.
1 Year
R
ecognize t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations
(
e.g., paint some
l
ines across t
h
e
paper with broad
strokes an
d
movements, using a
f
ew different
colors, and tell you
that it is a rainbow
)
.
g
2
Year
s
D
evelop finger
s
k
ills through man
y
f
orms of play (e.g.,
ma
k
e a snowman
o
ut of play dough
after watching an
o
l
d
er chil
d
make
b
alls and put t
h
em
together and
practice using
scissors to cut out
shapes, but be
u
nable to stay on
t
h
e lines
)
.
3
Year
s
1
.
Identify, describe,
and interpret
ob
served for
m
.
2.
Identify and
compare ways in
which selected
artwor
k
s represent
w
h
at people see,
k
now, feel, an
d
imagin
e
.
3.
Experiment wit
h
the elements of art
and principles of
d
esign to develop
personall
y
meaningful
composition
s
.
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
1
.
Identify,
d
escribe, and
interpret observed
fo
r
m
.
2.
Identify and
compare ways in
which selected
artwor
k
s represent
w
h
at people
s
ee,
know, feel, and
imagin
e
.
3.
Experiment wit
h
the elements of art
and principles of
d
esign to develop
personall
y
meaningful
composition
s
.
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
Identify,
d
escribe, and
interpret observed
fo
r
m
.
2.
Identify and
compare ways in
which selected
artwor
k
s represen
t
w
h
at people see,
know, feel, and
imagin
e
.
3.
Experiment wit
h
the elements of art
and principles of
d
esign to develop
personall
y
meaningful
composition
s
.
Gra
d
e
2
1
.
Identify,
d
escribe, and
interpret observed
fo
r
m
.
2.
Identify and
compare ways in
w
h
ic
h
sel
e
cte
d
artwor
k
s represent
w
h
at people see,
know, feel, and
imagin
e
.
3.
Experiment wit
h
the elements of art
and principles of
d
esign to develop
personall
y
meaningful
composition
s
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
V
isual Arts:
P
erceiving and Responding
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
A
esthetic Education: Students will demonstrate the ability to perceive, interpret, and respond to ideas, experiences, and
the environment through visual art.

130 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Visual Arts: Historical, Cultural, and Social Context
Standard: Students will demonstrate an understanding of visual arts as an essential aspect of history and human experience.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Determine ways
in which works of
art express ideas
about self, other
people, places, and
events.
2. Discuss reasons
why people
(including self)
create and use art by
studying artworks
and other sources of
information.
3. Differentiate
among works by
artists representative
of different cultures.
4. Describe
processes used to
interpret and
express ideas in the
visual arts and other
disciplines.
1. Determine ways
in which works of
art express ideas
about self, other
people, places, and
events.
2. Discuss reasons
why people
(including self)
create and use art
by studying
artworks and other
sources of
information.
3. Differentiate
among works by
artists
representative of
different cultures.
4. Describe
processes used to
interpret and
express ideas in the
visual arts and
other disciplines.
1. Determine ways
in which works of
art express ideas
about self, other
people, places, and
events.
2. Discuss reasons
why people
(including self)
create and use art
by studying
artworks and other
sources of
information.
3. Differentiate
among works by
artists
representative of
different cultures.
4. Describe
processes used to
interpret and
express ideas in the
visual arts and
other disciplines.
1. Determine ways
in which works of
art express ideas
about self, other
people, places, and
events.
2. Identify and
compare reasons
why people create
and use art by
studying artworks
and other sources
of information.
3. Differentiate
among works by
artists
representative of
different cultures.
4. Compare
processes used to
interpret and
express ideas in the
visual arts and
other disciplines.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
1
.
D
etermine ways
in which wor
k
s of
art express ideas
about self, other
people, places, and
even
ts
.
2.
D
iscuss reasons
w
h
y people
(
including self)
create and use art b
y
studying artworks
an
d
other sources of
inf
o
rmati
o
n
.
3.
D
ifferentiate
among works b
y
artists representative
o
f
d
ifferent culture
s
.
4.
D
e
s
cri
b
e
processes used to
interpret and
express ideas in the
visual arts and other
d
iscipline
s
.
4
Year
s
1
.
D
etermine ways
in which wor
k
s of
art express ideas
about self, other
people, places, and
even
ts
.
2.
D
iscuss reasons
w
h
y people
(
including self)
create an
d
us
e
ar
t
b
y studying
artworks and other
sources of
inf
o
rmati
o
n
.
3.
D
ifferentiate
among works b
y
artists
r
epresentative of
d
ifferent culture
s
.
4.
D
escri
b
e
processes used to
interpret and
express ideas in the
visual arts and
o
ther discipline
s
.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
D
etermine way
s
in which wor
k
s of
art express ideas
about self, other
people, places, and
even
ts
.
2.
D
iscuss reasons
w
h
y people
(
including self)
create an
d
use art
b
y studying
artworks and other
sources of
inf
o
rmati
o
n
.
3.
D
ifferentiate
among works b
y
artists
repre
s
entative of
d
ifferent culture
s
.
4.
D
escri
b
e
processes used to
interpret and
express ideas in the
v
isual arts and
v
v
o
ther discipline
s
.
1
.
D
etermine ways
in which wor
k
s of
art express ideas
about self, other
people, places, and
even
ts
.
2.
Identify and
compare reasons
w
h
y people create
and use art b
y
studying artworks
an
d
other sources
o
f inf
o
rmati
on
.
3.
D
ifferentiate
among works b
y
artists
representative of
d
ifferent culture
s
.
4.
C
ompare
processes used to
interpret and
express ideas in the
visual arts an
d
o
ther discipline
s
.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
V
isual Arts:
H
istorical, Cultural, and Socia
l
Co
ntext
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate an understanding of visual arts as an essential aspect of history and human experience.

Appendix | 131
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Visual Arts: Creative Expression and Production
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to organize knowledge and ideas for expression in the production of art.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Create images and
forms from
observation,
memory,
imagination, and
feelings.
2. Investigate a
variety of ways that
artists develop ideas
and organize the
elements of art in
response to what
they see, know, and
feel.
1. Create images
and forms from
observation,
memory,
imagination, and
feelings.
2. Investigate a
variety of ways that
artists develop
ideas and organize
the elements of art
in response to what
they see, know, and
feel.
1. Create images
and forms from
observation,
memory,
imagination, and
feelings.
2. Investigate a
variety of ways that
artists develop
ideas and organize
the elements of art
in response to what
they see, know, and
feel.
1. Create images
and forms from
observation,
memory,
imagination, and
feelings.
2. Investigate a
variety of ways that
artists develop ideas
and organize the
elements of art in
response to what
they see, know, and
feel.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
1
.
Create images and
f
orms from
o
bservation,
memo
r
y,
imagination, and
f
eeling
s
.
2.
Investigate a
variety of ways that
artists develop ideas
and organize the
elements of art in
response to w
h
at
they see, know, and
f
ee
l
.
4
Year
s
1
.
C
reate images
an
d
forms from
o
bservation,
memo
r
y,
imagination, and
f
eeling
s
.
2.
Investigate a
variety of ways that
artists develop
ideas and organize
the elements of art
in response to w
h
at
they see, know, and
f
ee
l
.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
C
reate images
an
d
forms
f
r
o
m
o
bservation,
memo
r
y,
imagination, and
f
eeling
s
.
2.
Investigate a
variety of ways that
artists develop
ideas and organize
the elements of art
in response to w
h
at
they see, know, and
f
ee
l
.
1
.
C
reate images
an
d
forms from
o
bservation,
memo
r
y,
imaginati
o
n
, and
f
eeling
s
.
2.
Investigate a
variety of ways that
artists develop ideas
and organize the
elements of art in
response to w
h
at
they see, know, and
f
ee
l
Gra
d
e
2
.
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
V
isual Arts: Creative Expression and Productio
n
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will demonstrate the ability to organize knowledge and ideas for expression in the production of art.

132 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Fine Arts
Strand: Visual Arts: Aesthetics and Criticism
Standard: Students will demonstrate the ability to make aesthetic judgments.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
1. Develop and
apply criteria to
analyze personally
created artworks and
the artworks of
others.
1. Develop and
apply criteria to
analyze personally
created artworks
and the artworks of
others.
1. Develop and
apply criteria to
analyze personally
created artworks
and the artworks of
others
1. Develop and
apply criteria to
analyze personally
created artworks
and the artworks of
others.
1 Year
2
Year
s
3
Year
s
1
.
D
evelop and
apply criteria to
analyze personall
y
created artworks and
the artwor
k
s of
o
t
h
er
s
.
4
Year
s
1
.
D
evelop and
apply criteria to
analyze personall
y
created artworks
and the artworks of
o
t
h
er
s
.
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
D
evelop and
apply criteria to
analyze personall
y
created artworks
and the artworks of
o
t
h
er
s
1
.
D
evelop and
apply criteria to
analyze personall
y
created artworks
and the artworks of
o
t
h
er
s
.
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
F
ine Art
s
S
tran
d:
V
isual Arts:
A
esthetics an
d
Criticis
m
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
S
tudents will
d
emonstrate the ability to make aesthetic
j
udgments.
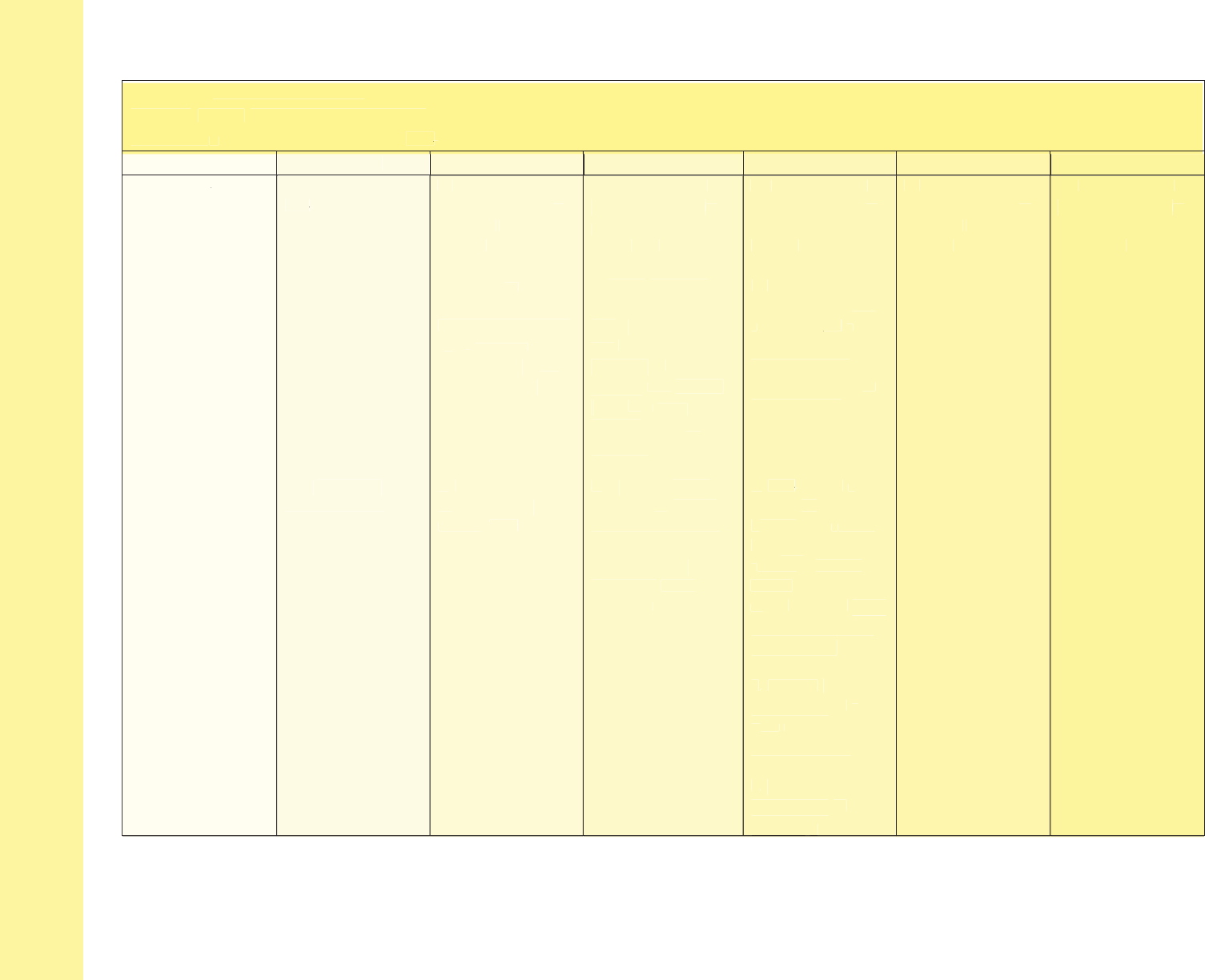
Appendix | 133
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: Social Emotional Regulation
Standard: Demonstrates healthy self-confidence.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Gain in self-
control/regulation.
Show increasing
self-regulation.
Play alongside
other children.
A.Demonstrates
Independence inD
range ofRoutines
and Tasks
1.Begins to actively
participate in
classroom activities
(e.g., answers
questions or joins
dramatic play).
2.Chooses where
to play during
center time.
A.Demonstrates
Independence inD
range of Routines
and Tasks
1. Seeks new and
varied experiences
and challenges (i.e.,
put materials
together in new
ways to test results;
joins in a peer
created game or
activity).
2. Requires fewer
prompts to follow
classroom routines
and is able to
independently
anticipate what
happens next.
A.Demonstrates
Independence inD
range ofRoutines
and Tasks
1. Transitions
between tasks and
routines with a
verbal and/or
visual warning (i.e.,
requires limited to
no additional
prompts).
2. Self-selects a
variety of activities
during free choice
and puts away
related materials
where they belong
when finished prior
to transitioning to
next activity.
3. Creates and/or
participates in a
new challenge
independently.
4. Actively
participates in
creating games or
A.Demonstrates
Independence inD
range ofRoutines
and Tasks
A.Demonstrates
Independence inD
range ofRoutines
and Tasks
1 Year
Gain in self
-
f
f
control
/
regulation.
2
Year
s
Sh
ow increasing
self
-
f
f
regulation.
P
la
y
alongsid
e
o
ther chil
d
ren.
3
Year
s
A.
D
emonstrate
s
Independence inD
r
ange
o
f
R
outines
an
d
Tas
ks
1
.
Begins
to
activel
y
participate i
n
classroom activitie
s
(
e.
g
., answe
rs
questions or
jo
in
s
d
ramatic play).
2.
C
h
oose
s
w
h
er
e
to
play during
c
en
t
er
t
ime.
t
t
4
Year
s
A.
D
emonstrate
s
Independence inD
r
ange
o
f
R
outine
s
an
d
T
as
ks
1
.
S
ee
ks
n
ew an
d
varie
d
experience
s
an
d
c
h
allenge
s
(
i.e.,
pu
t
material
s
toget
h
er in
n
e
w
ways
to
t
es
t
results;
j
o
in
s
in a peer
create
d
gam
e
or
activity
)
.
2.
R
equire
s
f
ewer
promp
ts
to
f
ollo
w
classroom routine
s
and is a
b
le t
o
independentl
y
anticipat
e
w
h
at
h
appens
n
ex
t.
A.
D
emonstrate
s
Independence inD
r
ange
o
f
R
outines
an
d
Tas
ks
1
.
T
ransition
s
b
etween task
s
an
d
r
o
utine
s
w
ith
w
w
a
verbal and
/
or
visual warning
(
i.e.,
requires limite
d
to
n
o a
dd
itional
prompts
)
.
2.
Self
-
f
f
select
s
a
variet
y
o
f activitie
s
d
u
ring
f
re
e
c
h
oi
ce
an
d
pu
t
s
awa
y
r
elate
d
m
aterial
s
w
h
er
e
they belong
w
h
en
f
inishe
d
prior
to transitioning t
o
n
ext activity.
3
.
C
reate
s
and
/
or
participate
s
in a
n
ew
c
h
alleng
e
independently.
4
.
A
ctivel
y
participate
s
in
creating
g
ame
s
or
Kindergarte
n
Gra
d
e
1
A.
D
emonstrate
s
Independence inD
r
ange
o
f
R
outines
an
d
Tas
ks
A.
D
emonstrate
s
Independence inD
r
ange
o
f
R
outines
an
d
Tas
ks
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Foun
d
ation
s
S
tran
d:
S
ocia
l
Emotional Regulation
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
D
emonstrate
s
h
ealt
hy
self
-
f
f
confi
d
ence.

