
1
ةروتاــف
Detailed Guidelines for
E-Invoicing
Version 2
MAY 2023
Fatoora

2
Contents
1. Introduction
1.1. E-Invoicing in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (linking E-Invoicing Regulation with
the VAT Legislations)
1.2. Benefits of E-Invoicing
1.3. E-Invoicing phases
1.4. The Authority
1.5. Scope of this Guideline
2. Clarifications of the main terms used
3. Scope of E-Invoicing
3.1. Taxable Persons subject to E-Invoicing
3.2. Requirements to generate Electronic Invoices
4. Types of E-Invoices
4.1. Tax Invoice
4.1.1. Tax Invoices for Phase 1 (Generation Phase)
4.1.2. Tax Invoices for Phase 2 (Integration Phase)
4.2. Simplified Tax Invoice
4.2.1. Simplified Tax Invoices for Phase 1 (Generation Phase)
4.2.2. Simplified Tax Invoices for Phase 2 (Integration Phase)
4.3. Credit and Debit Notes
05
05
05
06
07
07
08
13
13
13
14
14
14
15
17
17
18
19

3
4.4. Sample visual examples of E-Invoices
5. E-Invoice Generation Phase Requirements and Timelines (Tax Invoice
vs. Simplified Tax Invoice Solutions)
5.1. Solution Requirements
6. E-Invoice Integration Phase Requirements and Timelines (Tax Invoice vs.
Simplified Tax Invoice Solutions)
6.1. E-Invoice Integration Phase Requirements and Timelines (Tax Invoices.
Simplified Tax Invoice Solutions)
6.2. Timelines
6.3. Technical Requirements
6.4. Clearance and Reporting
6.5. Prohibited Functions
6.6. E-Invoice Format
7. Rights and Obligations of Taxable Persons
7.1 Right to deduct / refund VAT
7.2 Obligations of taxable persons subject to E-Invoice regulation
7.3. E-Invoicing Record Keeping
7.4. Additional E-Invoicing Obligations (e.g. using compliant solutions,
maintaining the cryptographic stamp, etc.)
7.5. E-Invoicing Compliance Audit
20
21
21
29
29
31
31
31
34
36
37
37
37
38
38
39

4
8. Advance Payments
9. Integration with ZATCA
10. Failure Scenarios
11. Tax Invoice and Simplified Tax Invoice QR Code validation
FAQs
Contact Us
40
44
45
56
57
65

5
1. Introduction
1.1. E-Invoicing in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (linking E-Invoicing Regulation
with the VAT Legislations)
Electronic Invoicing is a procedure that aims to convert the issuing of paper invoices as
well as credit and debit notes into an electronic process that allows the exchange and
processing of invoices, credit and debit notes in a structured electronic format between
the buyer and seller.
The E-Invoicing Regulation shall be read together with the Unified VAT Agreement (the
Agreement), the VAT Law published on 4/11/1438H and its amendments (the VAT Law), the
VAT Implementing Regulation (VAT Implementing Regulation) and the resolutions issued
pursuant to the Electronic Invoicing Regulation, including the resolution on the Controls,
Requirements, Technical Specifications and Procedural Rules (herein after referred to as
“E-Invoicing Resolution”) required for implementing Electronic Invoicing in the Kingdom
of Saudi Arabia.
1.2. Benefits of E-Invoicing
Electronic Invoicing has several benefits for both persons subject to E-Invoicing
Regulations and national economy, these benefits include but are not limited to:
A. Reduces cost of invoicing process
B. Prevents human error in invoicing process
C. Enhances digitalization in supply chain
D. Improves accounting and book keeping
E. Enhances business ecosystem with enriched fair competition and consumer protection
through provision of a unified process for validating and auditing invoices

6
F. Reduces hidden economy transactions
G. Reduces commercial concealment by increasing requirements related to invoice
tracking and data retention
H. Enriches the consumer experience and digitizing the consumer- supplier relationship
I. Increases compliance with tax obligations through enhanced verification of business
transactions
1.3. E-Invoicing phases
Electronic Invoicing is composed of two main phases, as follows:
1. Phase 1 (Generation Phase): Generation of Electronic Invoices Phase, where Persons
subject to the E-Invoicing Regulations must generate Electronic Invoices and associated
Electronic Notes in accordance with the clauses set forth under the Resolution on the
E-INVOICING BYLAW and The Controls, Requirements, Technical Specifications And
Procedural Rules For Implementing The Provisions Of The E-Invoicing Regulation and any
subsequent resolutions. This phase has been implemented effectively by 4th of December
2021.
2. Phase 2 (Integration Phase): Integration Phase, where Persons subject to the E-Invoicing
Regulations must integrate their systems with the Authority’s system (FATOORA) in
accordance with the clauses set forth under the Resolution on the Controls, Requirements,
Technical Specifications and Procedural Rules and any subsequent resolutions. The
second phase (integration phase) shall be implemented starting from 1st of January 2023
onwards. The second phase (integration phase) will be implemented in groups and will be
mandated to Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulations based on the criteria set by the
Authority. Notifications to the target groups will be initiated at least six months in advance.

7
1.4. The Authority
The Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority, also referred to as “the Authority” herein, is the
authority in charge of the implementation and administration of VAT (which may be referred
to hereinafter as “the Tax”) or (“VAT”). In addition to the registration and deregistration
of taxable persons for VAT, the administration of VAT return filing and VAT refunds, and
undertaking audits and field visits, the Authority also has the power to levy penalties for
noncompliance and is mandated to implement the E-Invoicing framework in KSA, which
was enforced through the E-Invoicing Regulations issued by the Board of Directors of the
Authority on December 4, 2020.
1.5. Scope of this Guideline
This Guideline addresses all Persons covered by the scope of application of Article (3) of
the E-Invoicing Regulation which covers:
● Taxable person that is a resident in KSA.
● The customer or any third party who issues a Tax Invoice on behalf of the taxable
person that is a resident in KSA according to the VAT Implementing Regulation.
This Guideline aims to provide more information on certain industries, transactions or
scenarios and provide more detailed information on how E-Invoicing will be applicable to
such industries, transactions or scenarios.
This Guideline contains and references several examples of electronic invoices against the
various invoices to be issued and the types of transactions. The complete list of examples
and the human readable format (PDF/A-3 with embedded XML) of the invoice and the XML
are included on the Authority’s Website. Please note that the Cryptographic Stamp value,
the QR Code value, and the Invoice Hash value in the XML examples are sample values.
This Guideline aims to simplify and clarify the end-to-end journey of the Taxable persons
through electronic invoicing, their obligations, and the overall solution requirements to
comply with electronic invoicing regulations.
This Guideline does not contain explanations of technical implementation details directed
at invoicing solution vendors.

8
2. Clarifications of the main terms used
This section provides clarifications of the definitions used under the Resolution, provides
some additional clarifications that will be helpful to better understand the terms used under
these guidelines, and clarifies the mechanism for applying the provisions related to the
Resolution.
2.1. Electronic Invoicing:
It is a mechanism that aims to transform the process of issuing paper invoices and notes
into an electronic process that allows the exchange of invoices and debit and credit notes
and their processing in a structured electronic format organized between the seller and the
buyer.
2.2. Tax Invoice:
A Tax Invoice as per Article 53(1) of VAT Implementing Regulations that is generated and
stored in a structured electronic format through electronic means. Standard Tax Invoices
are generally issued in Business to Business (B2B) transactions. A paper invoice that is
converted into an electronic format through copying, scanning, or any other method is not
considered an electronic invoice.
2.3. Simplified Tax Invoice:
A Simplified Tax Invoice as per Article 53(7) of VAT Implementing Regulations that is
generated and stored in a structured electronic format generally issued for a B2C (business
to consumer) transaction and does not generally include the buyer’s details
1
. Optionally,
Simplified Tax Invoices may also be issued for business-to-business transactions in case
the value of supply is below SAR 1,000.
1. Note that the buyer details may be required in specific cases where Simplified Tax Invoices are issued towards Supply of
Private Education and Private Health Care services to Saudi Citizens. These services are having a special tax treatment (treated
as “Zero Rated”) and the Kingdom bears the VAT for such services.

9
2.4. Electronic Note:
Debit and credit notes that must be issued in accordance with the Article 54 of VAT
Implementing Regulation, and which are generated and stored in a structured electronic
format through electronic means. Paper notes that are converted into electronic format
through copying, scanning, or any other method, are not considered electronic notes for
the purposes of this Regulation.
2.5. Debit Note:
Debit notes are issued by the sellers in order to issue a correction in value to buyers. Debit
notes are used for increasing the value of the original invoice or the VAT amount. Debit
notes follow the same format as the invoice for which they have been issued.
2.6. Credit Note:
Credit notes are issued by the sellers in order to refund buyers and are used to correct
invoices information if generated with an error. Credit notes follow the same format as the
invoice they have been issued upon.
2.7. E-Invoice Solution:
The compliant solution which is used for generating Electronic Invoices and Electronic
Notes. Such a solution must fulfil the specifications and requirements set forth under the
resolution on the Controls, Requirements, Technical Specifications and Procedural Rules
for Implementing the Provisions of the E-Invoicing Regulation. An E-Invoice Solution may
contain one or more Units.