134 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
B. Demonstrates
Age-Appropriate
Independence in
Decision-Making
1. Begins to
independently
select appropriate
materials during
specific activities
(i.e. when
presented with a
painting project
gets red and green
paint).
2. Recognizes the
appropriate place
for items (e.g., their
assigned seat, rest
spot, etc.).
B. Demonstrates
Age-Appropriate
Independence in
Decision-Making
1. Shows interest in
leading activities and
taking responsibility
during cleanup
activities.
2. Begins identifying
when things are not
put away in
designated areas.
3. Further expands
areas of decision
making (e.g., child
may say, "This
morning I'm going
to work on my Lego
building").
activities with
peers.
B. Demonstrates
Age-Appropriate
Independence in
Decision-Making
1. Independently
takes initiative to
solve problems
occurring within
activities without
immediately
requiring adult
support (e.g., the
child will search for
the missing piece in
a game for several
minutes before
asking for help).
1. Identify how to
make a good
choice/decision.
1. Identify choices
available in order to
make a decision.
B
.
D
emonstrates
A
g
e
-
A
ppropriate
I
ndependence in
D
ecisio
n
-
M
a
k
ing
1
.
Begins to
independentl
y
select appro
p
riate
materials during
specific activities
(
i.e. w
h
en
presented with a
painting
p
ro
j
ect
gets red and green
paint
)
t
t
.
2.
R
ecognizes t
h
e
appropriate place
fo
r item
s
(
e.g., t
h
eir
assigned seat, rest
spo
t
, etc.
)
.
B
.
D
emonstrates
A
g
e
-
A
ppropriate
Independence in
D
ecision
-
M
a
k
ing
1
.
Sh
ows interest in
leading activities and
ta
k
i
n
g responsibilit
y
d
uring cleanup
activities.
2.
Begins identifying
w
h
en t
h
ings are not
put away in
d
esignated areas.
3
.
F
urther expands
areas of
d
ecision
ma
k
ing
(
e.g
.
, child
may say,
"
This
morning I
'
m g
o
ing
to
wor
k
on my Lego
b
uilding
")
.
activitie
s
wit
h
peers.
B
.
D
emonstrates
A
g
e
-
A
ppropriate
Independence in
D
ecision
-
M
a
k
ing
1
.
Independentl
y
ta
k
es initiative to
solv
e
prob
l
ems
o
ccurring wit
h
in
activities wit
h
out
immediatel
y
requiring adult
support (e.g., t
h
e
child will search for
t
he
missing piece in
a game for severa
l
minutes
b
efore
as
k
ing for help).
1
.
Identify how to
make a good
choice
/
decision.
1
.
Identify choices
availa
b
le in order to
make a
d
ecision.

Appendix | 135
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: Social & Emotional Regulation
Standard: Initiates and maintains relations.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Begin to express a
variety of feelings.
Show more
awareness of the
feelings of another
child.
Use coping skills
with tasks, and
interactions with
peers and adults.
Show more
awareness of the
feelings of another
A. Expresses,
Understands, and
Responds to
Feelings/Emotions
of Others
1. Identifies basic
feelings (e.g., sad,
mad, happy).
2. Begins to express
emotions through
non-verbal cues
with adult
modeling and
support (e.g., body
language, facial
expressions, crosses
arms, and frowns).
3. Recognizes when
someone needs
help, but may not
A. Expresses,
Understands, and
Responds to
Feelings/Emotions
of Others
1. Communicates
negative and
positive emotions
verbally and
responds to teacher
prompts or
directions.
2. Understands
wider array of
feelings (e.g.,
frustrated, scared,
lonely) and
expresses them to
others.
3. Seeks adult
assistance for
classmates who need
A. Expresses,
Understands, and
Responds to
Feelings/Emotions
of Others
1. Identifies
feelings and
expresses them to
others (e.g., lets
another child know
they are happy, sad,
mad, etc.) and is
able to explain why
(e.g., “I’m mad
because you took
my toy”).
2. Communicates
negative emotions
in an appropriate
way and proposes a
solution (e.g., says,
“No” or “stop”
and proposes a
solution to their
problem - “Please
give me back the
book”).
3. Provides
comfort and
support for peers
1. Examine
emotions and
responses to
various situations.
(FROM HEALTH:
MENTAL
EMOTIONAL
HEALTH
FRAMEWORK)
Recognize methods
of communication.
1. Examine
emotions and
responses to
various situations.
(FROM HEALTH:
MENTAL
EMOTIONAL
HEALTH
FRAMEWORK)
Recognize
appropriate
methods of
communication.
1 Year
Begin to express a
variety of feelings.
2
Year
s
Sh
ow more
awareness of the
f
eelings of another
chil
d
.
Use coping s
k
ills
wit
h
tasks, and
interactions wit
h
peers and adults.
Sh
ow more
awareness of the
f
eelings of another
3
Year
s
A.
Express
e
s
,
U
n
derstands, a
nd
R
esponds to
F
eeling
s
/
Emotions
o
f Ot
h
er
s
1
.
I
d
entifies
b
asic
f
eelings (
e
.g
.
, sad,
mad, happy).
2.
Begins to express
emotions t
h
roug
h
no
n
-
ver
b
al cues
wit
h
a
d
ult
modeling and
support
(
e.
g
., bod
y
language, facial
expressions, crosses
arms, and frowns
)
.
3.
R
ecognizes w
h
en
someone nee
d
s
h
elp, but ma
y
not
4
Year
s
A.
Express
e
s
,
Understands, and
R
esponds to
F
eeling
s
/
Emotions
o
f Ot
h
er
s
1
.
C
ommunicate
s
n
egativ
e
an
d
positive emotions
verbally and
respond
s
to
tea
ch
er
promp
ts
or
d
irecti
o
n
s
.
2.
Un
d
erstan
ds
wider a
rr
a
y
o
f
f
eelings (
e.
g
.,
f
rustrated, scared,
lonely) an
d
expresses t
h
em t
o
o
t
h
ers.
3.
S
eeks a
d
ult
assistance for
classmates who need
Kindergarte
n
A.
Express
e
s
,
Understands, and
R
esponds to
F
eeling
s
/
Emotions
o
f Ot
h
er
s
1
.
I
d
entifie
s
f
eeling
s
an
d
expres
s
e
s
t
h
em t
o
o
t
h
er
s
(
e.
g
.,
l
e
ts
another chil
d
k
no
w
t
h
e
y
a
re
h
appy, sad,
mad, etc.
)
an
d
i
s
a
b
l
e
to
explain w
hy
(
e.g., “I
’m
ma
d
b
ecaus
e
you too
k
m
y
t
o
y
”)
.
2.
C
ommunicate
s
n
egativ
e
emotions
in an appropriat
e
way an
d
p
ropose
s
a
solution
(
e.g., says,
“No
”
o
r
“
s
top
”
an
d
proposes a
solution to t
h
eir
proble
m
-
“Please
give me back the
b
oo
k
”)
.
3.
P
rovides
comfort an
d
support for peers
Gra
d
e
1
1
.
Examine
emotions an
d
responses
t
o
various situations.
(
FROM HEALTH:
M
ENTAL
EMOTIONAL
H
EAL
T
H
F
RAMEWORK
)
R
ecognize methods
o
f
c
ommuni
c
ation.
Gra
d
e
2
1
.
Examine
emotions an
d
responses
t
o
various situations.
(
FROM
H
EALTH
:
M
ENTAL
EMOTIONAL
H
EAL
T
H
F
RAMEWORK
)
R
ecognize
appropriate
metho
d
s of
c
ommuni
c
ation.
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Foun
d
ation
s
S
tran
d:
S
ocial & Emotional Regulation
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Initiates an
d
maintains relations.

136 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Interact with other
children.
child.
Share his feelings
through talking and
pretend play.
respond every time.
B. Plays or Works
with Others
Cooperatively
1. Plays alongside
other children (e.g.,
dramatic play,
block table).
2. Begins to
understand the
concept of sharing
with adult
modeling and
support.
C. Recognizes
Differences or
Similarities
Between Self as
support.
4. Shows concern
for peers who are
upset or hurt.
B. Plays or Works
with Others
Cooperatively
1. Has one or more
special friendships.
2. Initiates
interactions (e.g.,
talking, playing).
3. Shares materials
and equipment with
other children with
adult modeling and
support.
C. Recognizes
Differences or
Similarities Between
Self as Compared to
who are upset.
4. Determines
when adult
assistance is
needed.
B. Plays or Works
with Others
Cooperatively
1. Chooses and
maintains
friendships.
2. Asks permission
to use others’
materials and
accepts peer’s
response.
3. Communicates
to others about his
friendships (e.g.,
tells parent at pick-
up about a new
friend).
C. Recognizes
Differences or
Similarities
Between Self as
Identify
relationships and
behavioral skills to
develop a sense of
community in
physical activity
settings.
Identify positive
and negative
character traits,
contributing to
Identify
relationships and
behavioral skills to
develop a sense of
community in
physical activity
settings.
Identify positive
and negative
character traits,
contributing to
Interact wit
h
ot
h
er
chil
d
ren.
chil
d
.
S
hare his feelings
through talking and
pretend play.
respond every time.
B
.
P
lays or Wor
k
s
wit
h
Ot
h
ers
C
o
operativel
y
1
.
Pl
ays alongside
o
ther children
(
e.
g
.,
d
ramatic play,
b
lock table
)
.
2.
Begins to
u
n
d
erstan
d
the
concept of sharing
with adult
modeling and
suppor
t
.
C.
R
ecognizes
D
ifferences or
S
imilarities
Between Self as
suppor
t
.
4.
Sh
ows concern
f
or peers who are
u
pset or
h
urt.
B
.
P
lays or Wor
k
s
wit
h
Ot
h
ers
C
o
operativel
y
1
.
H
as one or more
special friendships.
2.
Initiates
interactions
(
e.
g
.,
tal
k
ing, playing).
3.
Sh
ares materials
and equipment with
o
ther children with
adult modeling and
suppor
t
.
C.
R
ecognizes
D
ifferences or
S
imilarities Between
S
elf as Compared to
w
h
o are upset.
4.
D
etermines
when adult
assistance is
n
ee
d
e
d
.
B
.
P
lays or Wor
k
s
wit
h
Ot
h
ers
C
o
operativel
y
1
.
Chooses an
d
maintains
f
riendships.
2
.
A
sks permission
to use ot
h
ers’
materials an
d
accepts peer
’
s
response.
3
.
C
ommunicates
t
o
o
t
h
ers a
b
out his
f
riendships (e.g.,
tells parent at pic
k
-
u
p about a ne
w
f
riend
)
.
C.
R
ecognizes
D
ifferences or
S
imilarities
Between
S
elf as
Identif
y
relationships and
b
ehavioral skills to
d
evelop a sense of
community in
p
h
ysical activit
y
settings.
Identify positive
and negative
c
h
aracter traits,
contributing to
Identif
y
relationships and
b
ehavioral skills to
d
evelop a sense of
community in
p
h
ysical activit
y
settings.
Identif
y
positive
and negative
c
h
aracter traits,
contributing to
continued on next page

Appendix | 137
M
Compared to
Others
1. Begins to
recognize
differences or
similarities between
self as compared to
others (e.g.,
children with
disabilities, gender,
hair color, etc.).
D. Shows Ability to
Resolve Conflicts
1. Accepts
compromise when
resolving conflicts
if suggested by an
adult (e.g., mom
says, "Jackson, you
can use that swing
as soon as Sheila
finishes her turn").
Others
1. Identifies
differences or
similarities between
self as compared to
others (e.g., children
with disability,
gender, hair color,
etc.).
2. Identifies and
negotiates when a
peer is not given the
same instructions or
structure (e.g.,
“William’s mommy
lets him watch Dora.
Why can’t I?”).
D. Shows Ability to
Resolve Conflicts
1. Identifies inter-
personal conflicts
and begins to
manage emotions
more effectively
using self-talk with
adult support and
modeling (e.g.,
“Take three deep
breaths, and then
ask Caleb for
Compared to
Others
1. Recognizes and
accepts differences
or similarities
between self as
compared to others
(e.g., children with
a disability, cultural
differences, gender,
etc.).
2. Understands and
accepts when a
peer is not given
the same
instructions or
structure (e.g.,
Alexander needs a
fidget toy to help
him stay calm when
he’s upset).
D. Shows Ability to
Resolve Conflicts
1. Begins to see the
point of view of
others (i.e., theory
of mind).
one’s uniqueness.
one’s uniqueness.
Compared to
O
t
h
er
s
1
.
Begins to
recognize
d
ifferences or
similarities between
self as compared to
o
t
h
er
s
(
e.
g
.,
children with
d
isabilities, gender,
h
air color, etc.
)
.
D.
S
hows Ability to
R
esolve
C
onf
licts
f
f
1
.
A
ccepts
compromise w
h
en
resolving conflicts
if suggested by an
adult (e.g., mom
says,
"
Jackson, you
can use t
h
at swing
a
s
s
o
on as S
h
eila
f
inishes her turn
")
.
O
t
h
er
s
1
.
I
d
entifies
d
ifferences or
similarities betwe
e
n
self as compared to
o
t
h
ers
(
e.
g
., children
with disability,
gender, hair color,
etc.
)
.
2.
I
d
entifies an
d
n
egotiates w
h
en a
peer is not given t
h
e
same instructions or
structure
(
e.g.,
“William’s momm
y
lets
h
im watc
h
Dora.
W
h
y can’t I?”).
D.
S
hows Ability to
R
esolve
C
o
nflict
s
1
.
I
d
entifies inter
-
personal conflicts
and begins to
manage emotions
more effectivel
y
using self
-
f
f
tal
k
with
adult support and
modeling (e.g.,
“Ta
k
e t
h
re
e
d
eep
b
reaths, and then
ask Cale
b
for
Compared to
O
t
h
er
s
1
.
R
ecognizes and
accepts differences
o
r similarities
b
etwe
e
n
self as
compared to others
(
e.
g
., children with
a disability, cultural
d
ifferences, gender,
etc.
)
.
2.
Un
d
erstan
d
s an
d
accepts w
h
en a
peer is not given
t
h
e same
instructions or
structure
(
e.g.,
A
lexan
d
er nee
d
s a
f
idget toy to help
h
im stay calm w
h
en
h
e’s upset).
D.
S
hows Ability to
R
esol
v
e
C
o
nflict
s
1
.
Begins to see t
h
e
point of view of
o
t
h
ers (i.e., t
h
eor
y
o
f mind
)
.
o
ne’s uniqueness.
o
ne’s uniqueness.
continued from previous page

138 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
2. Seeks adults' help
in resolving a
conflict (e.g., goes
to dad and says,
"Jacob took my
truck!").
3. Continues to
learn simple
alternatives to
aggressive ways of
dealing with
conflicts (e.g.,
trades one object
for a desired one).
another turn”).
2. Seeks adult help
when solving inter-
personal conflicts.
3. Discusses
possible solutions
with peers with
adult assistance.
4. Has an awareness
of conflict
resolution strategies
but is not able to
independently
implement
consistently (e.g.,
understands a story
when a social
strategy was used
but can’t adapt
functionally).
2. Identifies inter-
personal conflicts
and considers
verbal or nonverbal
solutions to the
conflict.
3. Negotiates with
others to solve
problems.
4. Accepts conflict
resolution strategies
as suggested by
others.
2.
S
eeks a
d
ults
'
h
elp
in resolving a
conflict
(
e.
g
., goe
s
to dad and says,
"
Jacob too
k
m
y
truck!
")
.
3.
C
ontinues to
learn simple
alternatives to
aggressive ways of
d
ealing with
conflicts
(
e.
g
.,
trades one ob
j
ect
f
or a desired one
)
.
an
o
t
h
er turn
”
)
.
2.
S
eeks adult help
w
h
en solving inter
-
personal con
f
licts.
3.
D
iscusses
possible solutions
wit
h
peers wit
h
a
d
ult assistance.
4.
H
as an awareness
o
f
c
onfli
c
t
resolution strategies
b
ut is not a
b
le to
indepen
d
entl
y
implement
consistently (
e.
g
.,
u
nderstands a stor
y
w
h
en a social
strategy was used
b
ut can’t adapt
f
unctionally).
2.
I
d
entifies inter
-
personal conflicts
an
d
consi
d
ers
ver
b
al or nonver
b
al
solutions to t
h
e
c
onfli
c
t.
3.
Negotiates wit
h
o
t
h
ers to solve
problems.
4.
A
ccepts
c
onfli
c
t
resolution strategies
as suggested b
y
o
t
h
er
s
.

Appendix | 139
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: Approaches to Learning & Executive Functioning.
Standard: Self-regulation/inhibitory control.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Gain in self-
control/regulation.
Show increasing
self-regulation.
A. Control
Impulses
1. Occasionally
avoids imitating the
negative behaviors
of peers with
prompting from an
adult.
2. Developing the
ability to control
impulses during
structured activities
with adult support
(e.g., resist the
impulse to call out
before raising hand
during group time).
3. May remind
other children to
control their
impulses and
follow rules when
not able to do so
oneself.
4. May need to be
reminded to stop a
habitual action
A. Control Impulses
1. Avoids imitating
the negative
behavior of peers
with minimal
prompting from
adults.
2. Can more reliably
control impulses
during structured
activities that are
familiar (e.g., raising
hand to talk).
3. Can play the role
of a teacher in game
and monitor other
children’s behavior
and remind them to
follow the rules.
4. Sometimes able to
resist habits when
they are no longer
A. Control
Impulses
1. Avoids imitating
the negative
behaviors of peers.
2. Can consistently
control impulses
during structured
activities that are
familiar (e.g.,
raising hand to
talk).
3. Enjoys working
collaboratively to
develop complex
rules for games
(particularly
dramatic play) and
provide reminders
of these rules when
necessary.
4. More able to
monitor behaviors
and resist habits
Gain in self
-
f
f
control
/
regulation.
1 Year
Sh
ow increasing
self
-
f
f
regulation.
2
Year
s
A.
Co
ntr
o
l
Impulse
s
1
.
O
ccasionall
y
avoids imitating the
n
egative behaviors
o
f peers with
prompting from an
a
d
ult.
2.
D
eveloping t
h
e
ability to control
impulses during
structured activities
with adult support
(
e
.
g
., resist t
h
e
impulse to call out
b
efore raising hand
d
uring group time)
.
3
.
M
ay remind
o
ther chil
d
ren to
c
ontrol t
h
eir
impulses and
f
ollow rules when
n
ot a
b
le to do so
o
neself.
4.
M
ay need to be
remin
d
e
d
t
o
s
t
op a
h
a
b
itual action
3
Year
s
A.
Control Impulse
s
1
.
A
voids imitating
t
h
e negative
b
ehavior of peers
wit
h
minimal
prompting from
a
d
ults.
2
.
Can more reliabl
y
control impulses
d
uring structured
activities t
h
at are
f
amiliar (e.g., raising
h
and to talk
)
.
3
.
Can play t
h
e role
o
f a teacher in game
an
d
monitor other
4
Year
s
children’s
b
ehavior
an
d
remin
d
them to
f
ollow the rules.
4.
S
ometimes a
b
le to
resist habits when
t
h
e
y
are no lon
g
er
Kindergarte
n
A.
Co
ntr
o
l
Impulse
s
1
.
A
voids imitating
t
h
e negative
b
ehaviors of peers.
2.
Can consistentl
y
control impulses
d
uring structured
activities t
h
at a
r
e
f
amiliar
(
e.g.,
raising hand to
tal
k)
.
3
.
En
j
oys wor
k
ing
collaboratively to
d
evelop complex
rules for games
(
particularl
y
d
ramatic play) and
provide reminders
o
f these rules when
n
ecessa
r
y.
4.
M
ore a
b
le to
monitor
b
ehaviors
and resist ha
b
its
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Foun
d
ation
s
S
tran
d:
A
pproaches to Learning & Executive Functioning.
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Self
-
f
f
regulation
/
inhibitory control.

140 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
when it is not
appropriate (e.g.
continuing to go to
the bathroom for
paper towels even
though they have
been moved into
the classroom).
5. Can enjoy games
like Red Light,
Green Light that
require waiting for
signal to do
something with
adult support.
B. Resist
Temptation
1. Briefly able to
wait for an object
without grabbing.
Can wait longer
with adult support.
2. Can wait for a
highly desired food
or object with adult
reminders (e.g., can
wait to eat the
cupcake in reach
until the birthday
song is complete).
3. Able to takes
turns with
preferred toys with
appropriate (e.g.,
may remember
while walking to the
bathroom that the
paper towels have
moved and change
course).
5. Able to play
games like Red
Light, Green light
that require waiting
for signal to do
something with
adult support.
B. Resist
Temptation
1. Independently
waits for an object
without grabbing
most of the time.
2. Able to take turns
with preferred toys
or classroom
materials (i.e., waits
for an object
without grabbing
with minimal
prompting).
3. Can wait for a
highly desired food
or object, although
when they are not
appropriate.
5. More skillful at
games like Red
Light, Green Light
that require waiting
for a signal to do
something.
B. Resist
Temptation
1. Consistently
waits for an object
without grabbing.
2. Able to take
turns with
preferred toys or
classroom
materials.
3. Can consistently
wait for a highly
desired food or
w
h
en it is not
appropriate (e.g.
continuing to go to
the bathroom for
paper towels even
t
h
oug
h
t
h
ey
h
ave
b
een moved into
t
h
e classroom
)
.
5
.
C
an en
j
oy games
like Red Light,
Green Lig
h
t t
h
at
require waiting for
signal to do
somet
h
ing wit
h
adult support.
B
.
R
esist
T
emptation
1
.
Briefly able to
wait for an ob
j
ect
without grabbing.
Can wait longer
with adult support.
2
.
Can wait for a
h
ighly desired food
o
r ob
j
ect with adult
reminders (e.g., can
wait to eat t
h
e
cupca
k
e in reach
u
ntil the birthda
y
song is complete).
3.
Ab
le to takes
turns wit
h
p
referred to
y
s with
appropriate (e.g.,
may remember
while wal
k
ing to the
b
athroom that the
paper towels
h
ave
moved and change
course
)
.
5
.
A
ble to pla
y
games like Red
L
ig
h
t, Green lig
h
t
t
h
at require waiting
f
or signal to do
somet
h
ing wit
h
adult support.
B
.
R
esist
T
emptatio
n
1
.
Independentl
y
waits for an ob
j
ect
without grabbing
most of the time.
2.
Ab
le to take turns
with preferred toys
o
r classroom
materials
(
i.e., waits
f
or an object
f
f
without grabbing
wit
h
minimal
prompting
)
.
3.
Can wait for a
h
ighly desired food
o
r ob
j
ect, althou
g
h
w
h
en t
h
ey are not
appropriate.
5.
M
ore s
k
illful at
games like Red
L
ig
h
t, Green Lig
h
t
t
h
at require waiting
f
or a signal to do
somet
h
ing.
B
.
R
esist
T
emptation
1
.
Consistentl
y
waits for an ob
j
ect
without grabbing.
2.
Ab
le to take
turns wit
h
preferred
t
oys or
classroom
materials.
3.
Can consistentl
y
wait for a highl
y
d
esire
d
foo
d
or
continued on next page

Appendix | 141
M
prompting from an
adult.
C. Refrains from
Emotional
Outbursts and
Unsafe Behaviors
1. Shows progress
in resisting the
impulse to harm
self, others or
property in difficult
situations or
conflicts and using
language to express
strong feelings
instead (e.g., says,
"I really, REALLY
need that swing!").
May still fall apart
under stress.
may occasionally
need reminders.
C. Refrains from
Emotional
Outbursts and
Unsafe Behaviors
1. Learns coping
strategies (e.g., using
words, pretend play,
drawing) to establish
greater control and
competence in
managing intense
emotions (e.g., after
going to the
emergency room, he
or she may
repeatedly play out
the experience with
dolls and stuffed
animals) and resist
impulse to harm
self, others or
property.
object when asked.
May decide
independently to
wait as well (e.g.,
decides to eat a
favorite food last).
C. Refrains from
Emotional
Outbursts and
Unsafe Behaviors
1. Uses physical,
imaginative, and
cognitive resources
to comfort self
(e.g., goes to his or
her desk or
designated quiet
area voluntarily
when upset) and
resist impulse to
harm self, others or
property.
2. Controls the
expression of
emotion; however,
he or she continues
to need adult
guidance in this
area.
prompting from an
a
d
ult.
C.
R
efrains from
Em
o
ti
o
nal
O
u
t
b
ursts and
Unsafe Behavior
s
1
.
Sh
ows progress
in resisting t
h
e
impulse to
h
arm
self, others or
property in difficult
situations or
conflicts and using
language to express
strong feelings
instead (e.g., says,
"
I really, REALL
Y
n
eed that swing!
"
)
.
M
a
y
still fall apart
u
n
d
er stress.
may occasionall
y
n
ee
d
remin
d
ers.
C.
R
efrains from
Em
o
ti
o
nal
O
ut
b
ursts and
Unsafe Behavior
s
1
.
L
earns coping
strategies (
e
.
g
.,
u
sing
words, pretend play,
d
rawing) to establish
greater control and
competence in
managing intense
emotions (e.g., after
going to t
h
e
emergency room,
h
e
o
r s
h
e ma
y
repeatedly play out
t
h
e experience wit
h
d
olls an
d
stuffe
d
animals
)
and resist
impulse to
h
arm
se
l
f
, others or
proper
t
y.
o
b
j
ect when asked.
M
ay decide
independently to
wait as well (e.g.,
d
eci
d
es to eat a
f
avorite food last
)
.
C.
R
efrains from
Em
o
ti
o
nal
O
ut
b
ursts and
Unsafe Behavior
s
1
.
Uses p
h
ysical,
imaginative, and
cognitive resources
to comfort self
(
e.g., goes to
h
is or
h
er
d
esk or
d
esignated quiet
area voluntaril
y
when upset) and
resist impulse to
h
arm self, others or
proper
t
y.
2.
Controls t
h
e
expression of
emotion;
h
owever,
h
e or s
h
e continues
to nee
d
a
d
ult
guidance in this
a
r
ea
.
continued from previous page