10
2.8. FATOORA Portal:
ZATCA’s portal through which Tax Invoice, Simplified Tax Invoice, and electronic credit/
debit note data is received, which are generated by the E-Invoice Solutions used by
Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulations. This portal aims to onboard the user’s EGS
Unit through generating cryptographic stamp identifier or renewing the existing one or
revoking it. In addition, the user can view the list of onboarded solutions and devices.
2.9. Cryptographic Stamp:
An electronic stamp which is created via cryptographic algorithms to ensure authenticity
of origin and integrity of content of the data for the Electronic Invoices and its associated
Electronic Notes, and to ensure the identity verification of the issuer for the Invoices and
Notes for the purpose of ensuring compliance with the provisions and controls of the VAT
Law and its Implementing Regulation regarding the generation of Electronic Invoices and
Notes. For technical details, please refer to the Security Features Implementation Standard.
2.10. Cryptographic Stamp Identifier (CSID):
A Cryptographic Stamp Identifier (CSID) is a unique identifier that links the E-Invoice
Solution Unit and a trusted third party able to confirm the identity of the Person subject
to the E-Invoicing Regulation and uniquely identify their unit. For technical details, please
refer to the Security Features Implementation Standard.
2.11. UUID:
A 128-bit number, generated by an algorithm chosen to make it unlikely that the same
identifier will be generated by anyone else in the known universe using the same algorithm.
The UUID is generated by a compliant E-Invoice Solution and stored inside the XML invoice.
Note: In Windows OS UUIDs are referred to by the term GUID.

11
2.12. QR Code:
A type of matrix barcode, with a pattern of black and white squares that is machine
readable by a QR code scanner or smart device camera in order to enable basic validation of
Electronic Invoices and Electronic Notes. For technical details, please refer to the Security
Features Implementation Standard.
2.13. Hash:
A hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to fixed-size
values called hashes that takes up minimal space. A hash procedure is deterministic -
meaning that for a given input value it must always generate the same hash value. It is not
possible to derive the original data from a hash; hence, hashing is meant to verify that a
file or piece of data hasn’t been altered. For technical details, please refer to the Security
Features Implementation Standard.
2.14. Invoice Reference Number:
A unique and sequential number that identifies the issued invoice by the E-Invoice Solution,
according to article 53 of the VAT Implementing Regulations. The VAT Implementing
Regulations did not specify a specific format for the Invoice Reference Number, and the
reference numbers may be different, for example, a different sequential reference number
for each branch, provided that the Tax Invoice is clearly and distinctly defined and follows
a sequence.

12
2.15. Clearance:
Clearance is the process where the Authority shall verify that the Electronic Tax Invoices
and their associated Electronic Notes transmitted to it (through integration) by the persons
subject to E-Invoicing Regulation, fulfil the controls and details specified in the E-Invoicing
Resolution, Annexes (1) and (2) of the Resolution, and the relevant technical documentation.
The Authority shall insert the Cryptographic Stamp only on the Invoices and Notes which
fulfil the aforementioned controls and details. Please note that the process of Clearance is
not applicable to Simplified Tax Invoices.
2.16. Reporting of Simplified Tax Invoices and their associated notes:
Reporting is the process of sharing of the Simplified Tax Invoices and their associated
Notes which are generated electronically - which include the Cryptographic Stamp as
specified in Clause (Fourth) of the E-Invoicing Resolution- with the Authority by the
persons subject to E-Invoicing Regulation. Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation
will be required to transmit all Simplified Tax Invoices to the FATOORA Portal within (24)
hours from its issuance.
2.17. Human Readable Format:
The human readable format of the invoice is a recognizable invoice that can be read and
understood by a human reader (including buyers and the Authority).
2.18. The Authority’s Toolkit:
The Authority toolkit is the testing toolkits provided by the Authority to allow Persons
subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation to verify that their solutions generate compliant
invoices and can be validated by the FATOORA Portal after integration. There are three
tools provided the sandbox, SDK and web-based validator, for more details please check
the sandbox webpage.

13
3. Scope of E-Invoicing
3.1. Taxable Persons subject to E-Invoicing
● All Taxable Persons subject to E-Invoicing Regulations are obliged to generate
E-Invoices for all their transactions for which Tax Invoices must be issued, in addition to
the electronic notes that must be issued in the cases stipulated in the VAT Law and its
implementing regulations
● Taxable Persons who are subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation include:
1. Taxable person that is a Resident in the Kingdom.
2. The customer or any third party that issues a Tax Invoice on behalf of the taxable
person that is a Resident in the Kingdom according to Article 53 (3), on the
amendment of VAT Implementing Regulations which was approved by the Authority
in 2021/11/09 that implemented in Dec. 4th 2021
● Taxable Persons who are not Residents in KSA are not required to issue Electronic
Invoices or Electronic Notes for supplies or amounts received which are subject to tax
in KSA.
3.2. Requirements to generate Electronic Invoices
Electronic invoicing has not changed the requirements for issuing invoices, debit notes
or credit notes, and therefore, the issuance of invoices, debit notes or credit notes must
be adhered to in accordance with the provisions of the VAT Law and its implementing
regulations.

14
4. Types of E-Invoices
4.1. Tax Invoice
4.1.1. Tax Invoices for Phase 1 (Generation Phase)
a. A Tax invoice is an invoice issued for most B2B and B2G transactions with fields defined
in Article 53 (5), VAT Implementing Regulations and Annex 2 of E Invoicing Resolution.
The fields required for Generation Phase and Integration Phase to be included within
the Tax Invoice are included in the Annex 2 of the E-Invoicing Resolution.
b. For Phase 1 (Generation Phase), the taxpayer must generate a Tax Invoice including
additional data fields prescribed in the Annex 2 of E-Invoicing Resolution in an electronic
format using a compliant E-Invoice Generation Solution (EGS). There is no specific
format prescribed for Phase 1 Tax Invoices (such as XML format or PDF/A-3 format).
Taxpayers can generate it in any electronic format, however, a paper invoice that is
converted into an electronic format through copying, scanning, or any other method is
not considered a compliant E-Invoice.
c. Also, for the Phase 1 (Generation Phase) invoices, there is no specific format prescribed
for sharing / presentment to the buyers. Phase 1 invoices can be presented in the any
electronic format.

15
4.1.2. Tax Invoices for Phase 2 (Integration Phase)
a. For Phase 2 (Integration Phase), the taxpayer must generate a Tax Invoice including
additional data fields prescribed in the Annex 2 of E-Invoicing Resolution in an electronic
format using a compliant E-Invoice Generation Solution (EGS) which is Onboarded (click
here for detailed technical guideline which defines the onboarding process). Phase 2
(Integration Phase) Tax Invoices must be generated in XML format or a PDF/A-3 (with
embedded XML).
b. Phase 2 (Integration Phase) Tax Invoices must be submitted in XML format (not
PDF/A-3) to FATOORA Platform for “Clearance” using APIs. FATOORA Platform will
validate whether the Tax Invoice is compliant with XML Implementation Standard
and run additional referential checks. Once the Tax Invoice pass validation checks,
FATOORA Platform will “Clear” the Tax Invoice by including a Cryptographic Stamp
and a QR Code to the XML. The “Cleared” XML will be sent back to the taxpayer using
APIs. Further details are provided in Section 7 of this guideline.
c. Phase 2 (Integration Phase) invoices must be shared / presentment to the buyers in
XML or PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML) format.
Tax Invoices contain fields as per VAT legislations including the seller and buyer information,
transaction and goods/services details in addition to other technical fields that are to be
generated by the electronic invoicing solution. Sample images of the human readable
format of the Tax Invoice are included in Section 4.6 of this guideline. Samples must be
different for Phase 1 and Phase 2.

16
Example:
Al Salam Supplies Co. LTD is, a registered taxpayer in Riyadh. Al Kawther Markets, a
registered taxpayer, contracts Al Salam for providing their stores with goods. Once the
items have been delivered, Al Salam issued an electronic invoice through their invoicing
solution. The technical fields of the invoice are automatically generated by the solution,
where Al Salam only inserts information about Al Kawther and their details, goods sold, and
the total value and VAT value of the transaction. Al Salam archives a copy of the Tax Invoice
in their records on a system according to the provisions in VAT Law, VAT Implementing
Regulation, E-Invoicing Regulation and resolutions and all other relevant Laws in KSA.
Example:
Capital National Bank, a registered bank in KSA provided Al Amaal Company with a
corporate loan to finance the company’s operations. The bank issued a Tax Invoice
containing two items, bank commission with an amount of SAR 6,250.00 and loan’s Profit
Element with an amount of SAR 50,000.00. The bank commission is subjected to VAT
with a rate of 15%. The loan Profit Element will be exempt from VAT, the Bank should
issue a Tax Invoice for the taxable supplies from the E-Invoice Solution used by the bank
and if the bank decided to issue one invoice for both the taxable and exempt supplies then
this invoice should meet the requirements of the Tax Invoices.

17
4.2. Simplified Tax Invoice
4.2.1. Simplified Tax Invoices for Phase 1 (Generation Phase)
a. A Simplified Tax invoice is an invoice issued mostly for B2C transactions with fields
defined in Article 53 (8), VAT Implementing Regulations and Annex 2 of E Invoicing
Resolution. The fields required for Generation Phase and Integration Phase to be
included within the Simplified Tax Invoice are included in the Annex 2 of the E-Invoicing
Resolution.
b. Also, taxpayers have an option to generate Simplified Tax Invoices for the B2B
transaction if the value of Taxable Supplies is less than 1,000 SAR. It must be noted
that for Simplified Invoices for B2C transaction can be generated for any value (even for
transactions where value of Taxable Supplies exceed 1,000 SAR). This limit of 1,000
SAR is only applicable when the supplier chooses to issue Simplified Tax Invoice for
B2B transactions.
c. For Phase 1 (Generation Phase), the taxpayer must generate a Simplified Tax Invoice
including additional data fields prescribed in the Annex 2 of E-Invoicing Resolution
electronically using a compliant E-Invoice Generation Solution (EGS). There is no
specific format prescribed for Phase 1 Simplified Tax Invoices (such as XML format or
PDF/A-3 format). Taxpayers can generate it in any electronic format, however, a paper
invoice that is converted into an electronic format through copying, scanning, or any
other method is not considered a compliant E-Invoice generated electronically.
d. Simplified Tax Invoices that has been generated electronically must be shared /
presented to the buyers in a printed copy. Alternatively, such Simplified Tax Invoice or
its associated Notes - upon the agreement between the transaction parties - may also
be shared with customers in its electronic format or any other human readable format
with customers.