142 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
D. Attentiveness—
Resists Distraction
to Maintain Focus
on Tasks of
Interest to the
Child
1. Maintains focus
on one activity for
longer periods of
time as long as the
activity is age-
appropriate and of
interest (e.g., can
repeatedly solve
and dump out a
wooden puzzle,
even with other
children playing in
the background).
D. Attentiveness—
Resists Distraction
to Maintain Focus
on Tasks of Interest
to the Child
1. Increases ability
to ignore
distractions and
sustain attention on
topics that are of
interest to the child
(e.g., can focus on a
drawing even when
other children are
nearby; might say,
“I’ll play with you
later. I want to finish
this”).
2. Capable of
sustaining focus on
longer-term or
complex projects,
with support from
an adult.
D. Attentiveness—
Resists Distraction
to Maintain Focus
on Tasks of
Interest to the
Child
1. Capable of
resisting
distractions and
keeping attention
focused on a task
of interest to the
child.
2. Able to
independently
maintain focus on a
project of interest
for a sustained
period of time (e.g.,
spends a rainy day
building a
complicated fort
out of chairs and
blankets, complete
with props and
signs).
D.
A
ttentivenes
s
—
R
esists Distraction
t
o
Maintain F
o
cu
s
o
n Tas
k
s of
Interest to t
h
e
Chil
d
1
.
M
aintains focus
o
n one activity for
longer periods of
time as long as t
h
e
activity is ag
e
-
appropriate and of
interest
(
e.g., can
repeatedly solve
and dump out a
wooden puzzle,
even wit
h
ot
h
er
children playing in
the background).
D.
A
ttentivenes
s
—
R
esists Distraction
to Maintain Focus
o
n Tas
k
s of Interest
to the Chil
d
1
.
Increases abilit
y
to ignore
d
istractions an
d
sustain attention on
topics that are of
interest to the chil
d
(
e.g., can focus on a
d
rawing even when
o
ther chil
d
ren are
n
earby; might say,
“I’ll play wit
h
y
o
u
later. I want to finish
t
h
i
s
”)
.
2.
Capable of
sustaining focus on
longer
-
t
erm
o
r
complex pro
j
ects,
with support from
an a
d
ult.
D.
A
ttentivenes
s
—
R
esists Distraction
to Maintain Focus
o
n Tas
k
s of
Interest to t
h
e
Chil
d
1
.
Capable of
resisting
d
istractions an
d
k
eeping attention
f
ocuse
d
on a tas
k
o
f interest to the
chil
d
.
2
.
Ab
le to
independentl
y
maintain focus on a
pro
j
ect of interest
f
or a sustaine
d
period of time (e.g.,
spends a rainy da
y
b
uilding a
complicated fort
o
ut of chairs an
d
b
lankets, complete
with props and
signs
)
.
continued on next page

Appendix | 143
M
E. Attentiveness—
Resists Distraction
to Maintain Focus
on Tasks Set By
Someone Else
1. Remains on task
during an activity
set by the teacher
for short periods of
time despite
distractions though
still may require
prompting from an
adult.
2. Can return to an
earlier task after an
interruption, with
adult reminders.
E. Attentiveness—
Resists Distraction
to Maintain Focus
on Tasks Set By
Someone Else
1. Remains on task
during an activity set
by the teacher for
short periods of
time despite
distractions with
minimal prompting
from adults (e.g.,
can ignore other
activities nearby and
hold focus on a
teacher directed
small group activity).
2. May need a
reminder to return
to an earlier task
after an interruption.
E. Attentiveness—
Resists Distraction
to Maintain Focus
on Tasks Set By
Someone Else
1. Independently
avoids distractions
and remains on
task for short
periods of time
during a teacher
directed activity.
2. Can
independently
pause and resume
an activity to
respond to an
interruption.
3. Uses self-talk
and other strategies
to maintain focus
on difficult tasks
and assignments
from adults (e.g.,
“There’s only three
more questions left.
If I finish these,
then I’ll be all done
with this project”).
E
.
A
ttentivenes
s
—
R
esists Distraction
to Maintain Focus
o
n Tas
k
s Set B
y
S
omeone Els
e
1
.
R
emains on tas
k
d
uring an activit
y
se
t
b
y the teacher
f
or short periods of
time despite
d
istractions though
still may require
prompting from an
a
d
ult.
2.
C
an return t
o
an
earlier tas
k
after an
interruption, wit
h
a
d
ult remin
d
ers.
E
.
A
ttentivenes
s
—
R
esists Distraction
t
o
M
aintain Focus
o
n Tas
k
s Set B
y
S
omeone Els
e
1
.
R
emains on tas
k
d
uring an activity set
b
y the teacher for
short periods of
time despite
d
istractions with
minimal prompting
f
rom adults (e.g.,
can ignore ot
h
er
activities nearby and
h
ol
d
focus on a
tea
ch
er
d
irecte
d
small group activity).
2.
M
ay need a
remin
d
er to return
to an earlier tas
k
after an interruption.
E
.
A
ttentivenes
s
—
R
esists Distraction
t
o
M
aintain Focus
o
n Tas
k
s Set B
y
S
omeone Els
e
1
.
Independentl
y
avoids distractions
an
d
remains on
tas
k
for short
periods of time
d
uring a teacher
d
irected activity.
2.
C
an
i
n
dependentl
y
pause and resume
an activity to
respond to an
interruption.
3.
Uses self
-
f
f
tal
k
and other strategies
to maintain focus
o
n
d
ifficult tasks
and assignments
f
rom adults (e.g.,
“T
h
ere’s onl
y
t
h
re
e
more questions left.
If I finish these,
t
h
en I’
l
l
b
e all done
wit
h
t
h
is pro
j
ect
”)
.
continued from previous page

144 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: Approaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
Standard: Working Memory
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Use objects and
toys more
purposefully.
Use imagination,
memory and
reasoning to plan
and make things
happen.
Improve memory
for details.
A. Demonstrate the
Ability to Hold and
Manipulate
Information
1. Can remember
and talk about what
has just happened
in a story and what
is happening now.
2. Can consider
two options and
make a choice
when asked.
3. Can hold two
rules in mind long
enough to
complete the tasks
(e.g., “Throw your
trash away, and
then put your
lunchbox in your
A. Demonstrate the
Ability to Hold and
Manipulate
Information
1. Can remember
recent events in a
story and use this
information to
shape predictions
and questions.
2. Will frequently
consider a couple of
possibilities before
making a choice.
3. Can remember
and follow multiple
classroom rules with
visual and auditory
cues.
A. Demonstrate the
Ability to Hold and
Manipulate
Information
1. Remembers
several key points
in a story and then
answers questions
accurately (e.g.,
how did the main
character feel when
she finds the dog?).
2. Spends time
deliberating and
weighing choices
(e.g., may spend a
long time thinking
about whether to
go to the store with
mom or to stay
home and help
dad).
3. Identifies and
can hold in mind
school rules
independently.
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Foun
d
ation
s
S
tran
d:
A
ppr
o
ac
h
es to Learning & Executive Functioning
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Wor
k
in
g
Memor
y
Use ob
j
ects and
t
oys more
purposefully.
1 Year
Use imagination,
memory and
reasoning to plan
and make things
h
appen.
Improve memor
y
f
or
d
etails.
gy
2
Year
s
A.
D
emonstrate t
h
e
A
bility to Hold and
M
anipulate
Inf
o
rmati
on
1
.
Can remem
b
er
and talk about what
h
as
j
ust happened
in a story and what
is
h
appening now.
2.
Can consi
d
er
two option
s
an
d
ma
k
e a
c
hoi
c
e
when asked.
3.
Can hold t
wo
tt
rules in mind long
enoug
h
to
complete the tas
k
s
(
e
.
g
., “T
h
row your
trash away, and
t
h
en put you
r
lunchbox in your
3
Year
s
A.
D
emonstrate t
h
e
A
bility to Hold and
M
anipulate
Inf
o
rmati
on
1
.
Can remem
b
er
recent events in a
story and use this
inf
o
rmati
o
n t
o
shape predictions
and questions.
2.
Will frequentl
y
consider a couple of
possibilities before
ma
k
ing a choice.
3.
Can remem
b
er
and follow multiple
classroom rules wit
h
visual and auditor
y
cue
s
.
4
Year
s
A.
D
emonstrate t
h
e
A
bility to Hold and
M
anipulate
Inf
o
rmati
on
1
.
R
emem
b
ers
several
k
ey points
in a story and then
Kindergarte
n
answers questions
accurately (e.g.,
h
ow did t
h
e main
ch
aracter feel when
she fin
d
s the
d
og?).
2.
S
pends time
d
eliberating and
weig
h
ing c
h
oices
(
e.g., may spend a
long time thin
k
ing
about whether to
go to t
h
e store wit
h
mom or
t
o s
t
a
y
h
ome and help
d
ad
)
.
3.
I
d
entifies an
d
can hol
d
in min
d
sc
h
ool r
u
les
independently.
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
continued on next page

Appendix | 145
M
cubby).
4. Can remember a
response to a
teacher’s question
long enough to
respond
appropriately after
waiting for a turn
during a short
group discussion.
5. Can put down a
toy and remember
its location for a
brief period of
time.
6. Can enjoy
success at simple
memory games
tracking a few
objects or pictures.
4. Can remember
and follow two-step
directions without
prompting.
5. Can hold in mind
the comments of
peers and respond
appropriately during
a short class
discussion.
6. Can keep track of
a few different
objects for short
periods of time.
7. Can enjoy more
complex memory
games with more
cards or objects.
4. Can contribute
appropriately to
more complex
group discussions,
holding in mind
both the topic of
discussion and the
contributions of
peers.
5. Can keep track
of the parts for
more complicated
projects involving
many pieces.
6. Can enjoy
success at complex
memory games,
including games
requiring the
tracking hidden
objects (e.g., a
memory game on a
rotating board).
cubby).
4.
Can remember a
response
t
o a
teac
h
er’s question
long enoug
h
to
respond
appropriately after
waiting for a turn
d
uring a short
group discussion.
5. Can put down a
toy and remember
its location for a
b
rief period of
time
.
6.
C
an en
j
o
y
success at simple
memo
r
y games
trac
k
ing a fe
w
o
b
j
ects or pictures.
4.
Can remember
and follow tw
o
-
s
te
p
d
irections without
prompting.
5. Can hol
d
in min
d
the comments of
peers and respond
appropriately during
a s
h
ort class
d
iscussion.
6.
Can
k
eep trac
k
of
a few different
o
b
j
ects for s
h
o
r
t
periods of time.
7.
C
an en
j
oy more
complex memor
y
games wit
h
more
cards or ob
j
ects.
4.
Can contribute
appropriately to
more complex
group discussions,
h
olding in mind
b
oth the topic of
d
iscussion an
d
the
contri
b
utions of
peers.
5. Can
k
eep trac
k
o
f the parts for
more complicated
pro
j
ects involving
many pieces.
6.
C
an en
j
o
y
success at complex
memo
r
y games,
including games
requiring t
h
e
tracking hidden
o
b
j
ects (e.g., a
memo
r
y game on a
rotating board).
continued from previous page