18
4.2.2. Simplified Tax Invoices for Phase 2 (Integration Phase)
a. The taxpayer must generate Simplified Tax Invoice including additional data fields
prescribed in the Annex 2 of E-Invoicing Resolution in an electronic format using a
compliant E-Invoice Generation Solution (EGS) which is Onboarded. Simplified Tax
Invoices must be generated in XML format or a PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML).
Taxpayer’s EGS solution must stamp the XML using CSID issued by ZATCA and also
include a QR Code which is compliant with Phase 2 requirements (9 tags in TLV base64
format).
b. Once a compliant Simplified Tax Invoice is generated (after stamping and applying
QR code), it must be shared / presented to the buyer immediately in a printed copy.
Alternatively, such Simplified Tax Invoice or its associated Notes - upon the agreement
between the transaction parties - may also be shared with customers in its electronic
format or any other human readable format with customers.
c. Taxpayers must submit the Simplified Tax Invoices in XML format (not PDF/A-3) to
FATOORA Platform for “Reporting” within 24 hours of generation using APIs. FATOORA
Platform will validate whether the Tax Invoice is compliant with XML Implementation
Standard and run additional referential checks. Once the Simplified Tax Invoice pass
validation checks, FATOORA Platform will provide an API response.
Example:
Al Salam Supplies Co. LTDs operate 3 stores in KSA with over 12 cash registers. Each cash
register generates Simplified Tax Invoices based on each sale to a customer, with a QR Code
applied to each invoice. All Simplified Tax Invoices that are generated by the cash registers
are then sent to Al Salam company’ central repository and finance management system.
Al Salam company archives copies of the E-Invoices in their records on a system according
to the provisions in VAT Law, VAT Implementing Regulation, E-Invoicing Regulation and
resolutions and all other relevant Laws in KSA. On 1st of January 2023 (according to the
phases and targeted groups of the integration), Al Salam company must report all invoices
issued within 24 hours from the time of issuance.

19
Example:
A Saudi citizen bought three items from Alwaha Pharmacy online store. Two items are
standard rated items with a VAT rate of 15% and the third item is zero rated since it›s
classified as medical goods according to the VAT law and regulations. Once the payment
has been made, the pharmacy issues a Simplified Tax Invoice through the pharmacy
application containing details on the items that the customer purchased and sends the
invoice to the customer’s registered email address.
Example:
Al Jouf Business School, a private university in KSA, issued a Simplified Tax Invoice for
term tuition to a female Saudi citizen. Since this is a private education service subject to the
standard tax rate, an invoice should be issued to the Saudi Citizen. This service is subject to
a special treatment which is considered as a “Zero Rated›› invoice as regulated by ZATCA,
the Saudi government will cover the VAT on behalf of the citizen. Therefore, the citizen
will not be charged VAT.
4.3. Credit and Debit Notes
Electronic Credit / Debit notes are issued for a Tax Invoices / Simplified Tax Invoices (after
an e- invoice has been issued), wherein the transaction is adjusted subject to Article 40 (1)
and Article 54(3) of VAT Implementing Regulations.
Credit and Debit notes must be issued with a reference to the original invoice(s) to which
they are issued. The reference fields can be used to indicate the Invoice Reference
Number(s) of Original Invoice(s) to which Credit Note pertains. In case, a single Credit
Note relates to multiple Original Invoices, then taxpayers can provide Invoice Reference
Numbers as a range (for example IRN from 001 to IRN 100 issued during the period 1 Jan
2022 to 31 March 2022). The type of credit/debit note follows the type of invoice that they
are issued against.

20
Example:
Data Extract Consulting company purchases several office furniture items from Zamil
Furniture Group. After they have been invoiced by Zamil, Data Extract wishes to return
several items that were defective. Zamil issues a credit note in order to refund the amount
paid, and the information is the same as the information contained in the Tax Invoice that was
issued for the sale. The credit note contains the Invoice Reference Number of the original
invoice. Data Extract archives a copy of the note in their records on a system according
to the provisions in VAT Law, VAT Implementing Regulation, E-Invoicing Regulation and
resolutions and all other relevant Laws in KSA.
4.4. Sample visual examples of E- invoices
Each type of E-Invoice and associated note may be presented in human readable form.
The fields required to be visible on such a representation are indicated in the E-Invoicing
Resolution in Annex (2). This section contains examples of fully compliant visualized
E-Invoices that contain the fields required starting 1st January 2023 (in waves by targeted
taxpayer groups).

21
5. E-Invoice Generation Phase Requirements and Timelines (Tax
Invoice vs. Simplified Tax Invoice Solutions)
5.1. Solution Requirements
Requirements for generating Tax Invoice and Simplified Tax Invoice starting from 4th
December 2021:
Requirements Tax Invoices Simplified Tax Invoices
Invoice
Generation
Invoice
generation
means
Electronic Invoices must be generated through electronic
means
Invoice fields
Generate electronic invoice with non-integration related
fields
Invoice format No format mandated
Invoice storage
Invoices must be archived as per VAT regulations and
accessible at any “ point in time to the Authority”

22
Security &
Integrity
QR code
QR code not mandated in the
Generation Phase
QR code included with
basic invoice and taxpayer
information
Crypto- graphic
stamp
No Cryptographic stamp mandated
Device
Registration
No device registration mandated
UUID Not mandated
Hash Not mandated
Integration
Connectivity Solution must be able to connect to the internet
Invoice
clearance
No invoice sharing / clearance
mandated
_
Invoice Upload _ No invoice upload mandated

23
Illustrative: Tax Invoice Generation for B2B/G transactions
Illustrative: Simplified Tax Invoice Generation for B2C transactions
Supplier Buyer
2
1
Supplier shares invoice with the buyer
Supplier system generates invoice file
in an electronic format
Supplier system generates invoice with
QR code in an electronic format
Invoice data is stored by the supplier system
under required structure
Customer can scan QR code
through the ZATCA mobile app to
view basic invoice information
Supplier Customer
1
3
2

24
5.2. Timelines
Taxable persons subject to E-Invoice Regulation are obliged to generate Electronic Invoices
and Electronic Notes starting from 4th of December 2021.
The second set of requirements for E-Invoice generation are required starting from 1st
January 2023 (in waves by targeted taxpayer groups) as part of the Integration Phase.
5.3. Technical Requirements
● All E-Invoice Solutions must be able to connect to the internet in order to share invoices
with the Authority.
● The E-Invoice Solutions must be able to connect with an API published by the Authority
in order to share invoices. Specific integration requirements are published on the
Authority’s website, and E-Invoice Solution vendors will have enough time to update
their products and services.
● The E-Invoice Solutions must have tamper-proofing mechanisms that prevent any
modification or tampering with invoices or the solution itself, and must be able to record
and detect any tampering attempts.

25
5.4. Information Security
● Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation must ensure that their Compliant
E-Invoice Solutions must be tamper-resistant and include a mechanism which prevents
tampering and reveals tampering attempts that might occur.
1. These solutions contain functionalities that prohibit users from directly changing
the solution and invoice generation.
2. The anti-tampering mechanisms include:
Prevention of invoice counter reset:
Resetting the invoice counter should not be a function available in an E-Invoice
Solution and access to the counter value should be protected from system users.
Prevention of date changes:
Resetting the system date should be inaccessible to system users.
Prevention of deletion or modification of invoices:
Users of the E-Invoice Solution should not have the ability to delete or change
E-Invoice and associated Note XML documents stored on by the solution. The
solution should be equipped with sufficient memory to store the E-Invoice and
associated Note XML documents generated by it.
Prevention of uncontrolled access:
Access to E-Invoice Solution functions must always be via a logged in user who is
granted access only to functions that are necessary to perform their role.

26
● As per VAT Implementing Regulations, if the data is hosted on the cloud, it must be
accessible through a direct link that can be made available to the Authority. This
requirement is mandatory for audit purposes as per VAT Implementing Regulations
● The system must allow Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation to export and
save their invoices onto an external archival system
● Each stored invoice must follow a naming convention for naming of the file: VAT
Registration (tax registration number) + Timestamp (date and time at the point of
invoice generation) + Invoice Reference Number
● Taxpayer’s E-Invoice Solutions may reside on the cloud in accordance with VAT
Implementing Regulation, however additional non-tax-related regulations may apply
to the taxpayer entity, such as National Cybersecurity Authority published laws and
any other applicable regulations or controls
Prevention of export of stamping keys:
The cryptographic stamp identifier is associated with a unique private key that
should be generated by the solution, so that it may not be viewed or copied during
system initialization. Export of the key would enable theft of the E-Invoice Solution’s
identity, and so should be blocked by the solution vendor using a software or
hardware key vault.
● The Compliant Solution must be able to protect the generated Electronic Invoices
and Electronic Notes from any alteration or undetected deletion and contain some
functionalities which enable the taxable person to save Electronic Invoices and
Electronic Notes and archive them in XML format without Internet connection.
1. Once invoices are generated, they should not be deleted or altered by any user
2. The solution will also allow Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation to store
the invoices once they are generated in a safe and secure manner to avoid leakage
or loss of information

27
5.5. Data Storage and Archival
Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation may store their electronic invoices in a server
on-premises in the KSA or in the cloud as per their solution requirements and storage
requirements and according to the provisions in VAT Law, VAT Implementing Regulation,
E-Invoicing Regulation and Resolutions and all other relevant Laws in KSA.
5.6. Prohibited Functions
Starting the Generation Phase, an E-Invoice Solution must not have the following functions:
Function Definition
Anonymous access
Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation cannot access the
system without logging into the system using unique login and
password or biometrics.
Ability to operate with
default password
Having a default password or factory password is not allowed.
Each system must require the user to reset the password on
first use.
Absence of user session
management
The system must log all user activities associated with the
invoice generating process, starting with login authentication and
continuing to all system functions.
Allow alteration or
deletion of generated
E-Invoices or their
associated notes
Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation are not allowed to
modify or delete invoices once they are issued whether these are
generated by the system or outside it. If a user wishes to “cancel”
an invoice, this may only be done through issuing an associated
credit note and reissuance of a new invoice.
Allow for log
modification/deletion
The system must not allow any modification on system logs that
store the system’s activities.
All user activities can be logged and stored without any changes to
the system generated logs.
Generated with
inaccurate timestamps
Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation are not allowed to
change time or date on the E-Invoice Solution in a way that would
result in the generated documents to contain false information.

28
Non-sequential log
generation
All log entries of the E-Invoice Solution must be time stamped and
linked by placing the hash of the previous invoice in the associated
field of the next invoice in a sequence, so that their order cannot be
changed.
Invoice counter reset
The E-Invoice Solution must not provide a feature where the invoice
counting can be reset.
Allow ability to
generate more than
one invoice sequence
at any given time
The E-Invoice Solution unit must not generate more than one
sequence so that all invoices generated by an E-Invoice Solution
Unit are linked using “Previous Invoice Hash” value
into a single chain.
5.7. E-invoice Format
● Starting on 4th December 2021, persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation may
utilize any format as a human readable format to share their electronic invoices up until
the Integration Phase.
● The human readable format can be presented provided that it is in Arabic (in addition to
any other language) and Arabic or Hindi numerals can be used (either of which will be
considered as Arabic in the invoices).

29
6. E-Invoice Integration Phase Requirements and Timelines (Tax
Invoice vs. Simplified Tax Invoice Solutions)
6.1. E-Invoice Integration Phase Requirements and Timelines (Tax Invoices.
Simplified Tax Invoice Solutions)
Requirements for generating Tax Invoice and Simplified Tax Invoice starting from 1st
January 2023 (in waves by targeted taxpayer groups):
Requirements Tax Invoices Simplified Tax Invoices
Invoice
Generation
Invoice
generation
means
Invoices must be generated through electronic means
Invoice fields
Generate additional fields required for integration and
compliance features
Invoice format Invoices must be generated in XML format
Invoice
storage
Invoices must be archived as per VAT regulations and
accessible at any point in time by the Authority

30
Security &
Integrity
QR code
No requirement from the
taxpayer. The QR code value
will be generated by
the taxpayer’s solutions and
the FATOORA Portal will
update the code during the
Clearance process. The QR
code will then be printed to
be visualized on the human
readable invoice by the
taxpayer.
QR code mandated with
additional information
Cryptographic
stamp
No requirement from the
taxpayer. Cryptographic
stamps are applied by the
FATOORA Portal.
Cryptographic stamp
mandated
Device
Registration
Compliant solutions must
be registered on the
FATOORA Portal following
the on boarding process
Compliant solutions must be
registered on the FATOORA
Portal following the on
boarding process
UUID To be included as part of the E-Invoice
Hash To be included as part of the E-Invoice
Connectivity
Solution must have ability
to connect to the internet for
invoice upload and clearance
Solution must have ability
to connect to the internet for
invoice reporting
Integration
Invoice
clearance
Sharing of invoices with the
FATOORA Portal in real- time
via API (for clearance)
_
Invoice
Reporting
_
Upload of invoices to the
FATOORA Portal via API
whenever connected

31
6.2. Timelines
Integration is the second phase of electronic invoicing where the Persons subject to the
E-Invoicing Regulation will be integrated with the FATOORA Portal through an Application
Programmable Interface (API) and will share invoices to the Authority.
Integration of the Persons with the Authority’s system (FATOORA) shall happen starting
from 1st January 2023 (in waves by targeted taxpayer groups).
6.3. Technical Requirements
Phase 2, which will be implemented in waves by target taxpayer groups starting from
January 1, 2023, entails additional technical requirements that e-invoicing solutions must
comply with, the integration of taxpayer e-invoicing solutions with ZATCA’s systems,
and the generation and storage of e-invoices in the required format (XML or PDF/A3 with
embedded XML).
6.4. Clearance and Reporting
Clearance: Each Tax Invoice generated electronically must be cleared by the Authority
as a prerequisite for sharing them with the buyers and for such Electronic Invoice to be
regarded as legal and valid.
Clearance is a real-time transaction integration model of Tax Invoices, where after
integration, the taxpayer directly sends the electronic invoice prior to sharing with the
buyer. Tax Invoices are then validated across several categories of varying level, and if
approved, are stamped by the Authority and returned to the taxpayer to be shared with the
buyer. Clearance applies to all Tax Invoices and their associated credit/debit notes.

32
Invoicing model for Tax Invoices (usually issued by a business to another business)
E-invoice information shared by
seller’s solution
ZATCA shares back “cleared” e-invoice
with QR code and ZATCA’s stamp
Ability to scan the QR code
using ZATCA App
Store the “cleared” e-invoice in XML or
PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML) format
Share “cleared” e-invoice in XML or
PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML) format
Supplier
Platform
Buyer
1
2
5
3
4
Reporting: Taxable persons must report the Simplified Tax Invoices to the Authority.
Reporting is a near-real time transaction model, where Simplified Tax Invoices and
their associated Credit/Debit notes are uploaded to the FATOORA Portal within 24
hours from issuance. Once uploaded, Simplified Tax Invoices are then validated, and an
acknowledgement through the API is reported back to the taxpayer. Simplified Tax Invoices
must be generated using compliant E-Invoice Solutions and stamped by such solutions
as set out by the Authority requirements under the Controls, Requirements, Technical
Specifications and Procedural Rules for Implementing the Provisions of the E-Invoicing
Regulation and further subsequent resolutions.

33
Invoicing model for Simplified Tax Invoices (usually issued by a business to customer)
Share e-invoice in human-readable format whether printed or electronic
Ability to scan the QR
code using ZATCA App
E-invoice information shared
by seller’s solution in XML
format within 24 hours
Store the e-invoice electronically in XML
or PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML) format
Supplier
Platform
Customer
1
3
2
4

34
6.5. Prohibited Functions
Starting the Integration Phase, an E-Invoice Solution must not have the following functions:
Function Definition
Anonymous access
Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation cannot access the
system without logging into the system using unique login and
password or biometrics.
Ability to operate with
default password
Having a default password or factory password is not allowed. Each
system must require the user to reset the password on first use.
Absence of user session
management
The system must log all user activities associated with the
invoice generating process, starting with login authentication and
continuing to all system functions.
Allow alteration or
deletion of generated
E-Invoices or their
associated notes
Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation are not allowed to
modify or delete invoices once they are issued whether these are
generated by the system or outside it.
If a user wishes to “cancel” an invoice, this may only be done
through issuing an associated credit note and reissuance of a new
invoice.
Allow for log
modification/deletion
The system must not allow any modification on system logs that
store the system’s activities.
All user activities can be logged and stored without any changes to
the system generated logs.
Generated with
inaccurate timestamps
Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation are not allowed to
change time or date on the E-Invoice Solution in a way that would
result in the generated documents to contain false information.
Non-sequential log
generation
All log entries of the E-Invoice Solution must be time stamped and
linked by placing the hash of the previous invoice in the associated
field of the next invoice in a sequence, so that their order cannot be
changed.

35
Invoice counter reset
The E-Invoice Solution must not provide a feature where the invoice
counting can be reset.
Allow ability to generate
more than one invoice
sequence at any given
time
The E-Invoice Solution unit must not generate more than one
sequence so that all invoices generated by an E-Invoice Solution
Unit are linked using “Previous Invoice Hash” value into a single
chain.
Time changes
The solution must not allow software time changes that will change
or modify the timestamp value during E-Invoice or Credit/Debit
Note issuing.
Export of stamping keys
The solution must not provide an option to export the cryptographic
stamp private stamping key of the solution.

36
6.6. E-Invoice Format
● After go-live of the Integration phase, electronic invoices must be produced in a specific
format with specific fields as per the Appendix (2) of the Electronic Invoicing Resolution.
E-Invoice Solution vendors are required to follow the specification as well as to certify
their product according to the process published by ZATCA.
● Once the integration resolution comes into full force starting from 1st January 2023 (in
waves by targeted taxpayer groups), E-Invoice Solutions must be able to generate
invoices and their associated notes in the XML format or PDF/A-3 format (with
embedded XML).
● For the Integration phase, persons subject to E-Invoicing Regulation must share the Tax
Invoice, or its associated Notes that has been electronically generated with customers
in the XML format or PDF/A-3 format (with embedded XML).
● For the Integration phase, persons subject to E-Invoicing Regulation must present to
their customers a printed copy of the Simplified Tax Invoice or its associated Notes
that has been generated electronically in the XML format or PDF/A-3 format (with
embedded XML) or, upon the agreement between the transaction parties, may also
share with customers in electronic format or any other human readable format. For
the Integration phase, human readable form includes the PDF or the printed Electronic
Invoice or Credit/Debit Note, with all required visible fields present.
● The human readable format can be presented provided that it is in Arabic (in addition to
any other language) and Arabic or Hindi numerals can be used (either of which will be
considered as Arabic in the invoices).