146 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: Approaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
Standard: Cognitive Flexibility
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Interact with other
children.
Share his feelings
through talking and
pretend play.
A. Can Flexibly
Apply Rules to
Games and
Behavior
1. Can take on a
character in
pretend play and
sustain this role
consistently for
approximately 5-10
minutes with adult
modeling and
support.
2. Can enjoy games
with rules and
follow the rules
some of the time.
3. Can learn to
follow different
rules in different
contexts and can
do so with
reminders (e.g., use
indoor voices
indoors but not
outdoors).
4. Can recognize
when making a
mistake and change
A. Can Flexibly
Apply Rules to
Games and
Behavior
1. Can
independently
sustain a character in
pretend play for ten
minutes or longer.
2. Can switch roles
in dramatic play.
3. Can enjoy games
like Simon Says that
require child to
follow two different
rules when cued
(copying, not
copying).
4. Can follow
different rules in
different familiar
A. Can Flexibly
Apply Rules to
Games and
Behavior
1. Sustains roles in
pretend play
independently and
negotiates the roles.
2. Can change roles
easily during the
play if necessary or
desired.
3. Become skilled at
games like Simon
Says that require
the child to follow
two different rules
and can shift rules
without direct
prompting.
4. Can consistently
follow different
rules in different
Interact wit
h
ot
h
er
chil
d
ren.
1 Year
S
hare his feelings
t
h
roug
h
talking and
pretend play.
2
Year
s
A
. Can Flexibl
y
A
p
ply Rules to
Games an
d
Be
h
avior
1
.
C
a
n
ta
k
e
o
n a
ch
ara
c
ter in
pretend play and
sustain t
h
is role
consistently for
approximately 5
-
10
minutes with adult
modeling and
suppor
t
.
2.
C
an en
j
oy games
with rules and
f
ollow the rules
some of the time.
3.
C
an learn t
o
f
ollow different
rules in
d
iffer
e
nt
contexts an
d
can
d
o so with
reminders (e.g., use
indoor voices
indoors
b
ut not
o
utdoors
)
.
4.
C
an recognize
when ma
k
ing a
mistake and change
3
Year
s
A.
Can Flexibl
y
A
pply Rules to
Games an
d
Be
h
avior
1
.
C
an
independentl
y
sustain a c
h
aracter in
pretend play for
t
en
minutes or longer.
2.
Can switc
h
roles
in dramatic play.
3.
C
an en
j
oy games
li
k
e Simon Says that
require child to
f
ollow two different
rules when cued
(
copying, not
copying
)
.
4.
Can follo
w
d
ifferent rules in
d
ifferent familiar
4
Year
s
A.
Can Flexibl
y
Kindergarte
n
A
pply Rules to
Games an
d
Be
h
avior
1
.
S
ustains roles in
pretend pla
y
independently and
n
egotiates t
h
e roles.
2.
Can c
h
ange roles
easily during the
play if necessary or
d
esire
d
.
3.
Become skille
d
at
games li
k
e Simon
S
ays t
h
at require
the child to follo
w
two different rules
an
d
can shift rules
without direct
prompting.
4.
Can consistentl
y
f
ollow different
rules in
d
ifferent
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Foun
d
ation
s
S
tran
d:
A
pproaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Cognitive Flexi
b
ilit
y
continued on next page

Appendix | 147
M
approach with adult
help.
5. Able to sort
materials by two
different
characteristics (e.g.,
blocks go here,
dolls go here).
B. Flexible Problem
Solving - Seeks
Multiple Solutions
to a Question,
Task, or Problem
1. Employs a
strategy to solve a
problem with adult
modeling,
prompting, and
support.
contexts with
minimal reminders
(e.g., take off shoes
at home but not at
school).
5. Will often
recognize and
correct mistakes
independently.
6. Able to change
the categories used
for sorting materials
with help (e.g., sort
by color then by
shape).
B. Flexible Problem
Solving - Seeks
Multiple Solutions
to a Question, Task,
or Problem
1. Begins to employ
their own solutions
to problems through
trial and error (e.g.,
tries different pegs
to see which one
fits).
contexts and
quickly learn and
follow new rules in
new contexts.
5. Able to
recognize and
correct mistakes.
6. Can sort by
different attributes
independently.
B. Flexible Problem
Solving - Seeks
Multiple Solutions
to a Question,
Task, or Problem
1. Solves problems
by planning and
carrying out a
sequence of
actions; may seek
more than one
solution, and
explain their
reasoning (e.g.,
discusses the
number of people
who want some
approach with adult
h
elp.
5.
Ab
le to s
o
r
t
materials by two
d
ifferent
c
h
aracteristics (e.g.,
b
locks go here,
d
olls go here).
B
.
F
lexi
b
le Pro
b
lem
S
olving
-
S
ee
k
s
M
ultiple S
o
lutions
to a Question,
Task, or Proble
m
1
.
Employs a
strategy to solve a
problem with adult
modeling,
prompting, and
suppor
t
.
contexts wit
h
minimal remin
d
ers
(
e.g., ta
k
e off shoes
at home but not at
sc
h
ool
)
.
5. Will often
recognize and
correct mista
k
es
independently.
6.
A
ble to change
the categories used
f
or sorting materials
wit
h
h
elp (e.g., sort
b
y color then b
y
s
h
ape)
.
B
.
F
lexi
b
le Pro
b
lem
S
olving
-
S
ee
k
s
M
ultiple
S
o
lutions
to a Question, Tas
k
,
o
r Pro
b
le
m
1
.
Begins to emplo
y
t
h
eir own soluti
o
ns
to problems through
trial and error (e.g.,
tries different pegs
to see w
h
ic
h
one
f
its
)
.
c
o
ntexts an
d
quickly learn and
f
ollow new rules in
n
ew con
t
ex
t
s.
5.
Ab
le to
recognize and
correct mista
k
es.
6.
Can sort b
y
d
ifferent attri
b
utes
independently.
B
.
F
lexi
b
le Pro
b
lem
S
olving
-
S
ee
k
s
M
ultiple S
o
lutions
to a Question,
Task, or Proble
m
1
.
S
olves problems
b
y planning and
carrying out a
sequence of
actions; may see
k
m
o
re t
h
an
o
ne
solution, and
explain t
h
eir
reasoning (
e
.
g
.,
d
iscusses the
n
umber of people
w
h
o want some
continued from previous page

148 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Begin to express a
variety of feelings.
Use coping skills
with tasks, and
interactions with
peers and adults.
2. Asks adults to
solve or “fix” a
problem.
3. Continues to
become more
flexible in problem-
solving and
thinking through
alternatives (e.g.,
when trying to put
on shoes, talks to
self about what to
do first. If the shoe
won't easily go on
2. Continues to
become more
cognitively flexible
and is able to draw
on varied resources
to solve problems
(e.g., tries to build a
large structure with
blocks, but the
building keeps
falling down. After
several failed
attempts, he or she
tries making a larger
base. May also look
at how other
children have made
their buildings).
3. When in conflict
with another child,
increasingly able to
suggest possible
solutions.
play dough,
suggests methods
for dividing it, and
how they might
determine if the
pieces are all the
same).
2. Becomes
increasingly able to
think creatively
about multiple
solutions to a
problem (i.e.,
analyzes possible
results).
3. Utilizes varied
and flexible
approaches to solve
longer-term or
more abstract
challenges (e.g.,
when planning to
have friends over
on a rainy day,
thinks about how
to deal with a
Begin to express a
variety of feelings.
Use coping s
k
ills
with tasks, and
interactions wit
h
peers and adults.
2.
A
sks a
d
ults to
solve or “fix” a
problem.
3.
C
ontinues to
b
ecome more
f
lexible in proble
m
-
solving and
thin
k
ing through
alternatives (e.g.,
w
h
en trying to put
o
n shoes, tal
k
s to
self about what to
d
o first. If the shoe
won
'
t easily go on
2.
C
ontinues to
b
ecome more
cognitively flexible
and is able to dra
w
o
n varied resources
to solve problems
(
e.g., tries to build a
large structure wit
h
b
locks, but the
b
uilding keeps
f
alling down. After
several failed
attempts,
h
e or s
h
e
tries ma
k
ing a larger
b
ase. May also loo
k
at
h
ow ot
h
er
ch
ildren have made
their building
s
)
.
3.
When in conflict
with another child,
increasingly able to
suggest possib
l
e
solutions.
play dough,
suggests methods
f
or dividing it, and
h
ow t
h
ey mig
h
t
d
etermi
n
e if the
pieces are all t
h
e
same
)
.
2.
Becomes
increasingly able to
thin
k
creativel
y
about multiple
solutions to a
problem (i.e.,
analyzes possible
results
)
.
3.
Utilizes varied
and flexi
b
le
approac
h
es to solve
longer
-
t
erm
o
r
more a
b
stract
ch
al
l
enges
(
e.g.,
w
h
en planning to
h
ave friends over
o
n a rainy day,
thinks about ho
w
to deal with a
continued on next page

Appendix | 149
M
one foot, he or she
tries the other
foot).
4. After a conflict
with another child,
can talk about
other ways the
problem might
have been resolved.
5. When faced with
a problem can slow
down and think
through options
with support from
an adult (e.g., “It
looks like someone
is in your way.
What could you do
to get him to
move?”).
4. When faced with
a problem, can be
reminded to slow
down and think
about what to do.
limited space to
play).
4. Able to negotiate
conflicts with other
children
independently by
considering a few
potential solutions.
5. May slow down
and use self-talk to
think about what to
do when
approaching
problem.
o
ne foot,
h
e or s
h
e
tries t
h
e ot
h
er
foot
).
t
4.
A
fter a
c
onfli
c
t
with another child,
can talk a
b
out
o
t
h
er ways t
h
e
problem might
h
ave
b
een resolved.
5. When faced with
a proble
m
can slo
w
d
own and thin
k
t
h
roug
h
options
with support from
an adult (e.g., “It
loo
k
s li
k
e someone
is in your way.
W
h
at co
u
ld you do
to get
h
im to
move?
”)
.
4.
When faced with
a problem, can be
reminded to slo
w
d
own and thin
k
about what to do.
limited space to
play).
4.
A
ble to negotiate
conflicts with other
chil
d
ren
independently b
y
considering a fe
w
potential solutions.
5.
M
ay slow down
an
d
use
self
-
f
f
tal
k
t
o
think about what to
d
o when
approac
h
ing
problem.
continued from previous page

150 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: $SSURDFKHVWR/HDUQLQJDQG([HFXWLYH)XQFWLRQLQJ
Standard: Initiative & Curiosity
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Understand
questions and
simple directions.
A. Desire to
Learn—Ask
Questions and
Seeks New
Information
1. Begins to ask
basic “wh”
questions related to
the environment
(e.g., “Where is
Sarah going?”).
2. Seeks
experiences with
new toys and
materials (e.g.,
listens to stories,
plays with friends
at the water table,
takes trips to the
fire station).
3. Generates ideas
with teachers and
peers with adult
modeling and
support.
A. Desire to
Learn—Ask
Questions and Seeks
New Information
1. Asks questions
about future events,
as well as about the
here and now (e.g.,
asks, "When will we
go to Val’s?).
2. Poses questions
to seek explanations
about topics of
interest with adult
support and
modeling.
3. Elaborates on
experiments by
attempting to
replicate results
using different
materials (e.g.,
gathers several
materials to drop in
the water table, then
A. Desire to
Learn—Ask
Questions and
Seeks New
Information
1. Asks higher-level
questions (e.g.,
"What would
happen if we had
no food?" or "Why
was Raymond mad
at me"?).
2. Poses questions
to seek explanation
on a variety of
topics.
3. Tries an even
wider range of new
experiences, both
independently and
with peers and
adults
Explain the
concept of effort.
Explain the concept
of effort.
1 Year
Un
d
erstan
d
questions and
simple
d
irections.
2
Year
s
A.
D
esire t
o
L
earn
—
Ask
—
Questions an
d
S
ee
k
s Ne
w
Inf
o
rmati
on
1
.
Begins to as
k
b
asic “wh”
questions related t
o
t
h
e environment
(
e.g., “W
h
ere i
s
S
ara
h
going?”).
2.
S
ee
ks
experiences wit
h
n
ew toys an
d
materials (e.g.,
listens to stories,
plays with friend
s
at the water table,
ta
k
es trips to th
e
f
ire station
)
.
3.
Generates i
d
ea
s
with teachers an
d
peers with adult
modeling an
d
suppor
t
.
3
Year
s
A.
D
esire t
o
L
earn
—
Ask
—
Questions and Seek
s
New Information
1
.
A
sks question
s
about future events,
as well as about th
e
h
ere and now (e.g.,
asks,
"
When will w
e
go to Val’s?)
.
2.
P
oses question
s
to see
k
explanation
s
about topics of
interest with adult
support an
d
modeling.
3.
Ela
b
orates o
n
experiments b
y
attempting t
o
replicate result
s
u
sing different
materials (e.g.,
gat
h
ers severa
l
materials to drop in
the water table, then
4
Year
s
A.
D
esire t
o
L
earn
—
Ask
—
Questions an
d
S
ee
k
s Ne
w
Inf
o
rmati
on
1
.
A
sks higher
-
leve
l
questions (e.g.,
Kindergarte
n
"
What woul
d
h
appen if we ha
d
n
o food?
"
or
"
Wh
y
was Raymond ma
d
at me
"
?
)
.
2.
P
oses question
s
to see
k
explanatio
n
o
n a variety of
topics.
3.
T
ries an eve
n
wider range of ne
w
experiences, bot
h
independently an
d
with peers an
d
a
d
ult
s
Gra
d
e
1
Explain t
h
e
concept of effort.
Gra
d
e
2
Explain t
h
e concept
o
f effort
.
D
o
main
:
S
ocia
l
F
oun
d
ations
S
tran
d:
$
SSURDFKHVWR/HDUQLQJDQG([HFXWLYH)XQFWLRQLQJ
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Initiative &
C
uriosit
y
continued on next page