37
7. Rights and Obligations of Taxable Persons
7.1 Right to deduct / refund VAT
Starting from 4th December 2021, the taxable persons (Buyers) will have the right to deduct
VAT charged by the taxable suppliers’ subject to electronic invoicing regulation, provided
that the invoices used are electronically generated and fulfil the Generation requirements.
7.2 Obligations of taxable persons subject to E-Invoice regulation
In addition to the general obligations prescribed in the VAT legislations, taxable persons
subject to E-Invoice regulation are obliged to:
● Generate all E-Invoices (Tax Invoices and Simplified Tax Invoices) and its associated
notes that must be issued within the timelines specified in the VAT legislations, in an
electronic form starting from 4th December 2021 (the day following the expiration date
of the grace period specified in Article (7), paragraph (B) of the E-Invoicing Regulation
for E-Invoices).
● Starting from the Integration phase, Tax E- invoices must be cleared before being
shared with the clients and Simplified Tax Invoices must be reported to the FATOORA
Portal within 24 hours.
● Comply with all the provisions set forth under the E-Invoicing Regulation in addition
to the controls, requirements, technical specification and procedural rules specified in
the resolution on the Controls, Requirements, Technical Specifications and Procedural
Rules for Implementing the Provisions of the E-Invoicing Regulation. Fulfilment of
this requirement may be met by the taxpayer through obtaining a compliant E-Invoice
Solution that produces the types of Tax Invoice and/or Simplified Tax Invoice documents
and associated Notes that the taxpayer required to conduct their business.

38
● Adhere to the specified timelines for compliance with the specifications and
requirements of Electronic Invoices specified in the resolution on the Controls,
Requirements, Technical Specifications and Procedural Rules for Implementing the
Provisions of the E-Invoicing Regulation and mentioned in Section 1.3 of this Guideline.
7.3. E-Invoicing Record Keeping
Taxable persons must adhere to the record keeping requirements of Electronic Invoices,
Electronic Notes and its associated data, and any other requirements as per the applicable
laws and regulations and as described in Section 5.5 of this Guideline under the subheading
Data Storage and Archival.
7.4. Additional E-Invoicing Obligations (e.g. using compliant solutions,
maintaining the cryptographic stamp, etc.)
The taxable persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulations must adhere to the following
obligations:
● Notify the Authority through the means specified by the Authority of any incidents,
technical error or emergency matters which hinder the generation of Electronic Invoices
or Electronic Notes and notify the Authority of recovery. Furthermore, to resume
generation and Clearance or Reporting of all E-Invoices and associated Notes as soon
as the Solution becomes operable.
● Not to use any E-Invoice Solution which is not compliant with the specifications and
requirements specified in the resolution on the Controls, Requirements, Technical
Specifications and Procedural Rules for Implementing the Provisions of the E-Invoicing
Regulation. Means of finding vendors, who have declared compliance or who have
been verified as compliant will be provided on ZATCA’s website with sufficient notice
to allow for necessary system purchase and/or upgrade.

39
● Register the E-Invoice Solution Units used for generating E-Invoices and their
associated Electronic Notes in accordance with the specified mechanisms and controls
specified in the resolution on the Controls, Requirements, Technical Specifications and
Procedural Rules for Implementing the Provisions of the E-Invoicing Regulation.
● Preserve the Cryptographic Stamp Identifiers and its associated components in a safe
way, and protect them from copying or illegal use, and not use them for purposes other
than those which they are intended for.
● Integrate with the Authority’s system (FATOORA) starting from the date specified in
the resolution on the Controls, Requirements, Technical Specifications and Procedural
Rules for Implementing the Provisions of the E-Invoicing Regulation and any subsequent
resolution in this regard.
7.5. E-Invoicing Compliance Audit
From time to time, Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation may be subject to ZATCA
tax audit. In such situations, the taxpayer should cooperate with ZATCA auditors and provide
them with all the data required to enable them to check the taxpayer compliance with the
requirements mentioned in VAT legislations, and E-Invoice regulations and associated
resolutions. Taxpayers should also provide ZATCA auditors with the archived E-Invoice
and associated note files. See Section 5.5 for Data Storage and Archival requirements.

40
8. Advance Payments
1. Invoice towards Advance Payments and adjustment thereof from subsequent invoices:
As per VAT Regulations, receipt of payment in advance towards taxable supplies
necessitates issuance of a tax Invoice. Currently, from the XML perspective the value
on which VAT was paid via advance payment invoice can be adjusted from subsequent
invoices using the tag <cbc:PrepaidAmount>. However, based on requests from taxpayers
and to cater to different scenarios involving advance payment adjustments, ZATCA has
introduced additional data fields in the Data Dictionary and XML Implementation Standard
as explained below:
a. Invoice Type Code (BT-3): An invoice that is issued at the time of receiving payment in
advance must have Invoice Type Code (BT-3) as a fixed value “386”. The subsequent
invoice(s) where the advance is adjusted should have Invoice Type Code “388”.
b. Reference to Advance Payment Invoice in the subsequent invoice(s) where it is
adjusted: When an adjustment is required to be made on an invoice towards the VAT
paid earlier via Advance Payment Invoice, such adjustment can be made by providing
the following additional reference data:
● Invoice Reference Number – IRN (BT-1) of the Prepayment invoice(s). Additionally,
the UUID (KSA-1) of Advance Payment Invoice can also be provided (currently
optional but it shall be mandated in future)
● Issue date (BT-2) of the prepayment invoice(s)
● Issue time (KSA-25) of the prepayment invoice(s)
● The Invoice line document reference “Prepayment Document Type Code (KSA-
30)” must be provided as a fixed value “386”.

41
c. How to adjust the values on which VAT was paid upon issuance of Advance Payment
invoice from the subsequent invoice(s):
For adjusting the value, the taxpayer must provide the amount under the tag
<cbc:PrepaidAmount> (BT-113) as the Amount inclusive of VAT. Please note that this
field should be populated only if the taxpayer has issued a separate invoice at the time
of receiving payment in advance and not otherwise.
Once the field <cbc:PrepaidAmount> (BT-113) is populated, then corresponding rules
get triggered requiring the taxpayer to provide reference information (as explained
above) and quantitative information as described below:
● The adjustment has to be made by providing one consolidated sum per VAT
Category and per rate. For example, if Advance Payment was made with 10 line
items having VAT Category Code “S” and “Z” then only 2 consolidated lines must
be provided in subsequent invoice(s) while adjusting the advance as one line for
VAT Category Code “S” and another line for “Z”. This value has to be provided in
Prepayment VAT category Taxable Amount (KSA-31).
● Similarly, the VAT amount shall be provided for specific VAT Category Code under
Prepayment VAT Category Tax Amount (KSA-32) as sum total of tax amounts
subject to specific VAT Category code of the prepayment invoice(s).
● Each line should mandatorily contain the VAT Category Code of the associated
Prepayment invoice(s) under the prepayment VAT category code (KSA-33)
● Each line should also contain the VAT rate of the specific VAT Category code of the
prepayment invoice(s) as the prepayment VAT rate (KSA-34). Please note that
this rate may also be 5% in case advance payment was received when the VAT
Rate was 5%. This field addresses the concerns about VAT Rate change in handling
advance payment adjustments.

42
d. Validation of calculations related to adjustment of advance payment:
Please note that there is no real-time cross-check between data of Advance Payment
Invoice that is adjusted from subsequent invoices. However, such checks will be made
on the backend as part of analytics and discrepancies may be further investigated
resulting in initiation of audits.
There will be bare minimum arithmetic checks on a real-time basis as below:
● The Prepayment VAT Category Tax Amount (KSA-32) must be = Prepayment VAT
category Taxable Amount (KSA-31) x Prepayment VAT rate (KSA-34) /100) and
● If Pre-Paid amount (BT-113) is provided then the Pre-Paid amount (BT-113) must
equal the sum total of the Prepayment VAT category Taxable Amount (KSA-31)
and Prepayment VAT Category Tax Amount (KSA-32)
e. Rounding rules related to advance payment adjustments:
The following amounts related to adjustment of advance payment must be rounded to
two decimals:
● Pre-Paid amount (BT-113).
● Prepayment VAT Category Taxable Amount (KSA-31)
● Prepayment VAT Category Tax Amount (KSA-32).
f. Currency of the advance payment adjustments:
The currency of advance payment adjustments should be same as the currency used in
the invoice. In other words, all currencyID attributes (BT-5) must have the same value
as the invoice currency code (BT-5).

43
g. What if the amount paid in advance is more than that is being adjusted?
In case the amount paid in advance is more than the amount of the subsequent invoice
that is being adjusted, the taxpayer has the option either to provide the full value on
which VAT was paid in advance (though being higher than the subsequent invoice) or to
limit the adjustment to the value of the current invoice. Both options are valid and XML
will not be rejected just because the advance payment value is higher than the current
invoice value.
For example, if the advance was received on 1 Jan 2023 for SAR 115,000 (100,000
+ 15,000 VAT) and this is being adjusted from a subsequent invoice of SAR 92,000
(80,000 + 12000 VAT) on 1 July 2023, then <cbc:PrepaidAmount> (BT-113) can either
be provided with the full value of advance payment as 115,000 which will result in
Amount Due for Payment as -23,000 or it can be limited to 92,000 resulting in Amount
Due for Payment as 0. Both options are valid, and decision may be taken based on
reconciliation process followed by the taxpayer.
Please note that, in the above scenario, if the full value of advance payment is adjusted
resulting in negative amount under the Amount Due for Payment and this amount has
to be refunded back to the customer, then a Credit Note for 23,000 has to be issued.
Such Credit Note should also be sent for Clearance / Reporting.
h. Technical details:
Developers may kindly refer to paragraph 9.5 of the XML Implementation Standard
to see the usage of UBL tags for advance payment adjustment. The examples cover
scenarios of one-to-one adjustment and many-to-one adjustments (where advances
received under multiple invoices can be adjusted against one final invoice).
It is important to note that some mandatory UBL tags which must be present in advance
payment adjustment lines with fixed value as “zero” (0) to avoid schema validation
errors or XSD errors. Therefore, it is important for developers to make use of all UBL
tags provided in paragraph 9.5 of the XML Implementation Standard to avoid errors/
warnings related to advance payment adjustments.

44
9. Integration with ZATCA
[for more details, please refer to detailed technical guideline]
Persons subject to the E-Invoicing Regulation will be integrated with the FATOORA Portal
starting from 1st January 2023 (in waves by targeted taxpayer groups), where compliant
E-Invoice Solutions will be able to connect to the API of the FATOORA Portal by following
the below steps:
● Taxpayer accesses FATOORA portal website (FATOORA.zatca.gov.sa) and logs in
using ERAD credentials
● Taxpayer requests OTP code(s) for solution(s) to integrate
● Taxpayer populates OTP code(s) in E-Invoice Solution(s)
● Taxpayer reviews if solution was successfully on-boarded
45
10. Failure Scenarios
Generated
e-invoices?
Supplier
YES
7. NO
6. NO
5. NO
1. Accepted
3. Rejected
4. Failed to connect
2. Accepted with warnings
YES
YES
Able to submit
e-invoice to
ZATCA?
Received
response from
ZATCA?
What is the
response?
Example reason
1. Fully compliant invoice
2. Minor mistake -e.g. missing building number
in address
3. Significant mistake -missing mandatory
fields, wrongly populated VAT values
4. Server overloaded by too many requests
5. ZATCA servers are down
6. No internet connectivity at the supplier
7. No electricity or broken device
Required action
No action required
No immediate action required-warnings should be investigated and
amended for next invoice
Invoice should be corrected based on the response and re-submitted
System should continue re-submitting same invoice until ZATCA servers
are responding
Share generated e-invoice and re-submit once issue fixed
Report failure to ZATCA, share e-invoice and re-submit once issue fixed
Report failure to ZATCA, continue business and re-generate once fixed
Deep-dive on the next pages

46
Failure to receive response from ZATCA - B2C scenario
Example scenario during temporary ZATCA issues
Supermarket is selling groceries to
walk-in clients
Supermarket issues
simplified tax invoice
to walk-in clients and
completes the transaction
1. TP should keep evidence of trying to clear the invoice to ZATCA.
Within 24 hours of the transaction,
supermarket needs to report the
simplified tax invoice to ZATCA
1
In case ZATCA's servers
are non-responsive, the
supermarket's server
should continue attempting
to report the simplified tax
invoice in regular intervals
until successful
1
2
3
4

47
Failure to receive response from ZATCA - B2B scenario
Example scenario during temporary ZATCA issues
Bank wants to issue standard tax invoices
to its business clients
ZATCA's servers are down and
bank cannot clear their invoices
Bank would re-try clearance for ~5
minutes (timing TBC)
If ZATCA servers remain non-
responsive, bank shares uncleared
invoice
1
, keeps records of the
transaction (Art. 7.5) and confirms the
existing contact details of buyer
Bank would continue attempting reaching
to ZATCA in regular intervals (~every 15
minutes - timing TBC with Technology)
Once clearance is successful,
bank shares the cleared
e-invoices with the buyers
by any preferred means
electronically
1
2
3
4
5
6
Since ZATCA is aware when the servers are
down, notifying ZATCA is not required. If
TP is unsure, they can always fill the failure
notifications as in other scenarios.
In case of extended outage, ZATCA might
notify taxpayers on its website.
1. Invoice will not be fully compliant but will be considered as VAT invoice until fully compliant invoices is issued immediately once the connection is back.
48
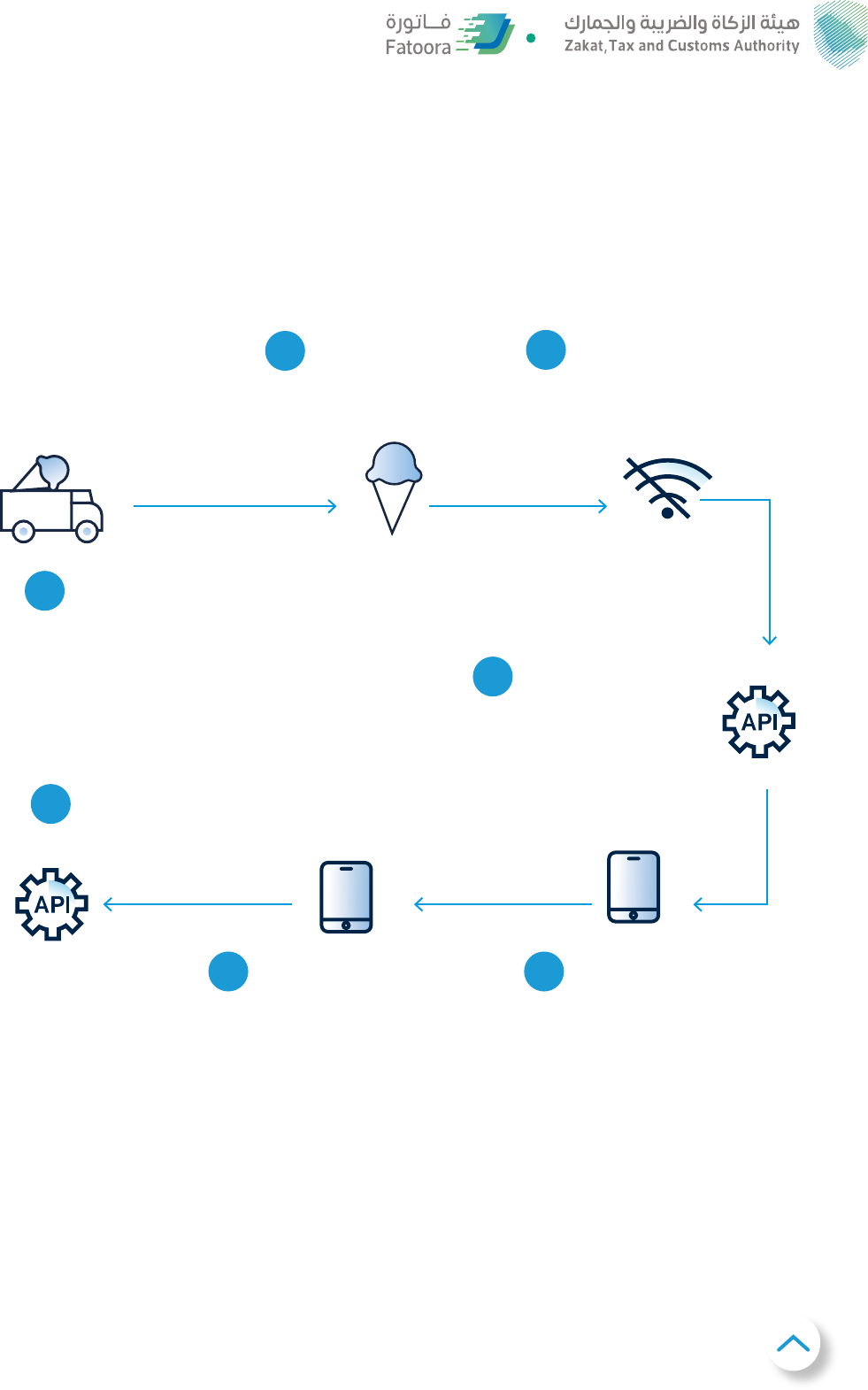
Failure to submit e-invoice to ZATCA- B2C scenario
Ice-cream truck is
selling ice-cream to
kids in schools in
remote areas
Merchants sells the
ice-cream and gives
simplified tax invoice
to the kids
As the school is in the remote
area, there is no internet
connection to report the
invoice immediately
The seller has officially
24 hours to report the
invoice to ZATCA - device
can automatically share
the invoice anytime the
connection is restored
In case the seller does
not manage to share the
invoice within 24 hours,
he should notify ZATCA
via a dedicated form on
ZATCA's website
Once the connection is
restored, merchant should
notify ZATCA again
Seller should immediately
report the transaction to
ZATCA
1
2
3
4
56
7
49
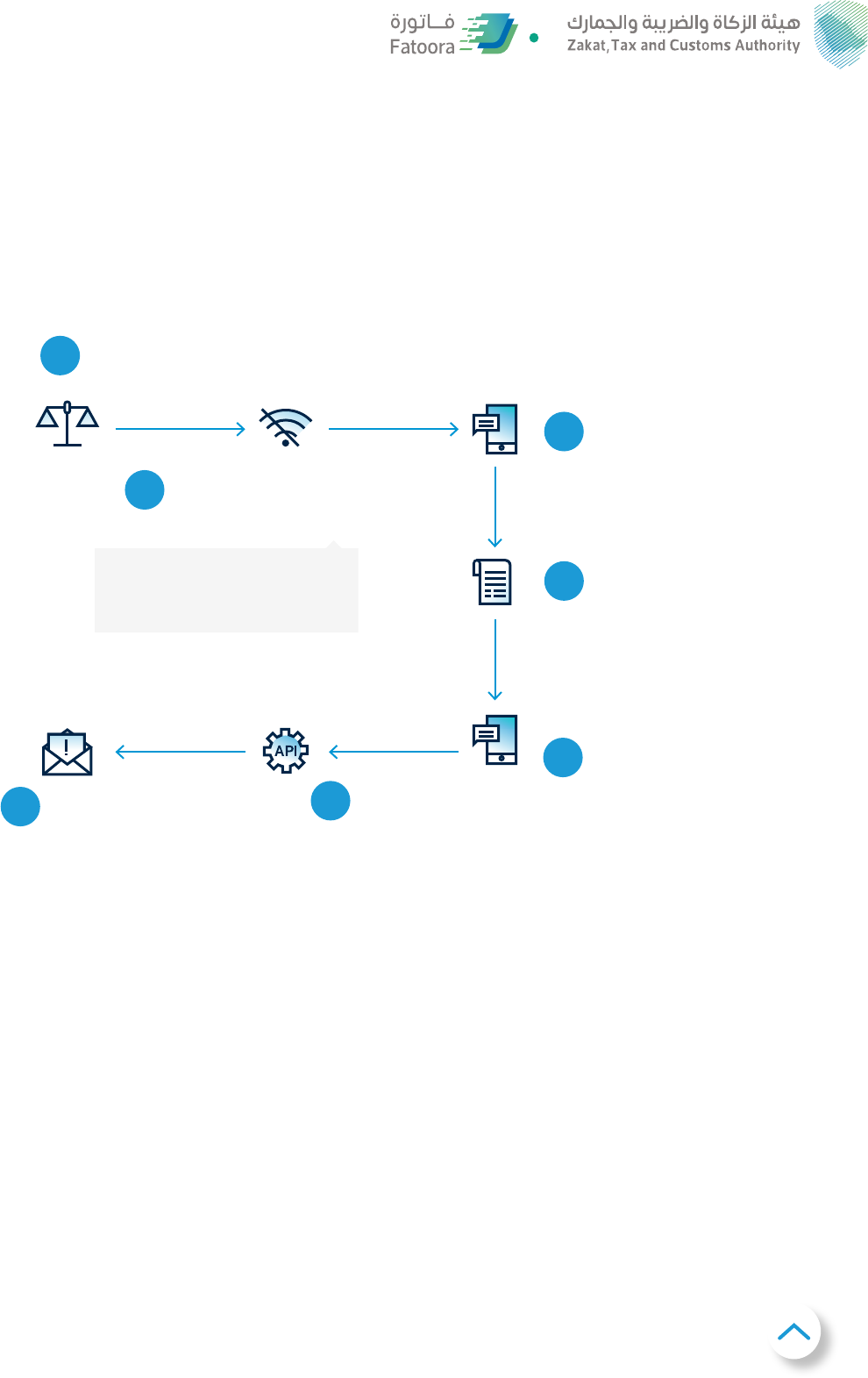
Failure to submite-invoice to ZATCA -B2B scenario
Lawyer wants to clear
and issue an invoice to
their business client
Due to extended internet
connectivity outage, lawyer cannot
submit invoice for clearance within
the 15 days of the following month
Merchant processes transactions,
shares uncleared invoice
1
, keeps
records of the transaction (Art.
7.5) and confirms the existing
contact details of buyer
Once internet connectivity is
restored, lawyer notifies ZATCA
that issue has been resolved
Lawyer submits
e-invoice for
clearance and issues
the invoice to the
customer
Lawyer shares the cleared
e-invoice with the buyer by any
preferred means electronically
Lawyer notifies ZATCA via a
dedicated form on ZATCA's
website on their mobile
1
2
4
5
6
7
3
As per Article (1)53 of KSA VAT
Regulations, Standard Tax Invoices
(B2B) can be issued within 15 days from the end
of the month in which supply takes place
1. Invoice will not be fully compliant but will be considered as VAT invoice until fully compliant invoice is issued immediately once the connection is
restored. Uncleared invoices will not be eligible for VAT deduction. TP should keep evidence of trying to clear the invoice to ZATCA (e.g. API log).