Appendix | 151
M
B. Desire to
Learn—Interest in
Challenges
1. Continues to ask
numerous
questions, which
are becoming more
verbally complex
(e.g., asks, "How
do we get to Nana's
house?").
2. Starts to
demonstrate
enthusiasm for new
challenges and
experiences.
sorts what sinks vs.
what floats).
4. Asks to
participate in new
experiences that he
or she has observed
or has heard of
others participating
in (e.g., says, "Janice
goes fishing. Can
I?").
B. Desire to
Learn—Interest in
Challenges
1. Asks questions
about future events,
as well as about the
here and now (e.g.,
asks "When will we
go to Sarah's house
again?").
2. Starts to show an
increase in
enthusiasm for
learning letters,
shapes, and
numbers (e.g., while
looking at a book
with dad, points to a
word that contains
the letter "S" and
says, "S! That's in
4. Expands verbal
and nonverbal
enthusiasm for
learning new
things, including
academic (e.g.,
reading, writing)
and physical skills
(e.g., riding a bike).
B. Desire to
Learn—Interest in
Challenges
1. Attempts
activities that are
new and
challenging. May
deliberately take
risks when learning
new skills.
2. Shows interest
and skill in more
complex self-help
skills (e.g., zips
jacket, prepares a
snack).
B
.
D
esire to
L
earn
—
I
n
terest in
C
h
allenge
s
1
.
Continues to as
k
n
ume
r
ous
questions, w
h
ic
h
a
r
e
b
ecoming more
verbally complex
(
e.g., asks,
"
Ho
w
d
o we get to Nana
'
s
h
ouse?
")
.
2.
S
tarts to
d
emonstrate
enthusiasm for ne
w
challenges and
experiences.
sorts what sin
k
s vs.
w
h
at
f
loats
)
.
4.
A
sks to
participate in ne
w
experiences t
h
at
h
e
o
r she has o
b
served
o
r has hear
d
of
o
t
h
ers participating
in (e.g., says,
"
Janice
goes fishing. Can
I?
")
.
B
.
D
esire to
L
earn
—
I
n
terest in
C
h
allenge
s
1
.
A
sks questions
about future events,
a
s
well as about the
h
ere and now (e.g.,
asks
"
When will we
go to Sarah
'
s house
again?
"
).
2.
S
tarts to s
h
ow an
increase in
enthusiasm for
learning letters,
shapes, and
n
umbers (e.g., while
looking at a boo
k
with dad, points to a
word that contains
t
h
e lett
e
r
"
S
"
an
d
says,
"
S! That
'
s in
4.
Expands verbal
and nonver
b
al
enthusiasm for
learning ne
w
things, including
academic
(
e
.
g
.,
reading, writing)
and physical skill
s
(
e
.
g
., riding a bike).
B
.
D
esire to
L
earn
—
I
n
terest in
C
h
allenge
s
1
.
A
ttempts
activities t
h
at are
n
ew and
c
h
allenging. Ma
y
d
eliberately take
ris
k
s when learning
n
ew s
k
ills.
2.
Sh
ows interest
an
d
skill in more
complex self
-
f
f
h
elp
s
k
ills (e.g., zips
j
ac
k
et, prepares a
snac
k)
.
continued from previous page

152 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
C. Independence in
Learning—Plans
and Initiates
Projects
1. Begins to actively
participate in
classroom activities
(i.e. answers
questions or joins
dramatic play).
2. Chooses where
to play during
center time.
my name! What is
that word?").
3. Seeks new and
varied experiences
and challenges (e.g.,
puts materials
together in new
ways to test results;
joins in a peer-
created game or
activity, tries to
dress a new doll or
builds a new
construction toy).
C. Independence in
Learning—Plans
and Initiates
Projects
1. When prompted,
initiates plan of
activities.
2. Shows interest in
leading activities and
taking responsibility
during cleanup
activities.
C. Independence in
Learning—Plans
and Initiates
Projects
1. Independently
plans a project and
gathers materials
needed to execute
the project.
2. Self-selects a
variety of activities
during free choice
and puts away
related materials
where they belong
when finished prior
to transitioning to
next activity.
C.
Independence in
Learning
—
g
g
P
lans
an
d
Initiates
P
ro
j
ect
s
1
.
Begins to activel
y
participate in
classroom activities
(
i.e. answers
questions or
j
oins
d
ramatic play).
2.
C
h
ooses w
h
ere
to play during
c
enter time.
my name! W
h
at is
that word?
")
.
3.
S
eeks new and
varied experiences
and challenges (e.g.,
puts materials
toget
h
er in ne
w
ways
t
o
t
es
t
results;
j
oins in a peer
-
created game or
activity, tries to
d
ress a new doll or
b
uilds a ne
w
construction toy
)
.
C.
Independence in
Learning
—
g
g
P
lans
an
d
Initiates
P
ro
j
ect
s
1
.
When prompted,
initiates plan of
activitie
s
.
2.
Sh
ows interest in
leading activities and
taking responsibilit
y
d
uring cleanup
activities.
C.
I
ndependence in
Learning
—
g
g
P
lans
an
d
Initiates
P
ro
j
ect
s
1
.
Independentl
y
plans a pro
j
ect and
gat
h
ers materials
n
ee
d
e
d
to execute
t
h
e pro
j
ect.
2.
Self
-
f
f
selects a
variety of activities
d
uring free choice
and puts awa
y
relate
d
materials
w
h
ere t
h
e
y
b
elong
when finished prior
to transitioning to
n
ext activity.
continued on next page

Appendix | 153
M
3. Begins to
independently
select appropriate
materials during
specific activities
(e.g., when
presented with a
painting project
gets red and green
paint).
3. Further expands
areas of decision-
making (e.g., child
may say, "This
morning I'm going
to work on my Lego
building").
4. Develops greater
ability to set goals
and follow a plan
(e.g., child says, "I'm
going to pick up all
these branches," and
then works until it is
done).
3. Actively
participates in
creating games or
activities with
peers.
4. Independently
takes initiative to
solve problems
occurring within
activities without
immediately
requiring adult
support (e.g., the
child will search for
the missing piece in
the doctor’s kit for
several minutes
before asking for
help).
3.
Begins to
independentl
y
select appropriate
materials during
specific activities
(
e.g., w
h
en
presented with a
painting
p
ro
j
ect
gets red and green
paint
)
t
t
.
3.
F
urther expands
a
r
eas
o
f
d
ecisio
n
-
making (e.g., child
may say,
"
This
morning I
'
m g
o
ing
to wor
k
on my Lego
b
uilding
")
.
4.
D
evelops greater
ability to set goals
and follow a plan
(
e
.
g
., child says,
"
I
'
m
going to pic
k
up all
these branches,
"
and
then wor
k
s until it is
d
one
)
.
3.
A
ctivel
y
participates in
creating games or
activities wit
h
peers.
4.
Independentl
y
ta
k
es initiative to
solve problems
o
ccurring wit
h
in
activities wit
h
out
immediatel
y
requiring adult
support (e.g., t
h
e
child will search for
t
h
e missing piece in
the
d
octor’s kit for
several minutes
b
efore asking for
h
elp).
continued from previous page

154 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: Approaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
Standard: Demonstrates Persistence
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Persists in an
Activity From Start
to Finish
(Complete a Task)-
-Independently
1. Persists with a
wider variety of
tasks, activities, and
experiences with
adult prompting.
2. Keeps working
to complete a task
even if it is
moderately difficult
(e.g., persists with a
somewhat
challenging wooden
puzzle).
3. Notes sense of
accomplishment
when finishing a
planned activity
(e.g., successfully
drawing a figure).
A. Persists in an
Activity From Start
to Finish (Complete
a Task)--
Independently
1. Persists with a
wider variety of
tasks, activities, and
experiences with
adult prompting.
2. Keeps working to
complete a task even
if it is moderately
difficult (e.g.,
persists with a
somewhat
challenging wooden
puzzle).
3. Will often persist
in working to
complete all aspects
of a planned task
(e.g., when building
a zoo in the block
area, will keep
working until every
animal has a cage).
A. Persists in an
Activity From Start
to Finish
(Complete a Task)-
-Independently
1. Persists with a
wider variety of
tasks, activities, and
experiences with
adult prompting.
2. Keeps working
to complete a task
even if it is
moderately difficult
(e.g., persists with a
somewhat
challenging wooden
puzzle).
3. Can persist in
completing a
complicated plan
(e.g., creating a
parade in the
classroom that
involves making
instruments,
costumes and
decorations).
1 Year
2
Year
s
A.
P
ersists in an
A
ctivity From Start
to Finis
h
(C
o
m
p
lete a Tas
k)
-
-
I
n
dependentl
y
1
.
P
ersists wit
h
a
wider variety of
tasks, activities, and
experiences wit
h
adult prompting.
2.
Keeps wor
k
ing
to complete a tas
k
even if it is
moderately difficult
(
e.g., persists wit
h
a
somew
h
at
challenging wooden
puzzle).
3.
Notes sense of
accompli
s
h
ment
when finishing a
planned activit
y
(
e
.
g
., successfull
y
d
rawing a figure).
3
Year
s
A.
P
ersists in an
A
ctivity From Start
to Finis
h
(C
o
m
p
lete
a Tas
k)
--
I
n
dependentl
y
1
.
P
ersists wit
h
a
wider variety of
tasks, activities, and
experiences wit
h
adult prompting.
2.
Keeps wor
k
ing to
complete a tas
k
even
if it is moderatel
y
d
ifficult (e.g.,
persists wit
h
a
somew
h
at
challenging wooden
puzzle).
3.
Will often persist
in wor
k
ing to
complete all aspects
o
f a planned tas
k
(
e.g., when building
a zoo in the
b
loc
k
area, will
k
eep
wor
k
ing until ever
y
animal
h
as a cage).
4
Year
s
A.
P
ersists in an
A
ctivity From Start
to Finis
h
(C
o
m
p
Kindergarte
n
lete a Tas
k)
-
-
I
n
dependentl
y
1
.
P
ersists wit
h
a
wider variety of
tasks, activities, and
experiences wit
h
adult prompting.
2.
Keeps wor
k
ing
to complete a tas
k
even if it is
moderately difficult
(
e.g., persists wit
h
a
somew
h
at
challenging wooden
puzzle).
3.
C
an persist in
completing a
complicated plan
(
e.g., creating a
parade in the
classroom t
h
at
involves ma
k
ing
instruments,
costumes an
d
d
ecorations
)
.
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Foun
d
ation
s
S
tran
d:
A
pproaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
D
emonstrates Persistenc
e
continued on next page

Appendix | 155
M
B. Persists in the
Face of Failure
1. Insists upon
putting on coat
independently,
even though prior
attempts have been
unsuccessful.
2. Continues to
stack cups or
complete a simple
puzzle
unsuccessfully
without an
emotional outburst
with adult support.
3. Can adjust
approach to a task
to resolve
difficulties with
adult help (e.g., if
teacher suggests the
child rotate a
puzzle piece to find
a better fit).
B. Persists in the
Face of Failure
1. Continues to
attempt to build a
tower even after
three or more
unsuccessful
attempts with adult
support and
encouragement.
2. Experiences
difficulty with
drawing, cutting,
and writing, but
persists with adult
support and
encouragement until
task is complete.
3. Will often notice
that a problem can
be resolved by a
change in approach
(e.g., trying to fit a
puzzle piece a few
times and then
rotating to find a
better fit).
B Persists in the
Face of Failure
1. Continues to
attempt to build a
tower even after
three or more
unsuccessful
attempts
independently.
2. Experiences
difficulty with
writing, however
continues to try
write letters and
numbers
independently, until
the task is
completed.
3. Will consistently
try a new approach
to a problem when
the old one is not
working (e.g.,
immediately
rotating a puzzle
piece to find a
better fit).
B
.
P
ersists in t
h
e
F
a
c
e of Failur
e
1
.
Insists upon
putting on coat
independently,
even t
h
oug
h
prior
attempts have been
u
nsuccessful.
2.
C
ontinues to
stac
k
cups or
comp
l
ete a simple
puzzle
u
nsuccessfull
y
wit
h
out an
emotional out
b
urst
with adult support.
3.
Can ad
j
ust
approach to a tas
k
to resolve
d
ifficulties with
adult help (e.g., if
teac
h
er suggests t
h
e
chil
d
rotate a
puzzle piece to find
a better fit
)
.
B
.
P
ersists in t
h
e
F
a
c
e of Failur
e
1
.
Con
tinues to
attempt to build a
tower even after
t
h
re
e
or
m
or
e
u
nsuccessful
attempts with adult
support and
encouragemen
t
.
2.
Experiences
d
ifficulty with
d
rawing, cutting,
and writing, but
persists with adult
support and
encouragement until
tas
k
is complete.
3.
Will often notice
that a problem can
b
e resolved by a
c
h
ange in approac
h
(
e.g., trying to fit a
puzzle piece a fe
w
times an
d
then
rotating to find a
b
etter fit
)
.
B
P
ersists in t
h
e
F
a
c
e of Failur
e
1
.
C
ontinues to
attempt to build a
tower even after
t
h
ree
or
m
or
e
u
nsuccessful
a
tt
emp
t
s
independent
l
y.
2.
Experiences
d
ifficulty with
writing,
h
owever
continues to tr
y
write letters and
n
um
b
ers
independently, until
the tas
k
is
completed.
3.
Will consistentl
y
try a new approac
h
to a problem when
the ol
d
one is not
wor
k
ing (e.g.,
immediatel
y
rotating a puzzle
piece to find a
b
etter fit
)
.
continued from previous page

156 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: Approaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
Standard: Demonstrates Cooperation
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Play alongside
other children.
Show more
awareness of the
feelings of another
child.
A. Positively
Participates in
Cooperative Play
1. Offers basic help
to peers who are in
need, upset, hurt,
or angry (e.g., hug,
comfort object, pat,
encouraging word).
2. Attempts to give
aid may not take
into account the
other child's
characteristics or
needs (e.g., offers a
crying classmate his
or her own stuffed
animal, even
though the child
has another
comfort object).
A. Positively
Participates in
Cooperative Play
1. Responds more
appropriately and
sympathetically to
peers who are in
need, upset, hurt, or
angry (e.g., says,
"Don't cry, Willy.
My daddy can fix
that bike. He knows
how").
A. Positively
Participates in
Cooperative Play
1. Uses a wider
array of words or
actions to
demonstrate
awareness,
understanding, and
concern for what
others are feeling
(e.g., goes over to a
child whose block
building has fallen
down and says,
"Don't worry,
Manuel. I'll help
you build it up
again").
1 Year
P
lay alongside
o
ther chil
d
ren.
Sh
ow more
awareness of the
f
eelings of another
chil
d
.
p
2
Year
s
A.
P
ositiv
e
l
y
P
articipates in
Cooperative Pla
y
1
.
O
ffers basic help
to peers w
h
o are in
n
eed, upset, hurt,
o
r angry (e.g.,
h
ug,
comfort ob
j
ect, pat,
encouraging word).
2.
A
ttempts to give
aid may not take
into a
cc
ount t
h
e
o
ther chil
d'
s
ch
ara
c
t
e
ristics or
n
ee
d
s
(
e.g.,
o
ffers a
crying classmate
h
is
o
r her own stuffed
animal, even
though the child
h
as anot
h
er
comfort ob
j
ect).
3
Year
s
A.
P
ositiv
e
l
y
P
articipates in
Cooperative Pla
y
1
.
R
esponds more
appropriately and
sympat
h
etically to
peers w
h
o are in
n
eed, upset, hurt, or
angry
(
e.g., say
s
,
"
Don
'
t cry, Willy.
M
y dadd
y
c
an fix
that
b
ike. He
k
n
ows
h
o
w
")
.
4
Year
s
A.
P
ositiv
e
l
y
P
articipates in
Cooperative Pla
y
1
.
Uses a wi
d
e
r
array of words or
actions to
d
emon
s
t
ra
t
e
awa
r
eness,
u
nderstanding, and
concern for what
o
thers are feeling
(
e.g., goes over to a
child whose bloc
k
b
uilding has fallen
d
own and says,
"
Don
'
t worry,
M
anuel
.
I
'
ll help
Kindergarte
n
you build it up
agai
n
")
.
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Foun
d
ation
s
S
tran
d:
A
pproaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Demonstrates Cooperation
continued on next page