50
Failure to generate e-invoice - B2C scenario
The store’s device
broke down
Merchant notifies ZATCA via
a dedicated form on ZATCA’s
website immediately
Merchant reaches out to
their solution provider
regarding the issue
Merchant processes
transactions, issues invoice
manually
1
and keeps records
of the transaction (Art. 7.5)
Once device is fixed, merchant
notifies ZATCA that issue has
been resolved immediately
Merchant generates e-invoice
and reports it to ZATCA with
transaction date immediately
[OPTIONAL]
If customer requests it, merchant
has to share the generated
invoice with buyer electronically
or informs that invoice can be
collected in the store (Art. 7.5)
1 2 3
4
56
7
If TP reports fixes frequently or for extended
period of time, TP will be investigated further
by ZATCA on individual basis
1. Invoice will not be fully compliant, but will be considered as VAT invoice until fully compliant invoice is issued immediately once the device is fixed.
Manual invoice will not be eligible for VAT deduction.

51
Failure to generate e-invoice - B2B scenario
Manufacture is selling
equipment to an oil refinery
Due to cyber attack, the
manufacture is not able to
generate standard tax invoice as
their systems are blocked
Transaction can be processed as seller
can issue standard tax invoice within
15 days from the following month in
which the supply takes place
1
In case the systems are not restored
within these timelines, seller notifies
ZATCA via a dedicated form on
ZATCA’s website
Merchant processes transactions,
issues invoice manually
2
and keeps
records of the transaction (Art. 7.5)
Once system is restored, merchant
notifies ZATCA that issue has been
resolved immediately
Merchant generates standard
tax invoice and submits it for
clearance with transaction
date immediately
Merchant shares the e-invoice
with the buyer by any preferred
means electronically
1 2 3
4
5
67
8
1. Unless continuous supply, where seller should notify ZATCA immediately at the end of the supply month.
2. Invoice will not be fully compliant, but will be considered as VAT invoice until fully compliant invoice is issued immediately once the device is fixed.
Manual invoice will not be eligible for VAT deduction.

52
Failure to generate e-invoice - B2B Scenario - Walk-in B2B
Customer & Continuous Supplies
The store's device
broke down
Merchant notifies ZATCA via a
dedicated form on ZATCA's website
immediately
Merchant reaches out to their
solution provider regarding the issue
Merchant processes transactions,
issues invoice manually
1
and keeps
records of the transaction (Art. 7.5)
Merchant shares the e-invoice with
the buyer by any preferred means
electronically
Merchant clears invoice with ZATCA
with transaction date immediately
Once device is fixed,
merchant notifies
ZATCA that issue has
been resolved
immediately
If TP reports fixes frequently or for extended
period of time, TP will be investigated further by
ZATCA on individual basis
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1. Invoice will not be fully compliant, but will be considered as VAT invoice until fully compliant invoice is issued immediately once the device is fixed.
Manual invoice will not be eligible for VAT deduction.

53
Overview of responses and required actions
Response Definition Required action
200
Action Successful N/A
202
Action Successful, but with
warnings
● Share warnings with solution provider
to correct at the earliest.
● Warnings are temporarily accepted and
might become rejections in the future.
● Continuous warnings by taxpayers
will be investigated by ZATCA and
taxpayers might be educated / audited
accordingly
303 Clearance switched off
Please submit via reporting
400 Action failed (rejected)
Review detailed message,
correct and resubmit
401 Unauthorized
Check authentication certificate and secret
and resubmit
413
Payload Too Large, invoice
not received
Please resend with smaller payload (invoice)
429
Too Many Requests, invoice
not received
Please resend
500
Internal Server Error, invoice
not received
Please resend
503
Service Unavailable, invoice
not received
Please resend
504
Request Timed Out, invoice
not received
Please resend

54
Overview of differences between responses to submitted documents
Response Definition Required action
Accepted
The document has
no fatal errors and no
warnings that results in
it being considered as a
valid document.
All information is fully in line with the XML
Implementation Standards, Data Dictionary and
E-invoicing Resolution
Accepted
with
warnings
The document has no
fatal errors but has
at least one warning
that results in it not
being considered as a
compliant document
however one that can
still be considered as an
accepted document
100+ possible combinations of warning messages,
e.g.:
● An Invoice shall have an Invoice number (BT-1).
● An Invoice shall contain the Seller name (BT-27).
● An Invoice shall contain the Seller postal address
(BG-5).
● The Seller postal address (BG-5) shall contain a
Seller country code (BT-40).
● Each Invoice line (BG-25) shall contain the Item
name (BT-153).
● The allowed maximum number of decimals for
the Paid amount (BT-113) is 2.
● Allowance amount (BT-92, BT-136) must equal
base amount (BT-93, BT-137) * percentage
(BT-94, BT-138) / 100 if base amount and
percentage exists.
● Previous invoice hash (KSA-13) must exist in an
invoice.

55
Response Definition Required action
Rejected
The document has at
least one fatal error
that results in it not
being considered as a
valid document
100+ possible combinations of error messages, e.g.:
● The VAT rates (BT-96119, BT-152)
● must be from 0.00 to 100.00, with maximum
two decimals. Only numerals are accepted, the
percentage symbol (%) is not allowed.
● An Invoice shall have an Invoice issue date (BT-2).
● An Invoice shall have an Invoice type code (BT-3).
● Base quantity (BT-149) must be a positive number
above zero.
● The document issue date (BT-2) must be less or
equal to the current date.

56
11. Tax Invoice and Simplified Tax Invoice QR Code validation
Customers and related stakeholders may validate the Tax Invoices and Simplified Tax
Invoice through scanning the QR code available on the invoice, by following the below
steps:
● Customer scans E-Invoice’s QR code content via VAT App
● VAT App verifies the E-Invoice’s QR code content is compliant
● VAT App displays the QR code content as well as the E-Invoice’s verification results

57
FAQs
What is Phase 2? When will it be enforced and to whom does it apply?
Phase 2 known as the Integration phase, during this phase, subjective taxpayers must
comply with Phase 2 business and technical requirements for the electronic invoices and
E-Invoice Solutions, and the integration with ZATCA’s system.
Phase 2 is enforceable starting from January 1, 2023 and implemented in waves by targeted
taxpayer groups. Taxpayers will be notified by ZATCA on the date of their integration at
least 6 months in advance.
How will ZATCA notify taxpayers about their integration wave?
The enforcement date for the first target group will not be earlier than January 1, 2023.
ZATCA will notify taxpayers of their Phase 2 wave at least six months in advance through
Official emails & SMS registered with ZATCA
What are the requirements for Phase 2?
Phase 2, which will be implemented in waves by target taxpayer groups starting from
January 1, 2023, entails additional technical requirements that E-Invoice solutions must
comply with, the integration of taxpayer E-Invoice Solutions with FATOORA Platform and
the issuance of electronic invoices in a specific format.
Due to the technical nature of the published requirements, it is recommended for
taxpayers to approach a solution provider or their internal technical teams to ensure their
E-Invoice Solutions are compliant with ZATCA’s regulations. In addition, developers and
subject matter experts may visit ZATCA’s website for viewing all requirements (business,
technical, security, etc.). Further details on the integration mechanisms and specifications
are published by ZATCA on the developer page on ZATCA’s E-Invoicing webpage https://
zatca.gov.sa/ar/E-Invoicing/Pages/ default.aspx.

58
Can a taxpayer use the same E-Invoice Solution that was used for Phase 1?
A taxpayer can use the same E-Invoice Solution that was used for Phase 1, by updating the
E-Invoice Solution to comply with the Phase 2 requirements.
Should a taxpayer continue following Phase 1 requirements until Phase 2
applies to them?
Yes, a taxpayer should continue following Phase 1 requirements until the integration
enforcement date of the taxpayer’s wave, in which the taxpayer is required to start
following Phase 2 requirements. However, taxpayers have the option to start following
Phase 2 requirements (which build on Phase 1 requirements) on a voluntary basis before
their integration enforcement date [based on final integration roll-out strategy].
If a taxpayer is complaint with Phase 1 requirements, and was not yet
notified by ZATCA to integrate, is the taxpayer required to implement Phase
2 requirements?
The taxpayer is not required to implement Phase 2 requirements until notified by ZATCA
about the integration enforcement date of the taxpayer’s wave, in which the taxpayer
is required to start following phase 1 requirements. However, it is recommended for
taxpayers to start following phase 2 requirements on a voluntary basis before their
integration enforcement date [based on final integration roll-out strategy].

59
How can a taxpayer integrate their E-Invoice Solution with ZATCA’s
systems?
Taxpayer updates the E-Invoice Solution to comply with Phase 2 requirements Taxpayer
accesses dedicated FATOORA portal (https://FATOORA.zatca.gov.sa/) using Taxpayer
Portal credentials and requests OTP .
Taxpayer inputs the OTP code generated into their E-Invoice Solution being integrated, in
addition to the required information for E-Invoice Solution integration.
After successful E-Invoice Solution integration, taxpayer starts issuing invoices via their
integrated E-Invoice Solution.
Please refer to the detailed technical guideline for more information (here)
How can a taxpayer verify that their E-Invoice Solution has been successfully
integrated?
After a taxpayer integrates an E-Invoice Solution, a message will be displayed indicating
whether the E-Invoice Solution has been successfully integrated. Also, taxpayers can use
the FATOORA Portal (https://FATOORA.zatca.gov.sa/) in order to view a summary list of
all their integrated E-Invoice Solutions (section View List of Solutions and Devices).
If one VAT Registration Number has multiple devices, should each device be
registered?
Yes, every device issuing invoices with the same VAT number should be registered.

60
What should be the language of the invoice shared with ZATCA?
As per Article 53 of VAT Regulations, invoices must be in Arabic. The technical aspects
of XML will be in English, however, the data for invoices (that will be visible once XML is
visualized) must be in Arabic. Other languages can be present on the Invoice as well.
In some cases, an invoice may go into an approval process which can take
up to 2 weeks after its generation. Which invoice issue date should be used?
Invoice Issue Date must be the date on which final Tax Invoice is generated. If there are
internal processes for approvals, you may consider treating invoice as final only once
all internal approvals are obtained, and then submit final invoice to ZATCA. Please note
that Tax Invoices may be issued within 15 days of the month following the month in which
supply takes place. However, for Simplified Tax Invoices, taxpayers must report them to
ZATCA within 24 hours of generation.
When will the QR code string be generated by ZATCA for Tax Invoices
(B2B)?
For the Tax Invoice (B2B), the QR Code string will be generated by ZATCA at the time of
Clearance (along with ZATCA’s stamp). Taxpayers are expected just to visualize the QR
Code based on the QR Code string received from ZATCA.
Can I submit the same invoice twice?
No, ZATCA does not allow the same document to be submitted twice. However, this will
not be rejected at the time of submission.

61
What is the maximum size allowed for an invoice?
Around 10mb. If this value is exceeded, the relevant API will return an Error 413 response
as “Request Entity is too large”
Is it mandatory to generate and store E-Invoices in XML or PDF/A3 (with
embedded XML) format?
Once the taxpayer is part of the integration phase, XML or PDF/A3 (with embedded XML)
format will be mandatory.
For Tax Invoices (B2B), is it mandatory to provide the customer with a PDF/
A3 (with embedded XML) document or would the invoice in XML format
suffice?
E invoicing Resolution provides option to either share XML or PDF/A-3 (with embedded
XML). If the buyer is able to process XML and agrees to receive file in XML format, then it
is valid compliance to send XML.
For Tax Invoices, what should be done if the clearance fails before issuing
the invoice to the buyer?
In case of Tax Invoices, if clearing fails (Response is 400 Error), then the taxpayer must
submit another invoice for clearance after rectifying the errors. Please note that every
document shall have its own hash and counter value. Rejected document’s hash and
counter value should not be changed or updated.

62
What is the difference between Invoice Reference Number and Invoice
sequence number?
“As clearly mentioned in the Annex 2 of E Invoicing Resolution, Invoice Reference Number
(IRN): A unique, sequential note number, issued by taxpayer, as per Article 53(5)(b) of the
VAT Implementing Regulation. This implies IRN is just another name for Invoice Sequence
Number.
Again, as specified in E Invoicing Resolution, the Compliant E-Invoice solution must have
a tamper-resistant Electronic Invoice counter that cannot be reset or reformatted. The
counter must increment for each generated Electronic Invoice or associated note and
the Compliant Solution must record the value of this counter in each Electronic Invoice or
associated Notes. Example 1,2,3,4,5... “
Is it possible to issue a credit note without a reference to an invoice?
Issuing Credit Note without reference to Original Invoice will be violating requirements of
Article 54 of KSA VAT Regulations.
Do we need to send to ZATCA the Invoices where all sold items and services
are “Services outside scope of tax / Not subject to VAT”?
“The Tax Category Code O is for those transactions where invoice may contain a line item
with Standard Rate supply and other with” “Not Subject to VAT”. There is no need to issue
a Tax Invoice (or E Invoice) where the transaction solely covers supplies which are “Not
Subject to VAT”. Note: If the “Not Subject to VAT” Supply Invoices are generated using
same Billing Solution that generates invoices for Standard Rate, it would be worth noting
that there should not be gaps in Counter Value and the sequence of Previous Invoice Hash.”

63
If the tax invoice includes remarks, notes, or addition- al clarification due to
export shipping service and customs related, will the Arabic Translation be
required in this case along with the English text?
Any information contained in the human readable form of the Tax Invoice must be in Arabic
including notes. Any additional translation is also allowed.
Is the PDF/A-3 format mandatory in case that the taxpayer wants to send
the invoice in PDF format or it is only a recommendation from ZATCA?
PDF-A/3 (with embedded XML) is mandatory
How can the customers manage the credit notes in case it refers to multiple
invoices?
Where one credit note refers to multiple invoices, it is expected that Invoice Reference
Numbers are mentioned for the Original Invoices that the Credit Note relates to. The field
is a “text” field and can accommodate reference as a range where the number of Original
Invoices are too many.
In case a standard Invoice is rejected (not cleared) from ZATCA, then should
the team cancel and regenerate the in- voice and resubmit again?
Invoices cannot be cancelled. If invoice is rejected by ZATCA, then tax payers can fix the
errors and submit the XML just like a new invoice having its own Invoice Counter Value and
Hash.

64
The additional Buyer ID: In case we don’t have any additional ID for a B2B
non-registered customer, can we still issue a standard tax invoice? We need
to confirm that the missing additional buyer ID on the standard invoice will
not be a reason for rejection?
In case additional Buyer ID is missing, invoice may be accepted with warnings. It is
recommended that taxpayers update their customer mater data and meet all the
requirements.
Other Seller ID: As we are adding our VAT ID on the invoices, do we still need
to add additional ID?
Other seller ID is a mandatory field. The condition is that in case a tax- payer has multiple
IDs, then the ID must be provided in the order of sequence of the list of IDs with priority
from the top of the list.
We have some customers that issue invoices to companies with VAT in
Saudi Arabia, but that are non-residents as they have no physical address in
KSA territory. Is it possible to indicate a foreign address although the VAT is
registered in Saudi Arabia?
Yes. It is possible to indicate a foreign address although the buyer is VAT is registered in
KSA.

65
Contact Us
For any further information, please visit us on www.zatca.gov.sa or reach out to our
customer service center on the following numbers and email:
● (Local) 19993
● (International) +966112048998

66
zatca.gov.sa
scan this code to view the last
version and all published documents
or visit the website zatca.gov.sa
External document
This guide has been prepared for educational purposes
only, and its content may be modified at any time. It is not
considered mandatory by the Authority, nor as a legal advice,
and it cannot be relied and acted upon without reference to
the relevant statutory provisions. Every person subject to
Zakat, Tax, and Customs Laws must check their duties and
obligations; they are solely responsible for the compliance
with these regulations. ZATCA shall not be responsible in
any way for any damages or losses incurred to the taxpayer
as a result of not complying with the applicable regulations.