Appendix | 157
M
Show his feelings
through talking and
pretend play.
Use coping skills
with tasks, and
interactions with
peers and adults.
3. Begins to have
real friendships,
even though he or
she may not
understand the
concept of
friendship or that
these relationships
may not last (e.g.,
says “my best
friends are Nathan,
Sharon, Enrique,
Cassidy…” and all
others in his or her
class).
4. Accepts
compromise when
resolving conflicts
if it is suggested by
an adult (e.g., mom
says, "Jackson, you
can use that swing
as soon as Sheila
has finished").
5. Seeks adults' help
in resolving a
conflict (e.g., goes
to dad and says,
"Jacob took my
truck!").
3. Shows further
progress in
developing
friendships with
peers, even if a bond
is formed with just
one other child.
4. Begins to try to
please other children
(e.g., says, "You can
come to my birthday
party, ok?").
5. Suggests solutions
to problems with
other children, while
continuing to seek
adults' help (e.g.,
says, "Hey,
Benjamin! We can
3. Continues to
establish and
maintain
friendships with
other children.
Seeks others'
acceptance and
friendship (e.g.,
says, "We're
buddies, right?").
4. Uses a broader
repertoire of
strategies, including
negotiation and
compromise, to
resolve conflicts
before seeking
adult help (e.g.,
says, "I have a great
idea, Henry! You
be the bear, and I
will be the lion.
Then we can
switch!").
5.Uses more
complex language
to express his or
her understanding
of feelings and their
causes (e.g., says, "I
want to try riding
S
how his feelings
through talking and
pretend play.
Use coping s
k
ills
with tasks, and
interactions wit
h
peers and adults.
3.
Begins to
h
ave
real friendships,
even t
h
oug
h
h
e or
s
h
e may not
u
n
d
erstan
d
the
concept of
f
riendship or that
t
h
ese relations
h
ips
may no
t
last (e.g.,
says “my best
f
rien
d
s are Nathan,
Sh
aron, Enrique,
Cassidy…” and all
o
t
h
ers in
h
is or
h
er
class
)
.
4.
A
ccepts
compromise w
h
en
resolving conflicts
if it is suggested b
y
an adult (e.g., mom
says,
"
Jackson, you
can use t
h
at swing
as soon as S
he
i
l
a
h
as finishe
d
")
.
5.
S
eeks adults
'
help
in resolving a
conflict (e.g., goes
to dad and says,
"
Jacob took m
y
truck!
")
.
3.
S
hows further
progress in
d
eveloping
f
riendships with
peers, even if a bond
is formed with
j
ust
o
ne other chil
d
.
4.
Begins to try to
please other children
(
e.g., says,
"
You can
come to my birthda
y
party, ok?
"
).
5.
S
uggests solutions
to problems with
o
ther children, while
continuing to see
k
adults
'
help (e.g.,
says,
"
Hey,
Ben
j
amin! We can
3.
C
ontinues to
esta
b
lish and
maintain
f
riendships with
o
ther chil
d
ren.
S
eeks others
'
acceptance and
f
riendship (e.g.,
says,
"
We
'
re
b
uddies, right?
"
).
4.
Uses a
b
roader
repertoire of
strategies, including
n
egotiation and
compromise, to
resolve conflicts
b
efore seeking
adult help (e.g.,
says,
"
I have a great
idea, Henry! You
b
e the bear, and I
will be the lion.
T
h
en we can
switch!
")
.
5.Uses more
complex language
to express
h
is or
h
er understanding
o
f
f
eelings and their
ff
causes
(
e.g., says,
"
I
want to tr
y
ridin
g
continued from previous page

158 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
6. Continues to
learn simple
alternatives to
aggressive ways of
dealing with
conflicts (e.g.,
trades one doll for
a desired one by
saying, "You have
THIS dolly,
okay?").
BOTH be
firemen!").
on that, but I'm
sort of scared,
too").
6.
C
ontinues to
learn simple
alternatives to
aggressive ways of
d
ealing with
conflicts (e.g.,
tra
d
es one
d
oll for
a
d
esire
d
one
by
saying,
"
You have
THIS dolly,
o
kay?
"
).
BOTH
b
e
f
iremen!
")
.
o
n that, but I
'
m
s
o
rt of scared,
too
")
.

Appendix | 159
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: Approaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
Standard: Understanding & complying with classroom rules, routines, & expectations.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Gain in self-
control/regulation.
Show increasing
self-regulation.
A. Follows
Routines, Rules,
and Directions
1. Follows
classroom rules
frequently
2. Behaves
appropriately
within the context
of the classroom
routines (e.g., sits
for brief periods
during circle or
washes hands for
lunch time.
3. Begins to
anticipate the next
activity in the
routine (e.g., asking
“Are we going
outside?” during
snack time).
A. Follows
Routines, Rules, and
Directions
1. Helps to create
classroom rules.
2. Responds to
teacher directions or
signals consistently.
3. Takes initiative
with assigned or
chosen tasks relating
to classroom
routines.
4. Behaves
appropriately within
the context of the
classroom routines
with adult modeling
and support (i.e.
listens when
A. Follows
Routines, Rules,
and Directions
1. Able to answer
why specific rules
exist (i.e., safety
rules).
2. Able to help
create school rules.
3. Able to
recognize rules as
fair or unfair.
4. Able to help
problem solve rules
in support of fair
treatment of
everyone.
G
ain in
self
-
f
f
control
/
regulation.
1 Year
Sh
ow increasing
self
-
f
f
regulation.
2
Year
s
A
. Follows
R
outines, Rules,
an
d
Direction
s
1
.
F
ollows
classroom rules
f
requentl
y
2.
Be
h
aves
appropriatel
y
wit
h
in t
h
e cont
e
xt
o
f the classroom
routines
(
e.
g
., sits
f
or brief periods
d
uring circle or
washes hands for
lun
ch
time.
3.
Begins to
anticipate t
h
e next
activity in t
h
e
routine
(
e.
g
., as
k
ing
“Are we going
o
utside?” during
snac
k
time
)
.
3
Year
s
A.
F
ollows
R
outines, Rules, and
D
irection
s
1
.
H
elps to create
classroom rules.
2.
R
esponds to
teacher
d
irections or
signals consistently.
3.
Ta
k
es initiative
with assigned or
chosen tas
k
s relating
to classroom
routines.
4.
Be
h
aves
appropriatel
y
wit
h
in
the
c
ontext of the
classroom routines
with adult modeling
and support (i.e.
listens w
h
en
4
Year
s
A.
F
ollows
R
outines, Rules,
an
d
Direction
s
1
.
A
ble to answer
why specific rules
exist (i.e., safet
y
rules
)
.
2.
A
ble to help
create sc
h
ool rules.
3.
Ab
le to
Kindergarte
n
recognize rules as
f
air or unfair
.
4.
A
ble to help
problem solve rules
in support of fair
treatment
o
f
eve
r
yone.
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Foun
d
ation
s
S
tran
d:
A
pproaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Understanding & complying with classroom rules, routines, & expectations.

160 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
someone else is
talking or raises
hand to share).
5. Requires fewer
prompts to follow
classroom routines
and is able to
independently
anticipate what
happens next.
5. Able to plan
their activities
around the
classroom routine
6. Identifies
classroom routines
by day of the week
(e.g., understanding
on Monday music
is after lunch, etc.).
7. Behaves
appropriately
within the context
of school routines
(e.g., exiting the
bus or attending
school assemblies).
someone else is
tal
k
ing or raises
h
an
d
to shar
e
)
.
5.
R
equires fewer
prompts to follo
w
classroom routines
and is a
b
le to
independentl
y
anticipate w
h
at
h
appens
n
ex
t.
5.
A
ble to plan
t
h
eir activitie
s
aroun
d
the
classroom routin
e
6.
I
d
entifies
classroom routines
b
y day of the wee
k
(
e.
g
.,
u
nderstanding
o
n Monday music
is after lunch, etc.
)
.
7.
Be
h
aves
appropriatel
y
wit
h
in t
h
e
c
ontext
o
f school routines
(
e.
g
., exiting t
h
e
b
us
o
r attending
school assemblies
)
.

Appendix | 161
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: Approaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
Standard: Understanding & complying with classroom rules, routines, and expectations.
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
A. Demonstrates
the Ability to
Postpone Activity
and Start Another
1. Responds to
visual or auditory
prompts and cues
to transition to the
next activity with
adult support.
2. Moves from a
preferred activity to
a less preferable
activity with adult
support and
assistance.
3. Demonstrates
the ability to stop
an engaging activity
to help clean up
with adult support.
B. Demonstrates
the Ability to
Adopt to New
A. Demonstrates the
Ability to Postpone
Activity and Start
Another
1. Takes and gives
cues to other
children during
transition and
models their
appropriate behavior
with adult support.
2. Occasionally
demonstrates the
ability to stop an
engaging activity to
help clean up with
and requiring less
support and
guidance from an
adult.
B. Demonstrates the
Ability to Adopt to
New Environments
A. Demonstrates
the Ability to
Postpone Activity
and Start Another
1. Consistently
demonstrates the
ability to
independently stop
an engaging activity
to transition to
another less
desirable activity.
2. Responds to
visual or auditory
prompts and cues
to transition to the
next activity with
little or no adult
prompting.
B. Demonstrates
the Ability to
Adopt to New
1 Year
2
Year
s
A.
D
emonstrates
the Ability to
P
ostpone A
ct
ivity
tt
an
d
Start A
no
t
h
er
1
.
R
esponds to
visual or auditor
y
prompts and cues
to transition to t
h
e
n
ext activity wit
h
adult support.
2
.
M
oves from a
preferred activity t
o
a less preferable
activity with adult
support and
assistance.
3
.
D
emonstrates
the ability to stop
an engaging activit
y
to
h
elp clean up
with adult support.
B
.
D
emonstrates
the Ability to
A
dopt to
N
ew
3
Year
s
A.
D
emonstrates t
h
e
A
bility to Postpone
A
ct
ivity and Start
tt
A
no
t
h
er
1
.
Takes and gives
cues to ot
h
er
children durin
g
transition an
d
mo
d
els their
appropriate behavior
with adult support.
2.
O
ccasionall
y
d
emonstrates the
ability to stop an
engaging activity to
h
elp clean up wit
h
and requiring less
support and
guidance from an
a
d
ult.
B
.
D
emonstrates t
h
e
A
bility to
A
dopt to
New Environments
4
Year
s
A.
D
emonstrates
the Ability to
P
ostpone A
ct
ivity
t
t
Kindergarte
n
an
d
Start A
no
t
h
er
1
.
Consistentl
y
d
emonstrates the
ability to
independently stop
an engaging activit
y
to transition to
anot
h
er less
d
esirable activity.
2.
R
esponds to
visual or auditor
y
prompts and cues
to transition to t
h
e
n
ext activity wit
h
little or no a
d
ult
prompting.
B
.
D
emonstrates
the Ability to
A
dopt to Ne
w
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Foun
d
ation
s
S
tran
d:
A
pproaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Understanding & complying with classroom rules, routines, and expectations.

162 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Rely on trusted
adults to feel safe
trying new
activities.
Continues to need
adult approval but
show more
independence.
Environments with
Appropriate
Behaviors with
Adult Support
1. Demonstrates
comfort with the
transition from
home to the
classroom
environment (e.g.,
begins to calm
down quicker and
more frequently
when parents
leave).
2. Engages with
trusted adults
during transition
with support and
encouragement.
C. Demonstrates
Appropriate Use of
with Appropriate
Behaviors with
Adult Support
1. Manages
separation anxiety
from home to
school by kissing
caregiver goodbye
or waving from the
window every day.
2. Frequently
demonstrates
comfort with the
transition from
home to the
classroom
environment (e.g.,
easily calms down
when parents leave).
3.Engages in out of
the classroom
activities
(i.e., recess) and
successfully re-
enters classroom
without disruption.
C. Demonstrates
Appropriate Use of
Environments with
Appropriate
Behaviors with
Adult Support
1. Arrives at school
ready to engage in
the classroom
routine.
2. Consistently
transitions easily
from home to
school.
3. Engages in out
of classroom
activities and
successfully re-
enters the
classroom routine
without disruption
independently.
C. Demonstrates
Appropriate Use of
R
ely on trusted
a
d
ults to feel safe
trying ne
w
activities.
Continues to nee
d
adult approval but
s
h
o
w
m
or
e
independence.
Environments wit
h
A
ppropriate
Be
h
aviors wit
h
Ad
ult
S
u
ppor
t
1
.
D
emonstrates
comfort with the
transition
f
r
o
m
ho
me t
o
t
h
e
classroom
envir
o
nment
(
e.g.,
b
egins to calm
d
own quicker an
d
more frequentl
y
w
h
en parents
leave
)
.
2
.
En
g
ages wit
h
truste
d
a
d
ults
d
uring transition
with support and
encouragemen
t
.
C.
D
emonstrates
A
ppropriate Use of
with Appropriate
Be
h
aviors wit
h
A
dult Support
1
.
M
anages
separation anxiet
y
f
r
o
m h
o
me t
o
school by kissing
caregiver goodbye
or
waving from the
window every day.
2.
F
requentl
y
d
emonstrates
comfort with th
e
transiti
o
n fr
o
m
ho
me t
o
t
h
e
classroom
environme
n
t
(
e.g.,
easily calms down
w
h
en parents leav
e
)
.
3.
Engages in out of
t
h
e classroom
activitie
s
(
i.e., recess
)
and
successfully r
e
-
en
t
ers classroom
without disruption.
C.
D
emonstrates
A
ppropriate Use of
Environments wit
h
A
ppropriate
Be
h
aviors wit
h
A
dult Support
1
.
A
rrives at school
ready to engage in
t
he
classroom
routine
.
2.
Consistentl
y
transitions easil
y
f
r
o
m h
o
me t
o
sc
h
ool.
3.
Engages i
n
o
u
t
o
f classroom
activities an
d
successfully r
e
-
enters t
h
e
classroom routine
without disruption
independently.
C.
D
emonstrates
A
ppropriate Use of
continued on next page

Appendix | 163
M
Materials or
Belongings and
Those of Others
1. Begins to help
with clean up after
activities with
prompting and
adult assistance.
2. Begins to
recognize where
materials belong.
3. Begins to
understand how to
use age-appropriate
classroom materials
with modeling and
prompting. Follows
adult direction and
modeling for an
assigned task (e.g.,
turning pages of
book with care,
then puts book
back onto shelf
with prompting).
4. Begins to
reference past
Materials or
Belongings and
Those of Others
1. Helps with clean
up after activities
with prompting.
2. Begins to
demonstrate
appropriate use of
classroom materials
with modeling (e.g.,
using glue in an art
project appropriately
or turning book
pages with care).
3. Recognizes and is
responsible for
returning items to
appropriate location
with prompting.
4. Begins identifying
when things are not
Materials or
Belongings and
Those of Others
1. Cleans up after
activities, placing
items in their
appropriate place
independently.
2. Demonstrates
appropriate use of
classroom materials
with consistency
and independently.
3. Begins to
understand and
appropriately care
for items that
belong to someone
else.
4. Continues to
benefit from
M
aterials or
Belongings and
Those of Ot
h
er
s
1
.
Begins to
h
elp
with clean up after
activities wit
h
prompting and
a
d
ult assistance.
2.
Begins to
recognize w
h
ere
materials belong.
3.
Begins to
u
nderstand how to
us
e ag
e
-
appropriate
classroom materials
with modeling and
prompting. Follows
a
d
ult
d
irection an
d
modeling for an
assigned task (e.g.,
turning pages of
b
ook with care,
then puts boo
k
b
ack onto shelf
wit
h
prompting).
4.
Begins to
reference past
M
aterials
o
r
Belongings and
Those of Ot
h
er
s
1
.
H
elps wit
h
clean
u
p after activities
wit
h
prompting.
2.
Begi
n
s
t
o
d
emonstrate
appropriate use of
classroom materials
with modeling (e.g.,
u
sing glue in an art
pro
j
ect appropriatel
y
o
r turning boo
k
pages wit
h
care).
3.
R
ecognizes and is
responsible for
returning items to
appr
o
priate location
wit
h
prompting.
4
.
Begins identifying
w
h
en t
h
ings are not
M
aterials or
Belongings and
Those of Ot
h
er
s
1
.
Cleans up after
activities, placing
items in t
h
eir
appropriate place
independently.
2.
D
emons
t
ra
t
es
appropriate use of
classroom materials
wit
h
consistenc
y
and independently.
3.
Begins to
u
n
d
erstan
d
an
d
appropriately care
f
or items that
b
elong to someone
else.
4.
C
ontinues to
b
enefit from
continued from previous page

164 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
knowledge to
create
understanding of
new information
through pretend
play (e.g., says
“This game is like
the one we played
in Ms. Kim’s class).
put away in
designated areas.
hands- on
experiences to
support more
abstract thinking
skills (e.g., makes a
book about last
summer's vacation
trip, complete with
sections for each
place visited,
drawings to
illustrate, and labels
written with adult
help).
knowledge t
o
c
rea
t
e
u
nderstanding of
n
ew information
through pretend
play (e.g., says
“This game is li
k
e
the one we played
in Ms. Kim’s class
)
.
put away in
d
esignated areas.
h
an
ds
-
o
n
experiences to
suppor
t
more
abstract thinking
s
k
ills (e.g., ma
k
es a
b
ook a
b
out last
summer
'
s vacation
trip, complete wit
h
sections for ea
ch
place visited,
d
rawings to
illustrate, and labels
written with adult
h
elp).

Appendix | 165
M
Domain: Social Foundations
Strand: Approaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
Standard: Demonstrates cognitive flexibility—Understands symbolic representation
1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating.
Recognize that
drawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations.
A. Represents
People, Places, or
Things Through
Drawings,
Movement, and
Three Dimension
Objects
1. Develops generic
symbols for
repeated drawings
of common objects
like sun, dog and
house.
2. Begins drawing
in a more realistic
manner,
occasionally
oscillating between
realism and
scribbling.
A. Represents
People, Places, or
Things Through
Drawings,
Movement, and
Three Dimension
Objects
1. Begins to create
art that is more
realistic and includes
some details of
objects, animals or
people.
Such details are
typically
remembered
features that have
made an impression,
but do not include
all that is seen or
known (e.g., draws a
picture of a car with
four wheels but no
windows).
2. Uses art to reflect
thoughts and
feelings (e.g.,
transforms a list of
favorite foods that
his teacher had
recorded on paper
A. Represents
People, Places, or
Things Through
Drawings,
Movement, and
Three Dimension
Objects
1. Develops a set of
symbols to create a
landscape that
eventually becomes
a single variation
repeated endlessly.
2. Landscapes are
composed
carefully, giving the
impression that
removing any single
form would throw
off the balance of
Explore drawing,
painting and writing
as a way of
communicating.
1 Year
R
ecognize t
h
at
d
rawings, paintings
and writing are
meaningful
representations.
2
Year
s
A.
R
epresents
P
eople, Places, or
T
h
ings T
h
roug
h
D
rawings,
M
o
vem
e
n
t, and
T
h
ree Dimension
O
b
j
ect
s
1
.
D
evelops generic
symbols for
repeated drawings
o
f common ob
j
ects
like sun, dog and
h
ouse.
2.
Begins drawing
in a more realistic
manne
r
,
o
ccasionall
y
o
scillating between
realism an
d
scribblin
g
.
3
Year
s
A.
R
epresents
P
eople, Places, or
T
h
ings T
h
roug
h
D
rawings,
M
o
vem
e
n
t, and
T
h
ree Dimension
O
b
j
ect
s
1
.
Begins to create
art t
h
at is more
realistic an
d
inclu
d
es
some
d
etails of
o
b
j
ects, animals or
people.
S
uch
d
etails are
typicall
y
remem
b
ered
f
eatures that have
made an impression,
b
ut do not include
all t
h
at is seen or
known (e.g., draws a
picture of a car with
f
our wheels but no
windows
)
.
2.
Uses art to reflect
t
h
oug
h
ts an
d
f
eelings (e.g.,
transforms a list of
f
avorite foods that
h
is teacher ha
d
recorded on
p
a
p
er
4
Year
s
Kindergarte
n
A.
R
epresents
P
eople,
P
laces, or
T
h
ings T
h
roug
h
D
rawings,
M
o
vem
e
n
t, and
T
h
ree Dimension
O
b
j
ect
s
1
.
D
evelops a set of
symbols to create a
landscape that
eventually becomes
a single variation
repeated endlessly.
2.
L
andscapes are
composed
carefully, giving the
impression t
h
at
removing any single
f
orm would thro
w
o
ff the
b
alance of
Gra
d
e
1
Gra
d
e
2
D
o
main
:
S
ocial Foun
d
ation
s
S
tran
d:
A
pproaches to Learning & Executive Functioning
S
tan
d
ar
d
:
Demonstrates cognitive flexibility
—
y
y
Understands symbolic representation

166 | Maryland Early Learning Standards Birth - 8 Years
M
Interact with other
children.
Share his feelings
through talking and
pretend play.
B. Engages in
Pretend Play and
Acts Out Roles
1. Identifies
difference between
fantasy and reality
with adult support
and prompting.
2. Able to act out
simple roles (i.e.,
“Look, I am a dog,
ruff, ruff”).
C. Recognizes
Cause and Effect
1. Understands
explanations when
into a mobile from
which illustrations
of these foods are
hung).
B. Engages in
Pretend Play and
Acts Out Roles
1. Communicates
thoughts and
feelings through role
play though may still
need adult support
(e.g., play acts being
a kitten seeking
affection and hugs).
2. Uses objects as
symbolic props (e.g.,
places a shell on top
of a dollhouse and
declares it to be a
satellite dish).
3. Becomes more
animated in play
(e.g., using different
voices for the baby,
dog, etc.)
C. Recognizes Cause
and Effect
1. Increased ability
to understand
the whole picture.
B. Engages in
Pretend Play and
Acts Out Roles
1. Imitates and
sustains pretend
play independently
and negotiates the
roles.
2. Begins adhering
to social norms in
pretend play (e.g..,
only girls can be
mommies).
3. Demonstrates
understanding of
the world around
her/him.
C. Recognizes
Cause and Effect
1. Increased ability
to understand
Interact wit
h
ot
h
er
chil
d
ren.
S
hare his feelings
through talking and
pretend play.
B
.
Engages in
P
retend Play and
A
cts Out R
o
le
s
1
.
I
d
entifies
d
ifference between
f
antasy and realit
y
with adult support
and prompting.
2.
Ab
le to a
ct
ou
t
simple roles (i.e.,
“Look, I am a dog,
ruff, ruff
”).
f
f
C.
R
ecognizes
Cause an
d
Effect
1
.
Un
d
erstan
d
s
explanations w
h
en
into a mo
b
ile from
w
h
ic
h
illustrations
o
f these foo
d
s are
h
ung).
B
.
Engages in
P
retend Play and
A
cts Out R
o
le
s
1
.
C
ommunicates
thoughts and
f
eelings throug
h
r
o
le
play t
h
oug
h
may still
n
eed adult support
(
e.g., play acts being
a
k
itten see
k
ing
affection and hugs).
2.
Uses ob
j
ects as
symbolic props (e.g.,
places a s
h
ell on top
o
f a
d
ollhouse an
d
d
eclares it to
b
e a
satellite dish
)
.
3.
Becomes more
animate
d
in pla
y
(
e.g., using different
voices for the baby,
d
og, etc.)
C.
R
ecognizes
C
ause
an
d
Effect
1
.
Increased abilit
y
to un
d
erstan
d
t
h
e w
h
ole picture.
B
.
Engages in
P
retend Play and
A
cts Out R
o
le
s
1
.
Imitates an
d
sustains pretend
play independentl
y
and negotiates the
roles.
2.
Begins adhering
to social
n
orms in
pretend play (e.g..,
o
nly girls can be
mommies
)
.
3.
D
emonstrates
u
nderstanding of
the world around
h
er
/
him.
C.
R
ecognizes
Cause an
d
Effect
1
.
Increased abilit
y
to un
d
erstan
d
continued on next page

Appendix | 167
M
concrete objects
and actions support
the verbal
explanation, and
phenomena are
directly observable
(e.g., "When we
mix colors, we get a
new color. See
what color you get
when you mix
yellow with blue").
explanations when
concrete objects and
actions support the
verbal explanation,
and phenomena are
directly observable
(e.g., "When we mix
colors, we get a new
color. See what
color you get when
you mix yellow with
blue").
2. Begins to
understand
explanations of
events that have not
been experienced
directly, as long as
the child has had
similar experience.
verbal explanations
of phenomena that
are not directly
experienced, as
long as the child
has had similar
experiences (e.g.,
“The sun gives off
heat. Even though
you can’t see it, it’s
happening”).
2. Begins to
understand
consequences of
own action when
prompted by
teacher (e.g., “Tell
me what is a good
reward for helping
your friends clean
up their block
game”).
concrete ob
j
ects
and actions support
the verbal
explanation, and
p
h
enomena are
d
irectly observable
(
e.g.,
"
When we
mix colors, we get a
n
ew color. See
w
h
at color you g
e
t
w
h
en you mix
yellow with blu
e
")
.
explanations w
h
en
concrete ob
j
ects and
actions support t
h
e
verbal explanation,
and phenomena are
d
irectly observable
(
e.g.,
"
When we mix
colors, we get a ne
w
color. See w
h
at
color you g
e
t w
h
en
you mix yellow wit
h
b
lu
e
")
.
2.
Begins to
u
n
d
erstan
d
explanations of
events t
h
at
h
ave not
b
een experienced
d
irectly, as long as
the chil
d
has ha
d
similar experience.
verbal explanations
o
f phenomena that
are not directl
y
experienced, a
s
long as the child
h
as ha
d
similar
experiences (e.g.,
“The sun gives off
h
eat. Even t
h
oug
h
you can’t see it, it’s
h
appening”).
2.
Begins to
u
n
d
erstan
d
consequences of
o
wn action w
h
en
prompted b
y
teac
h
er (e.g., “Tell
me what is a good
reward for helpi
n
g
your friends clean
u
p their bloc
k
game
”
).
continued from previous page
